Does Noncompetitive Inhibition Change Km?
Understanding the relationship between noncompetitive inhibition and Km is crucial for anyone studying enzyme kinetics or biochemical processes. Noncompetitive inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor binds to a site different from the active site, affecting the enzyme’s activity. But does this process alter the Michaelis-Menten constant (Km)? Let’s delve into this question to clarify its impact on enzyme behavior, enzyme kinetics, and biochemical pathways.
What is Noncompetitive Inhibition?

Noncompetitive inhibition occurs when an inhibitor binds to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, forming an enzyme-inhibitor complex. This binding reduces the enzyme’s catalytic efficiency, regardless of the substrate concentration. Unlike competitive inhibition, noncompetitive inhibitors do not compete directly with the substrate for the active site, making them distinct in their mechanism of action, enzyme regulation, and metabolic pathways.
Understanding Km in Enzyme Kinetics
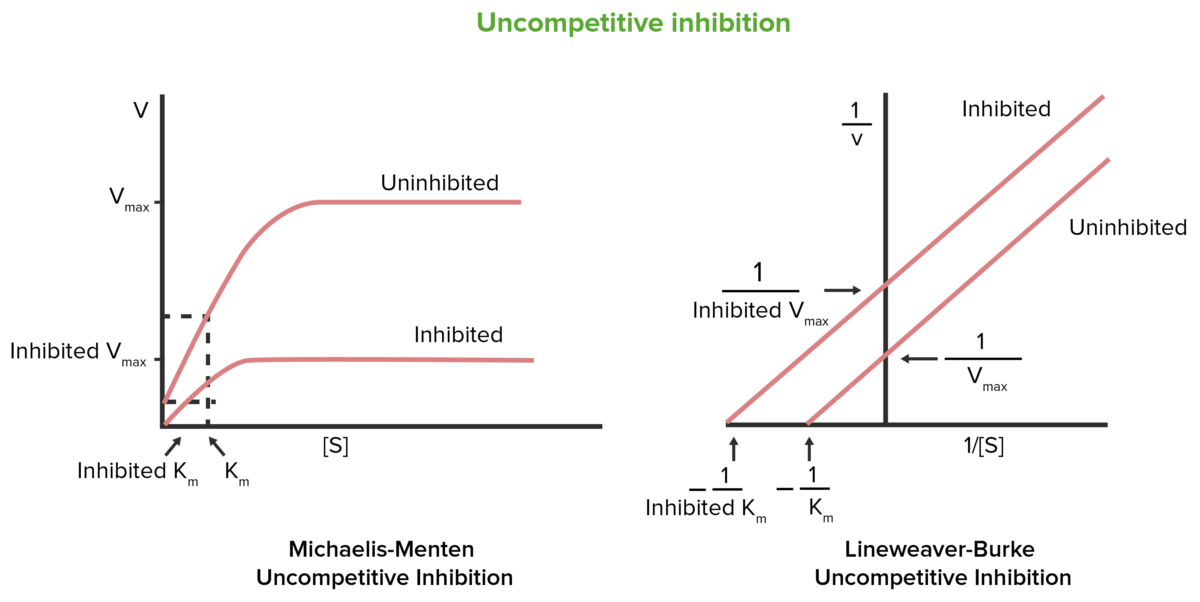
The Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) represents the substrate concentration at which an enzyme achieves half of its maximum reaction rate (Vmax). It is a measure of the enzyme’s affinity for its substrate. In enzyme kinetics studies, Km is a critical parameter for understanding how enzymes interact with substrates, reaction rates, and catalytic efficiency.
Does Noncompetitive Inhibition Change Km?
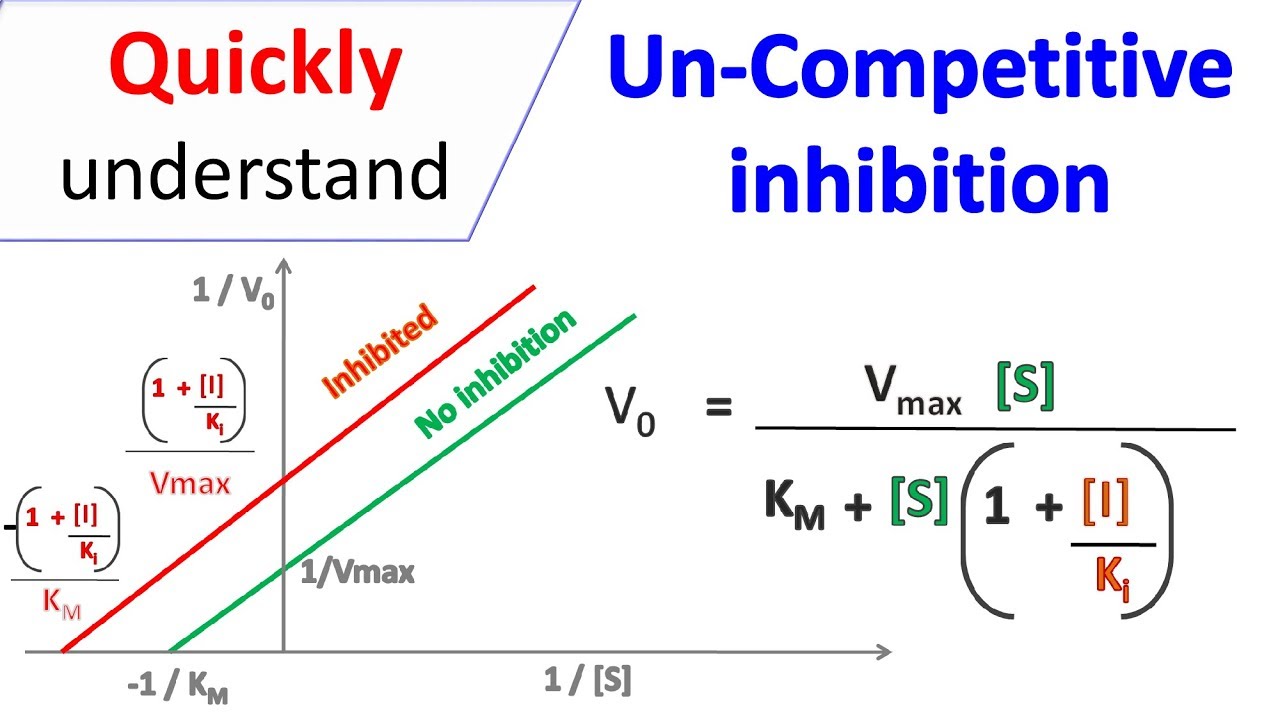
Noncompetitive inhibition does not change the Km value. This is because the inhibitor binds to a different site on the enzyme, altering the enzyme’s conformation and reducing its turnover number (kcat). However, the affinity of the enzyme for the substrate remains unchanged, as the active site is not directly affected. This distinction is vital in biochemical research, drug design, and understanding inhibition mechanisms.
| Type of Inhibition | Effect on Km | Effect on Vmax |
|---|---|---|
| Noncompetitive | No Change | Decreases |
| Competitive | Increases | No Change |
| Uncompetitive | Decreases | Decreases |

Implications in Biochemical Pathways

Understanding how noncompetitive inhibition affects biochemical pathways is essential for fields like pharmacology and metabolism research. Since Km remains unchanged, the substrate concentration required for half-maximal enzyme activity is consistent, but the overall reaction rate decreases. This knowledge aids in designing inhibitors for therapeutic purposes, drug development, and disease treatment.
📌 Note: Noncompetitive inhibition primarily affects Vmax, not Km, making it a unique regulatory mechanism in enzyme kinetics.
In summary, noncompetitive inhibition does not alter the Km value but reduces the enzyme’s catalytic efficiency by decreasing Vmax. This distinction is critical in enzyme studies, drug design, and understanding metabolic regulation. By grasping this concept, researchers can better predict enzyme behavior in various biochemical contexts, enzyme inhibition, and biochemical reactions.
What is the main difference between competitive and noncompetitive inhibition?
+Competitive inhibition directly competes with the substrate for the active site, increasing Km, while noncompetitive inhibition binds to a different site, reducing Vmax without changing Km, enzyme activity, substrate binding.
How does noncompetitive inhibition affect enzyme activity?
+Noncompetitive inhibition decreases the enzyme’s catalytic efficiency by reducing Vmax, but it does not alter the enzyme’s affinity for the substrate (Km), catalytic mechanisms, biochemical processes.
Why is understanding Km important in enzyme kinetics?
+Km helps determine the enzyme’s substrate affinity, which is crucial for analyzing reaction rates, optimizing biochemical pathways, and designing inhibitors, enzyme regulation, metabolic pathways.



