Carbon Monoxide Lewis Structure: Simple Guide
Understanding the Carbon Monoxide Lewis Structure is essential for anyone studying chemistry or working in fields related to chemical safety. Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless gas that can be deadly in high concentrations, making it crucial to comprehend its molecular structure. This guide will walk you through the process of drawing the Lewis structure of CO, ensuring you grasp the fundamentals with ease.
What is the Lewis Structure?

The Lewis structure is a diagram that represents the arrangement of atoms, electrons, and bonds in a molecule. It helps visualize how atoms share electrons to form stable compounds. For carbon monoxide (CO), understanding its Lewis structure is key to identifying its chemical properties and reactivity.
Step-by-Step Guide to Drawing the Carbon Monoxide Lewis Structure

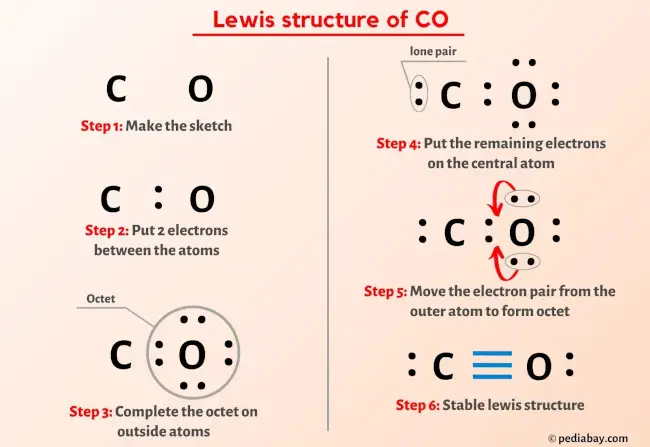
Step 1: Determine the Total Number of Valence Electrons
Carbon © has 4 valence electrons, and Oxygen (O) has 6 valence electrons. Together, CO has:
4 © + 6 (O) = 10 valence electrons.
Step 2: Identify the Central Atom
In CO, carbon © is the central atom because it is less electronegative than oxygen (O).
Step 3: Draw a Single Bond Between Atoms
Connect carbon and oxygen with a single bond, using 2 electrons. This leaves you with 8 remaining electrons.
Step 4: Complete the Octet for Oxygen
Place the remaining electrons around oxygen to complete its octet. Oxygen will have 6 non-bonding electrons (3 pairs).
Step 5: Check for Stability
The CO Lewis structure now has a triple bond between carbon and oxygen, ensuring both atoms achieve a stable electron configuration.
📌 Note: Carbon monoxide has a triple bond, which is unusual but explains its strong bonding and toxic nature.
Key Characteristics of the CO Lewis Structure

- Triple Bond: Carbon and oxygen are connected by one sigma bond and two pi bonds.
- Formal Charges: Both carbon and oxygen have a formal charge of 0, indicating stability.
- Linear Geometry: The molecule has a linear shape due to the triple bond.
Why is the CO Lewis Structure Important?

Understanding the Lewis structure of CO helps in predicting its reactivity, toxicity, and role in chemical reactions. It’s a foundational concept for students and professionals in chemistry, environmental science, and safety engineering.
Checklist for Drawing the CO Lewis Structure

- [ ] Count valence electrons (10 for CO).
- [ ] Place carbon as the central atom.
- [ ] Draw a triple bond between C and O.
- [ ] Complete the octet for oxygen with lone pairs.
- [ ] Verify formal charges and stability.
What is the bond type in carbon monoxide?
+Carbon monoxide (CO) has a triple bond consisting of one sigma bond and two pi bonds.
Why is carbon monoxide toxic?
+CO binds strongly to hemoglobin in the blood, preventing oxygen transport and leading to suffocation.
How does the CO Lewis structure explain its reactivity?
+The triple bond in CO makes it highly stable but also reactive in certain chemical processes, such as in industrial catalysis.
In summary, mastering the Carbon Monoxide Lewis Structure is a fundamental step in understanding its chemical behavior. By following the steps outlined above, you can confidently draw the structure and apply this knowledge in various scientific contexts. Whether you’re a student or a professional, this guide ensures clarity and precision in your chemical studies. (carbon monoxide toxicity,chemical bonding,lewis dot structure,molecular geometry)



