Sodium's Atomic Model Explained Simply Understanding Sodium's Atomic Structure The Science Behind Sodium's Atomic Model Sodium Atom: Structure & Function Exploring Sodium's Atomic Composition

Sodium, a key element in our daily lives, plays a vital role in various industries, from food preservation to medicine. But have you ever wondered about its atomic structure and how it contributes to its unique properties? In this blog post, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of sodium’s atomic model, exploring its composition, structure, and function.
Understanding Sodium’s Atomic Structure

Sodium, with the chemical symbol Na, is an alkali metal found in group 1 of the periodic table. Its atomic number is 11, meaning it has 11 protons in its nucleus. The atomic model of sodium consists of a central nucleus surrounded by electrons in specific energy levels or shells.
Sodium’s Electron Configuration
The electron configuration of sodium is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s¹, indicating that it has:
- 2 electrons in the first shell (1s)
- 8 electrons in the second shell (2s and 2p)
- 1 electron in the third shell (3s)
This single electron in the outermost shell makes sodium highly reactive, as it tends to lose this electron to achieve a stable configuration, sodium atomic model, atomic structure of sodium, sodium atom.
The Science Behind Sodium’s Atomic Model

The atomic model of sodium is based on the principles of quantum mechanics, which describe the behavior of electrons in atoms. According to this model, electrons occupy specific energy levels or orbitals around the nucleus.
Energy Levels and Orbitals
In sodium’s atomic model, the energy levels are represented as follows:
| Energy Level | Electron Configuration |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1s² |
| 2 | 2s² 2p⁶ |
| 3 | 3s¹ |
The outermost electron in the 3s orbital is the most significant, as it determines sodium’s chemical properties, sodium atomic composition, sodium atom structure, sodium’s atomic model explained.
Sodium Atom: Structure and Function

The structure of a sodium atom is relatively simple, consisting of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons, while the electrons occupy the energy levels around it.
Sodium’s Role in Chemical Reactions
Sodium’s unique atomic structure makes it an essential player in various chemical reactions. Its tendency to lose the outermost electron allows it to form ionic bonds with other elements, such as chlorine, to create sodium chloride (NaCl), a common salt used in food and industry, sodium’s atomic structure, sodium atomic model, sodium atom.
💡 Note: Sodium's reactivity is due to its low first ionization energy, making it easy to lose the outermost electron.
Exploring Sodium’s Atomic Composition
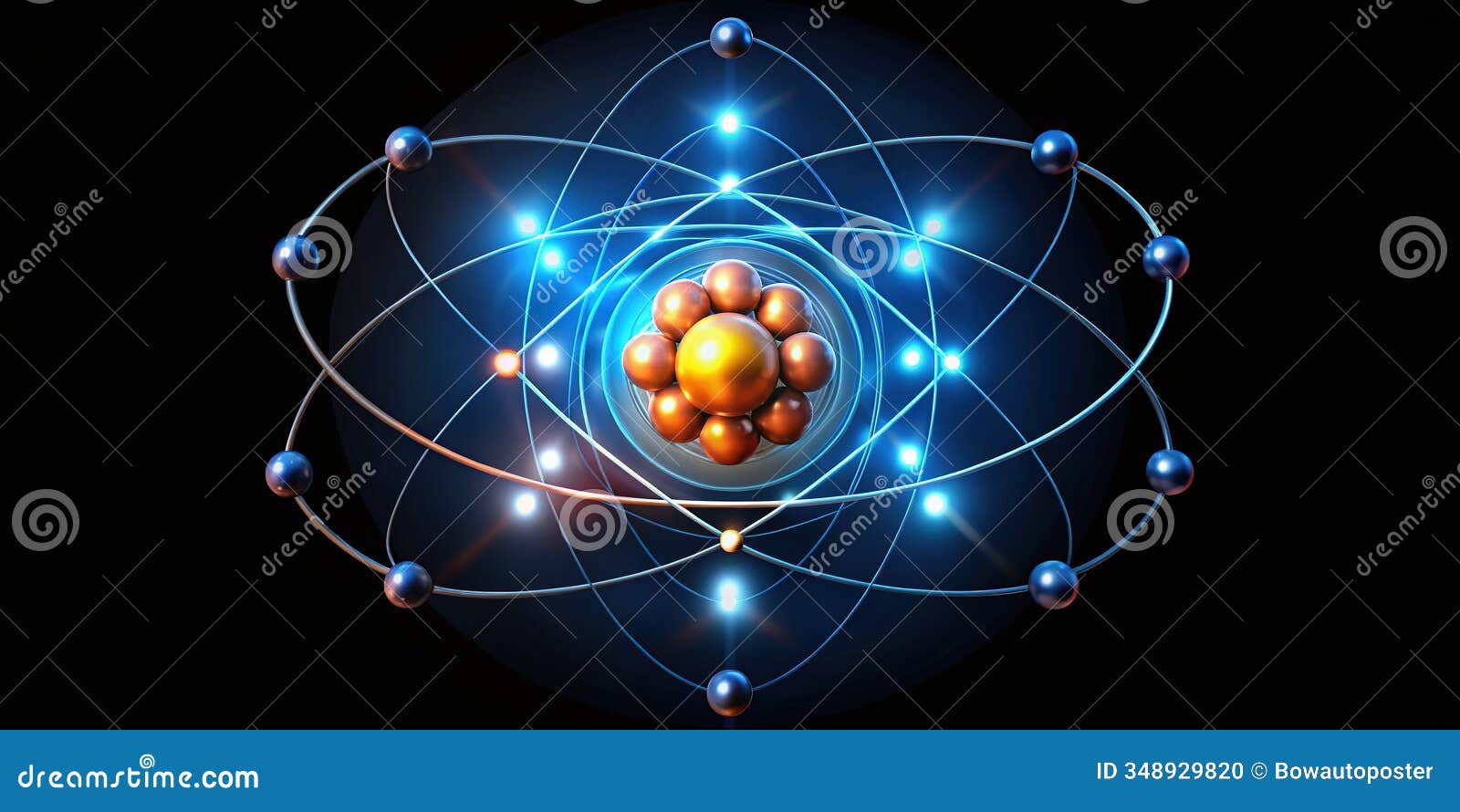
To better understand sodium’s atomic composition, let’s break it down into its fundamental components:
- Protons: 11 (atomic number)
- Neutrons: 12 (most common isotope, Na-23)
- Electrons: 11 (neutral atom)
This composition gives sodium its unique properties, including its low density, high reactivity, and excellent conductivity, sodium atomic composition, sodium’s atomic model, sodium atom structure.
Key Takeaways
- Sodium has 11 protons, 12 neutrons, and 11 electrons in its most common isotope.
- Its electron configuration (1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s¹) determines its chemical properties.
- The outermost electron in the 3s orbital is responsible for sodium’s reactivity.
In summary, sodium's atomic model is a fascinating subject that sheds light on its unique properties and behavior. By understanding its atomic structure, electron configuration, and composition, we can appreciate the role of sodium in various industries and applications, sodium atomic model explained, sodium's atomic structure, sodium atom, sodium atomic composition.
What is sodium’s atomic number?
+Sodium’s atomic number is 11, which means it has 11 protons in its nucleus.
Why is sodium so reactive?
+Sodium is highly reactive due to its single outermost electron in the 3s orbital, which it tends to lose to achieve a stable configuration.
What is the electron configuration of sodium?
+The electron configuration of sodium is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s¹, indicating its electron distribution across energy levels.
How does sodium’s atomic structure affect its properties?
+Sodium’s atomic structure, particularly its outermost electron, determines its low density, high reactivity, and excellent conductivity.
What is the most common isotope of sodium?
+The most common isotope of sodium is Na-23, which has 11 protons and 12 neutrons in its nucleus.



