Is BF3 Polar or Nonpolar? Uncover the Truth!
Is BF3 Polar or Nonpolar? Uncover the Truth!
Boron Trifluoride (BF3) is a chemical compound widely discussed in chemistry due to its unique molecular structure. The question of whether BF3 is polar or nonpolar often arises among students and enthusiasts. Understanding its polarity is crucial for grasping its chemical behavior and applications. In this post, we’ll explore the factors determining BF3’s polarity, backed by scientific principles and practical insights.
What Determines the Polarity of a Molecule?

The polarity of a molecule depends on two key factors: electronegativity differences and molecular geometry. Electronegativity measures an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a bond, while molecular geometry refers to the arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
- Electronegativity: If atoms in a molecule have significantly different electronegativities, the bond is polar.
- Molecular Geometry: Even with polar bonds, symmetrical geometry can cancel out the dipole moments, making the molecule nonpolar.
📌 Note: Polarity is not just about individual bonds but also the overall molecular structure.
Analyzing BF3: Electronegativity and Geometry

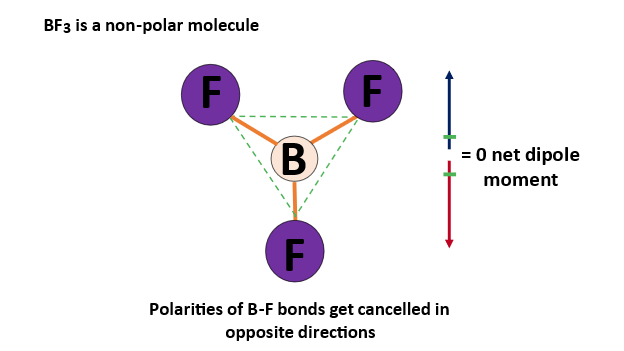
BF3 consists of one boron atom and three fluorine atoms. Fluorine is highly electronegative compared to boron, resulting in polar B-F bonds. However, BF3 has a trigonal planar geometry, where the three fluorine atoms are symmetrically arranged around the boron atom.
This symmetry ensures that the dipole moments of the B-F bonds cancel each other out, making BF3 a nonpolar molecule.
BF3 Polarity: A Summary

To summarize:
- B-F bonds: Polar due to electronegativity differences.
- Molecular geometry: Trigonal planar, leading to cancellation of dipole moments.
- Conclusion: BF3 is nonpolar.
Checklist: Determining Molecular Polarity
- Step 1: Identify electronegativity differences between atoms.
- Step 2: Analyze the molecular geometry.
- Step 3: Check if dipole moments cancel out.
Practical Applications of BF3

BF3 is widely used in organic synthesis as a catalyst, particularly in reactions like Friedel-Crafts alkylation. Its nonpolar nature makes it a versatile reagent in chemical processes.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Polarity | Nonpolar |
| Geometry | Trigonal Planar |
| Common Use | Catalyst in Organic Synthesis |
Wrapping Up
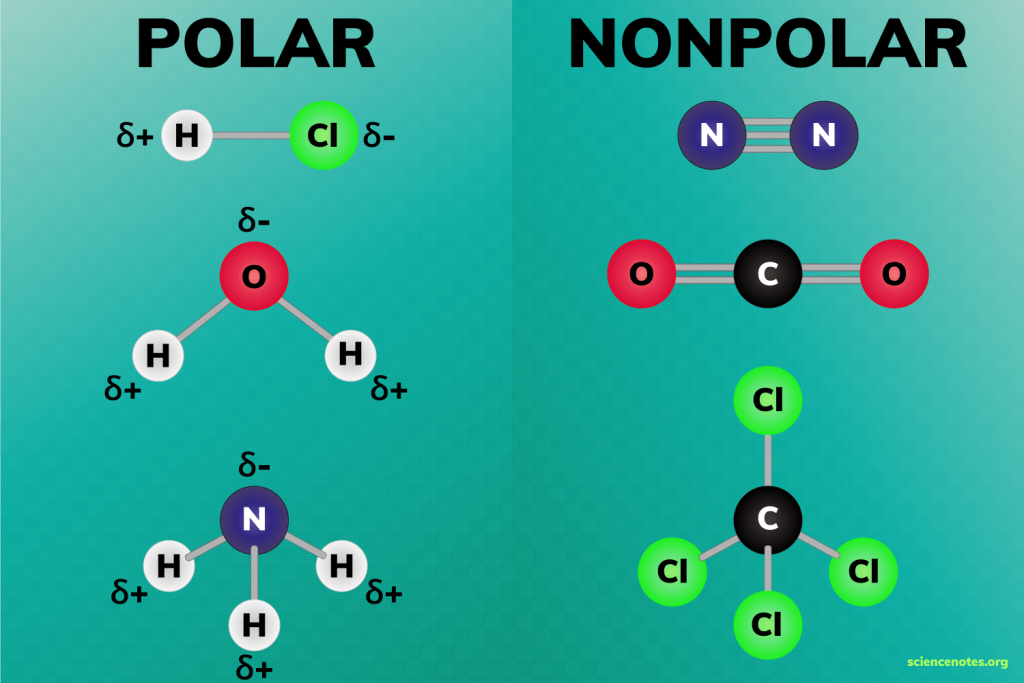
BF3 is a nonpolar molecule due to its symmetrical trigonal planar geometry, despite having polar B-F bonds. Understanding its polarity is essential for predicting its behavior in chemical reactions. Whether you’re a student or a professional, this knowledge will enhance your grasp of molecular chemistry.
Why is BF3 nonpolar despite having polar bonds?
+BF3 is nonpolar because its trigonal planar geometry causes the dipole moments of the polar B-F bonds to cancel each other out.
How does molecular geometry affect polarity?
+Symmetrical molecular geometry can cancel out dipole moments, making a molecule nonpolar, even if it has polar bonds.
What are the practical uses of BF3?
+BF3 is commonly used as a catalyst in organic synthesis, particularly in Friedel-Crafts alkylation reactions.
Related Keywords: BF3 polarity, molecular geometry, electronegativity, nonpolar molecules, chemical catalysts, organic synthesis.


