Understanding Joint Relative Frequency: A Clear Definition
<!DOCTYPE html>
Joint relative frequency is a fundamental concept in statistics and probability, offering insights into the relationship between two or more categorical variables. By understanding joint relative frequency, you can analyze how often specific combinations of events occur relative to the total number of observations. This concept is crucial for businesses, researchers, and analysts who need to make data-driven decisions, (data analysis, statistical insights, probability concepts).
What is Joint Relative Frequency?
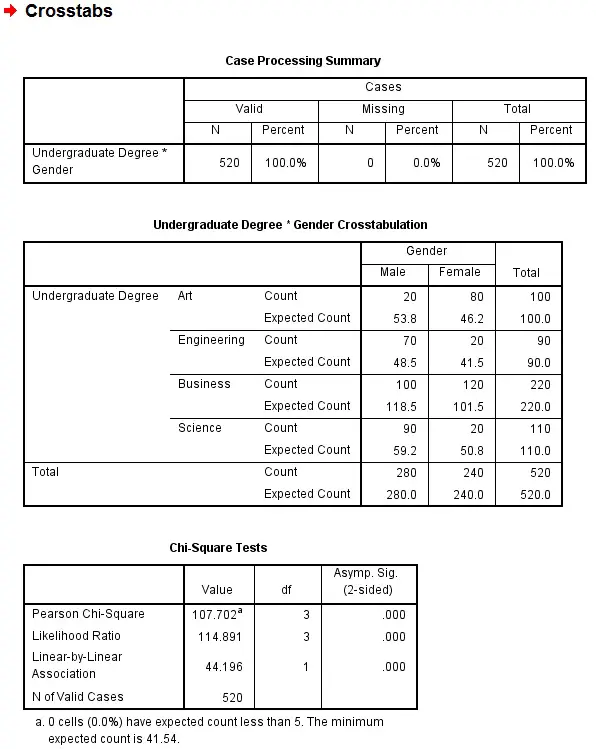
Joint relative frequency measures the proportion of times two or more events occur together in a dataset. It is calculated by dividing the frequency of the joint occurrence by the total number of observations. For example, if you’re analyzing the relationship between customer gender and product preference, joint relative frequency helps you determine how often male customers prefer a specific product compared to the total customer base, (statistical analysis, data interpretation, frequency distribution).
How to Calculate Joint Relative Frequency
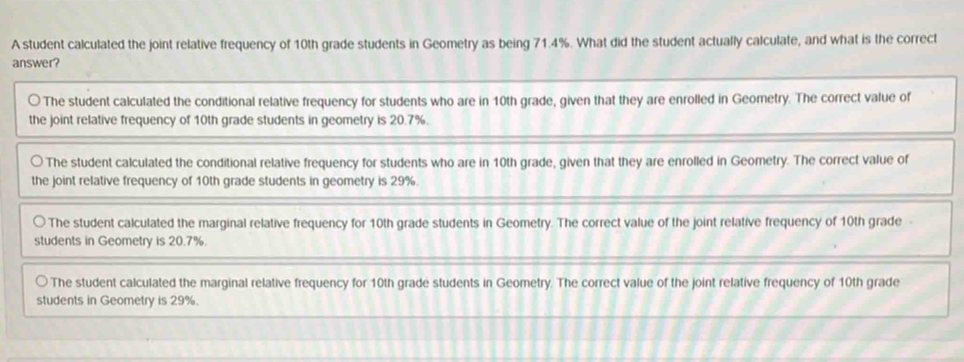
Calculating joint relative frequency involves a straightforward process:
- Step 1: Identify the Joint Frequency – Count how often two events occur together.
- Step 2: Determine the Total Frequency – Sum up all observations in the dataset.
- Step 3: Compute the Joint Relative Frequency – Divide the joint frequency by the total frequency.
📊 Note: Ensure your data is accurately categorized to avoid calculation errors.
Applications of Joint Relative Frequency

Joint relative frequency is widely used in various fields:
- Marketing – Analyze customer behavior and preferences.
- Healthcare – Study the relationship between diseases and risk factors.
- Finance – Assess the correlation between economic indicators and investment outcomes.
By leveraging this concept, professionals can uncover patterns and trends that inform strategic decisions, (market research, healthcare analytics, financial analysis).
Joint Relative Frequency vs. Marginal Relative Frequency

While joint relative frequency focuses on the co-occurrence of events, marginal relative frequency examines the occurrence of a single event. Understanding the difference helps in comprehensive data analysis, (statistical comparison, data visualization, analytical techniques).
| Aspect | Joint Relative Frequency | Marginal Relative Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Two or more events together | Single event |
| Calculation | Joint frequency / Total frequency | Frequency of event / Total frequency |

To effectively use joint relative frequency, follow this checklist:
- Ensure data is accurately categorized.
- Calculate joint frequencies for all relevant combinations.
- Compare results with marginal relative frequencies for deeper insights.
- Visualize data using tables or charts for clarity.
Joint relative frequency is a powerful tool for understanding relationships within data. By mastering this concept, you can enhance your analytical skills and make more informed decisions in both personal and professional contexts, (data-driven decisions, statistical mastery, analytical skills).
What is the difference between joint and marginal relative frequency?
+Joint relative frequency measures the co-occurrence of two or more events, while marginal relative frequency focuses on the occurrence of a single event.
How is joint relative frequency used in business?
+Businesses use joint relative frequency to analyze customer behavior, product preferences, and market trends, enabling data-driven decision-making.
Can joint relative frequency be applied to continuous data?
+Joint relative frequency is typically used for categorical data. For continuous data, other statistical methods like correlation analysis are more appropriate.



