Aesculin Hydrolysis Test: Quick Guide for Microbiologists Understanding the Aesculin Hydrolysis Test in Microbiology Aesculin Hydrolysis Test: Essential Lab Technique Explained How to Perform the Aesculin Hydrolysis Test Effectively Decoding the Aesculin Hydrolysis Test for Bacterial Identification

The Aesculin Hydrolysis Test is a crucial technique in microbiology, used to identify bacteria based on their ability to hydrolyze aesculin, a glycoside found in horse chestnut trees. This test is particularly useful for differentiating between various bacterial species, especially within the Enterococcus and Streptococcus genera. Understanding and mastering this test can significantly enhance your lab skills and accuracy in bacterial identification.
Understanding the Aesculin Hydrolysis Test in Microbiology

The Aesculin Hydrolysis Test relies on the enzyme beta-glucosidase, produced by certain bacteria, to break down aesculin into glucose and aesculetin. Aesculetin reacts with iron ions in the medium to form a black complex, indicating a positive result. This test is commonly performed using bile aesculin agar, which also contains bile salts to inhibit the growth of Gram-negative bacteria.
Key Components of the Test
- Aesculin: The substrate that undergoes hydrolysis.
- Beta-glucosidase: The enzyme responsible for breaking down aesculin.
- Iron ions: Required for the formation of the black complex.
- Bile aesculin agar: The growth medium used for the test.
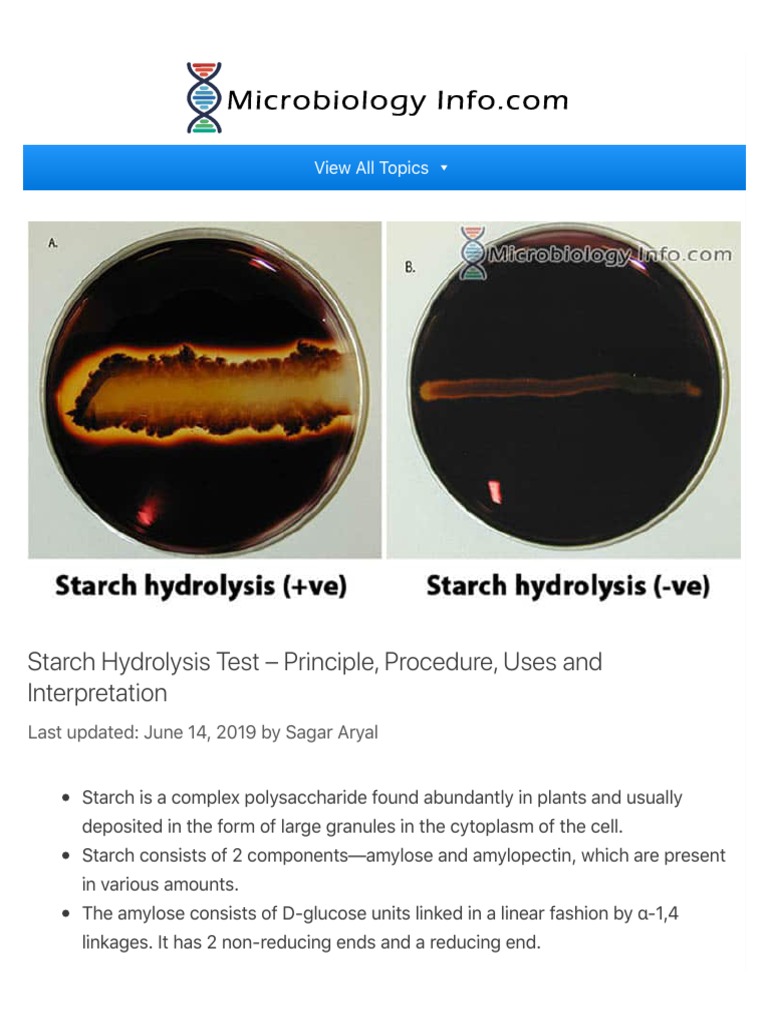
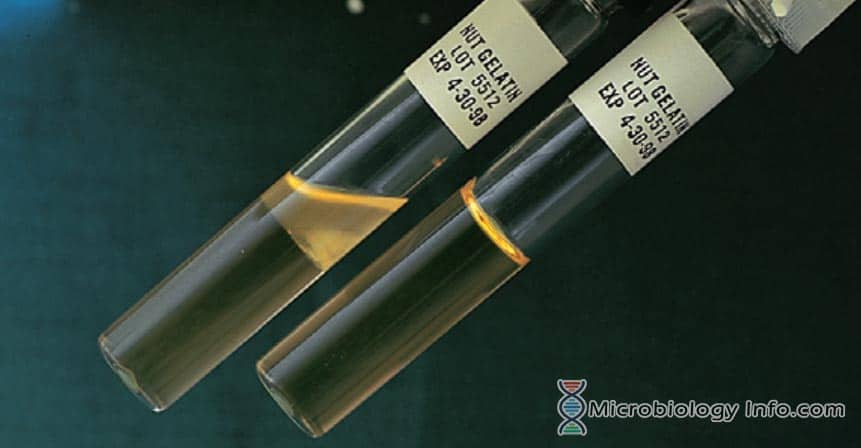
📌 Note: The presence of a black halo around the colonies indicates a positive result, while no color change suggests a negative result.
Aesculin Hydrolysis Test: Essential Lab Technique Explained

This test is essential for distinguishing between bacteria that produce beta-glucosidase and those that do not. For example, Enterococcus faecalis typically produces a positive result, while Streptococcus pyogenes does not. Understanding this distinction is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment in clinical settings.
Applications in Microbiology
- Clinical Diagnostics: Identifying pathogens in patient samples.
- Food Microbiology: Detecting contaminants in food products.
- Environmental Monitoring: Assessing bacterial populations in various environments.
How to Perform the Aesculin Hydrolysis Test Effectively
Performing the Aesculin Hydrolysis Test requires precision and attention to detail. Follow these steps for accurate results:
Step-by-Step Procedure
- Prepare the Medium: Sterilize bile aesculin agar and pour it into plates.
- Inoculate the Plates: Streak the bacterial isolate onto the agar surface using a sterile loop.
- Incubate: Place the plates in an incubator at 37°C for 24–48 hours.
- Observe Results: Check for the formation of a black halo around the colonies.
📌 Note: Ensure proper aseptic techniques to avoid contamination during inoculation.
Checklist for Successful Testing
- Use fresh bile aesculin agar for accurate results.
- Incubate at the correct temperature and duration.
- Observe plates under proper lighting to detect subtle color changes.
Decoding the Aesculin Hydrolysis Test for Bacterial Identification

Interpreting the results of the Aesculin Hydrolysis Test is straightforward but requires knowledge of the expected outcomes for different bacteria. A positive result (black halo) indicates the presence of beta-glucosidase, while a negative result suggests its absence.
| Bacterial Species | Expected Result |
|---|---|
| Enterococcus faecalis | Positive |
| Streptococcus pyogenes | Negative |
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Over-incubation: Can lead to false positives due to prolonged enzyme activity.
- Insufficient inoculum: May result in false negatives if too few bacteria are present.
- Contamination: Can interfere with accurate result interpretation.
The Aesculin Hydrolysis Test is a powerful tool in microbiology, offering valuable insights into bacterial identification. By understanding its principles, mastering the technique, and avoiding common pitfalls, you can enhance your lab skills and contribute to accurate diagnostic outcomes. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or clinical microbiologist, this test is an essential addition to your toolkit.
What is the Aesculin Hydrolysis Test used for?
+The Aesculin Hydrolysis Test is used to identify bacteria based on their ability to produce beta-glucosidase, an enzyme that breaks down aesculin into glucose and aesculetin.
How do you interpret a positive result in the Aesculin Hydrolysis Test?
+A positive result is indicated by the formation of a black halo around the bacterial colonies, due to the reaction of aesculetin with iron ions in the medium.
What bacteria typically produce a positive result in this test?
+Bacteria such as Enterococcus faecalis typically produce a positive result due to their ability to hydrolyze aesculin.
Related Keywords: Aesculin Hydrolysis Test Procedure, Bile Aesculin Agar Uses, Beta-glucosidase in Microbiology, Bacterial Identification Techniques, Clinical Microbiology Tests.



