Essential Airplane Wing Parts Explained: A Quick Guide
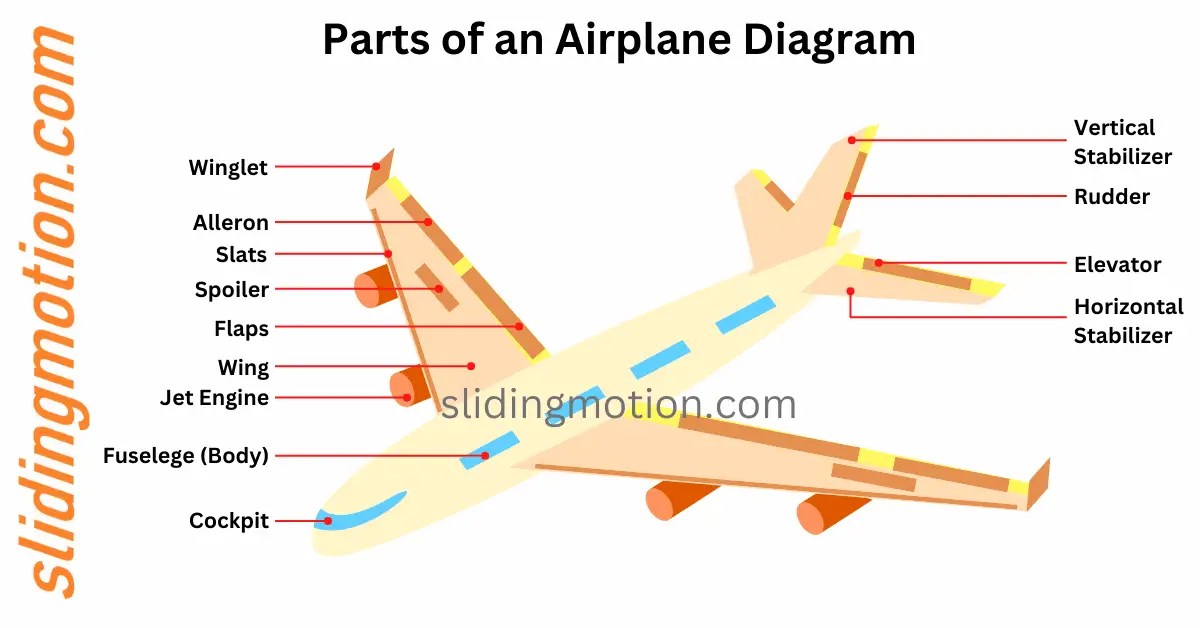
Ever wondered what makes an airplane soar through the skies with such grace and precision? The answer lies in its wings, which are marvels of engineering. Understanding the essential airplane wing parts not only satisfies curiosity but also enhances appreciation for aviation technology. Whether you're an aviation enthusiast or a curious traveler, this guide will walk you through the key components that make flight possible.
The Main Structure: Spars and Ribs

The foundation of any airplane wing is its spars and ribs. Spars are the primary structural elements that run horizontally across the wing, providing strength and stability. Think of them as the backbone of the wing. Ribs, on the other hand, are vertical components that give the wing its aerodynamic shape. Together, they ensure the wing can withstand the stresses of flight while maintaining its form. (aircraft structure, wing design, aviation engineering)
Aerodynamic Surfaces: Ailerons and Flaps

To control the airplane’s movement, wings are equipped with ailerons and flaps. Ailerons are located at the trailing edge of the wing and are responsible for rolling the aircraft, allowing it to turn. Flaps, also on the trailing edge, increase lift during takeoff and landing by altering the wing’s shape. These surfaces are crucial for maneuvering and ensuring safe flight operations. (flight control surfaces, aircraft maneuverability, wing components)
How Ailerons Work
- Controlled by the pilot’s yoke or stick.
- Move in opposite directions to tilt the aircraft.
- Essential for banking during turns.
Flap Functions
- Increase wing area and curvature.
- Enhance lift at lower speeds.
- Critical for short takeoff and landing distances.
Protective Layers: Skin and Winglets
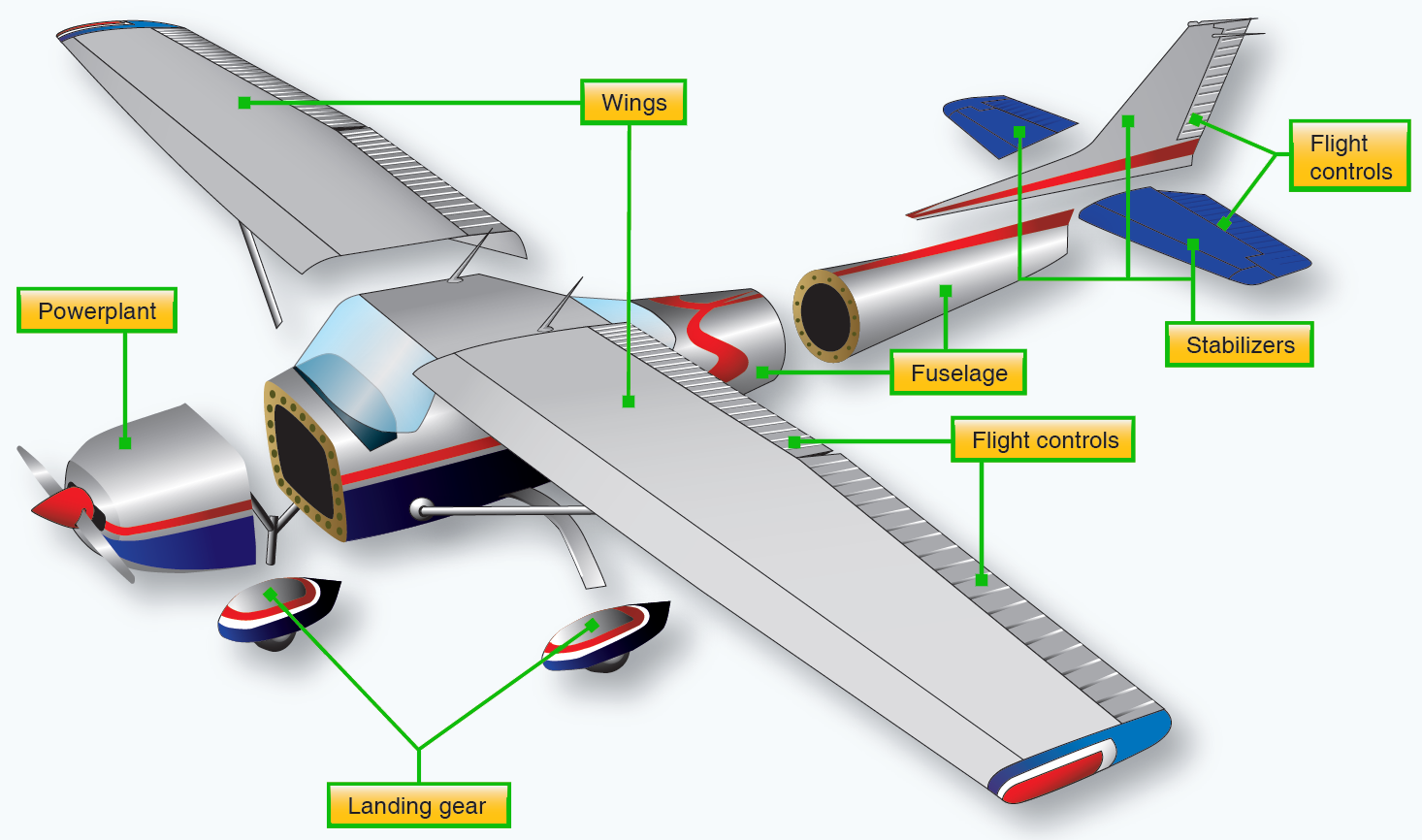
The outer layer of the wing, known as the skin, is a smooth, aerodynamic surface that reduces drag. It’s typically made of lightweight materials like aluminum or composite fibers. Winglets, found at the wingtips, are vertical extensions that minimize vortices and improve fuel efficiency. These components play a vital role in optimizing performance and reducing environmental impact. (aerodynamic efficiency, fuel efficiency, wingtip design)
✈️ Note: Winglets can reduce fuel consumption by up to 5%, making them a key feature in modern aircraft design.
Internal Systems: Fuel Tanks and Slats

Wings house fuel tanks, which store the majority of an aircraft’s fuel, ensuring proper weight distribution. Slats, located at the leading edge, extend to increase lift during low-speed operations, such as takeoff and landing. These internal systems are integral to the wing’s functionality and the aircraft’s overall performance. (aircraft fuel systems, leading-edge devices, wing efficiency)
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Spars | Provide structural strength |
| Ailerons | Control rolling motion |
| Flaps | Increase lift during takeoff/landing |
| Winglets | Reduce drag and improve efficiency |

In summary, airplane wings are a masterpiece of engineering, comprising spars, ribs, ailerons, flaps, skin, winglets, fuel tanks, and slats. Each part plays a critical role in ensuring safe, efficient, and controlled flight. Whether you’re marveling at aviation technology or considering a career in aerospace, understanding these components deepens your appreciation for the complexities of flight. (aviation technology, aircraft components, wing parts)
What are the main structural components of an airplane wing?
+
The main structural components are spars and ribs, which provide strength and shape to the wing.
How do ailerons and flaps work together?
+
Ailerons control the roll of the aircraft, while flaps increase lift during takeoff and landing by changing the wing’s shape.
Why are winglets important?
+
Winglets reduce drag, improve fuel efficiency, and minimize wingtip vortices, enhancing overall aircraft performance.


