Accrued Revenue on Balance Sheet: A Quick Guide

Understanding accrued revenue on the balance sheet is crucial for businesses to accurately reflect their financial health. Accrued revenue represents income earned but not yet received, playing a vital role in financial reporting. This guide breaks down its significance, calculation, and impact on your balance sheet, ensuring clarity for both informational and commercial audiences.
What is Accrued Revenue? (accrued revenue definition, revenue recognition)

Accrued revenue, also known as unearned revenue or deferred revenue, is income a company has earned but hasn’t yet received payment for. This often occurs when services are rendered or goods are delivered before the customer pays. It’s a key concept in accrual accounting, ensuring financial statements reflect the true financial position of a business.
Why is Accrued Revenue Important? (financial reporting, balance sheet accuracy)

Accrued revenue is essential for accurate financial reporting. It ensures that revenue is recognized in the period it’s earned, not when payment is received. This aligns with accounting principles like the matching principle, providing a clearer picture of a company’s performance and financial stability.
How to Calculate Accrued Revenue (accrued revenue formula, journal entry)
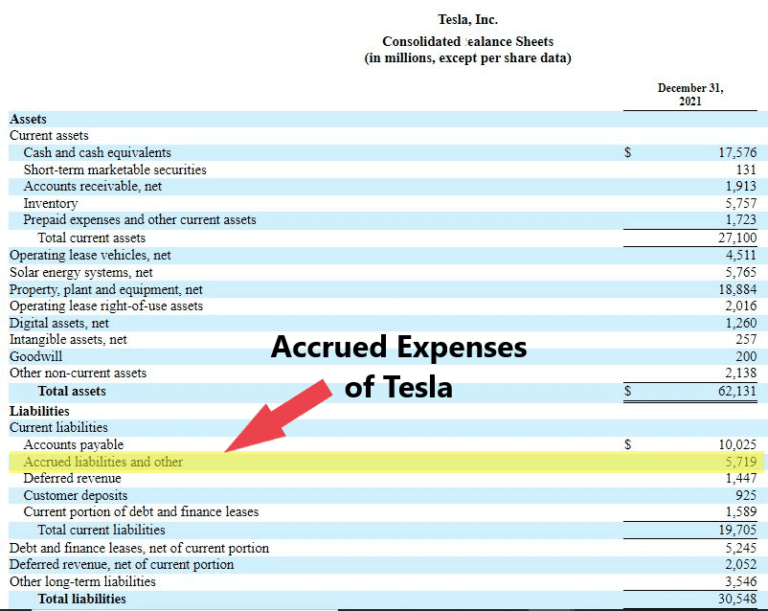
Calculating accrued revenue involves a straightforward formula:
Accrued Revenue = (Total Services/Goods Delivered) × (Price per Unit)
For example, if a company delivers $5,000 worth of services in December but gets paid in January, the $5,000 is recorded as accrued revenue in December.
📌 Note: Ensure proper journal entries are made to reflect accrued revenue accurately.
Accrued Revenue on the Balance Sheet (current assets, financial statements)

Accrued revenue is typically recorded as a current asset on the balance sheet. It’s listed under accounts receivable or a separate line item. This reflects the company’s right to receive payment in the near future, usually within a year.
| Balance Sheet Section | Where Accrued Revenue is Recorded |
|---|---|
| Current Assets | Accounts Receivable or Accrued Revenue |

Checklist for Managing Accrued Revenue (accounting best practices, financial management)

- Track all services/goods delivered before payment.
- Use the accrued revenue formula consistently.
- Record journal entries promptly.
- Review accrued revenue regularly for accuracy.
- Ensure compliance with GAAP or IFRS standards.
Mastering accrued revenue on the balance sheet is essential for maintaining accurate financial records. By understanding its definition, importance, and calculation, businesses can ensure transparency and compliance in their financial reporting. Whether you’re an informational reader or a commercial visitor, this guide provides the insights needed to navigate accrued revenue effectively. (accrued revenue management, financial transparency, accounting principles)
What is the difference between accrued revenue and accounts receivable?
+Accrued revenue is income earned but not yet billed, while accounts receivable is income billed but not yet received. Both are current assets but represent different stages of revenue recognition.
How does accrued revenue affect the income statement?
+Accrued revenue increases the revenue reported on the income statement for the period in which the service or goods were delivered, even if payment hasn’t been received.
Can accrued revenue be negative?
+No, accrued revenue cannot be negative. It represents income earned, so a negative value would indicate an error in accounting.



