Unveiling Antimony: Atomic Number 51 Explained
Antimony, a lesser-known element with atomic number 51, has been quietly shaping industries and technologies for centuries. Despite its obscurity, this metalloid plays a crucial role in everything from flame retardants to semiconductors. Whether you’re a chemistry enthusiast or simply curious about the elements around us, understanding antimony’s properties, uses, and significance can be both fascinating and enlightening. Let’s dive into the world of antimony and uncover why this element deserves more attention.
What is Antimony? A Brief Introduction

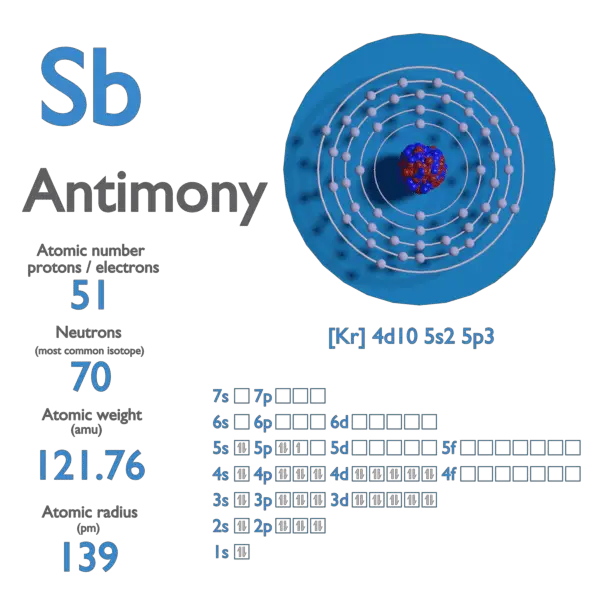
Antimony, represented by the symbol Sb (from its Latin name stibium), is a lustrous gray metalloid found in the Earth’s crust. It rarely exists in its pure form and is usually extracted from ores like stibnite. With atomic number 51, antimony sits in Group 15 of the periodic table, sharing similarities with arsenic and phosphorus. Its unique properties make it a versatile element in both industrial and commercial applications.
Key Properties of Antimony

Antimony’s distinct characteristics set it apart from other elements:
- Physical Properties: Brittle, silvery-white appearance with a metallic luster.
- Chemical Properties: Resists oxidation in air and is stable at room temperature.
- Alloying Ability: Improves hardness and mechanical properties when combined with metals like lead.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 51 |
| Symbol | Sb |
| Melting Point | 630.63°C (1167.13°F) |
| Density | 6.697 g/cm³ |
Industrial and Commercial Uses of Antimony

Antimony’s versatility makes it indispensable in various sectors:
Flame Retardants
One of the most significant applications of antimony is in flame retardant materials. Antimony trioxide (Sb₂O₃) is widely used in plastics, textiles, and electronics to inhibit the spread of fire.
Alloys and Batteries
Antimony alloys, particularly with lead, are used in batteries, cables, and solders. These alloys enhance durability and conductivity, making them ideal for industrial use.
Semiconductors and Electronics
In the tech industry, antimony is used in semiconductor devices and infrared detectors. Its unique electronic properties make it valuable for advanced technologies.
📌 Note: Antimony compounds must be handled with care, as some are toxic and require proper safety measures.
Antimony in History and Culture

Antimony has a rich history dating back to ancient times. The Egyptians used antimony sulfide (stibnite) for eye cosmetics, while alchemists sought it for its mysterious properties. Today, it remains a symbol of innovation and progress in modern science.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability

While antimony is essential for many industries, its extraction and use pose environmental challenges. Mining operations can lead to soil and water contamination, highlighting the need for sustainable practices. Recycling antimony from electronic waste is one way to reduce its environmental footprint.
Key Takeaways: Antimony at a Glance
- Atomic Number: 51
- Primary Uses: Flame retardants, alloys, semiconductors
- Historical Significance: Used in cosmetics and alchemy
- Environmental Concern: Requires sustainable mining and recycling
FAQ Section
What is the atomic number of antimony?
+The atomic number of antimony is 51.
What are the main uses of antimony?
+Antimony is primarily used in flame retardants, alloys, batteries, and semiconductors.
Is antimony safe to handle?
+Some antimony compounds are toxic, so proper safety measures are essential when handling them.
Antimony, with its atomic number 51, may not be a household name, but its impact on technology, safety, and history is undeniable. From ancient cosmetics to modern electronics, this metalloid continues to play a vital role in shaping our world. By understanding its properties and applications, we can appreciate the importance of even the lesser-known elements on the periodic table. Whether for industrial innovation or environmental sustainability, antimony remains a fascinating subject worth exploring further.
Keywords/Title: atomic number 51, antimony uses, flame retardants, antimony alloys, semiconductor materials, environmental impact of antimony



