ECF in Medicine: What Does It Stand For?

In the medical field, acronyms like ECF often spark curiosity. Whether you're a healthcare professional or a patient, understanding what ECF in medicine stands for is crucial. This blog post will break down the meaning, significance, and applications of ECF, ensuring you leave with a clear understanding of this essential term. (Extracellular Fluid, Medical Acronyms, Healthcare Basics)
What Does ECF Stand For in Medicine?
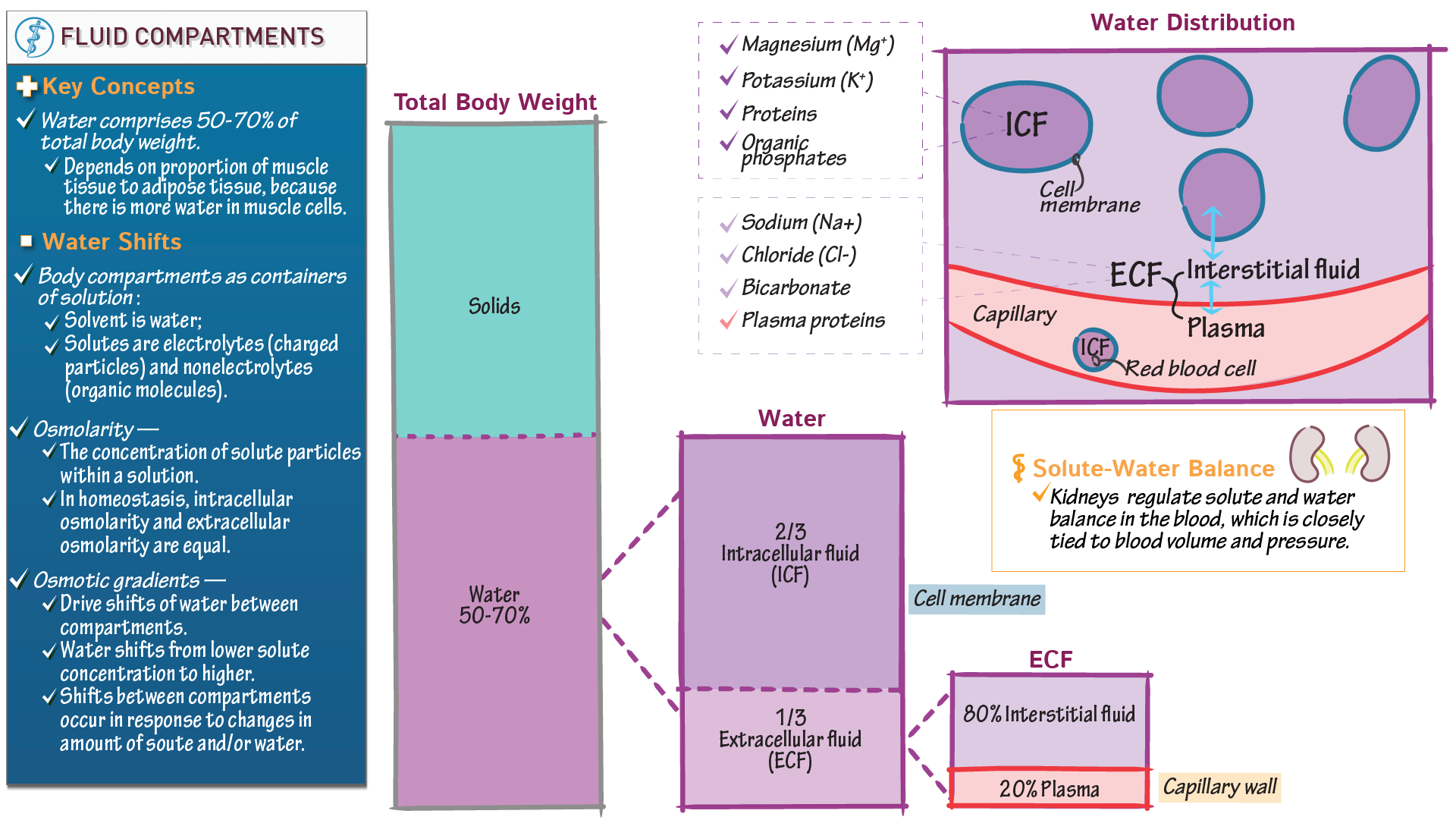
In medicine, ECF stands for Extracellular Fluid. This term refers to the bodily fluids found outside of cells, playing a vital role in maintaining homeostasis. Understanding ECF is key to grasping how the body regulates nutrient exchange, waste removal, and overall cellular function. (Extracellular Fluid, Homeostasis, Cellular Function)
The Role of ECF in the Body

Key Functions of Extracellular Fluid
Extracellular Fluid serves multiple critical functions, including:
- Nutrient Transport: Delivers essential nutrients to cells.
- Waste Removal: Helps eliminate cellular waste products.
- pH Balance: Maintains the body’s acid-base balance.
- Temperature Regulation: Assists in heat distribution.
These functions highlight the importance of ECF in overall health and wellness. (Nutrient Transport, Waste Removal, pH Balance)
ECF vs. ICF: Understanding the Difference

While ECF refers to fluids outside cells, ICF (Intracellular Fluid) refers to fluids inside cells. Together, they make up the body’s total fluid volume. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Aspect | ECF (Extracellular Fluid) | ICF (Intracellular Fluid) |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Outside cells | Inside cells |
| Primary Function | Transport and balance | Cellular metabolism |

📌 Note: Imbalances between ECF and ICF can lead to serious health issues, such as dehydration or edema. (ECF vs ICF, Fluid Balance, Health Imbalances)
Clinical Significance of ECF

Healthcare professionals often monitor ECF levels to diagnose and treat various conditions. For instance:
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Abnormal ECF levels can indicate issues like hypertension or kidney disease.
- Dehydration: Reduced ECF volume is a key indicator of dehydration.
- Edema: Excess ECF can cause swelling, often seen in heart or liver disease.
Understanding ECF is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment. (Clinical Significance, Electrolyte Imbalances, Dehydration)
ECF in Medicine: Key Takeaways
- ECF stands for Extracellular Fluid.
- It plays a critical role in nutrient transport, waste removal, and pH balance.
- Imbalances in ECF can lead to health issues like dehydration or edema.
- ECF is distinct from ICF, which refers to intracellular fluid.
In summary, ECF in medicine is a fundamental concept that underpins many physiological processes. Whether you're a medical professional or simply curious about how the body works, understanding Extracellular Fluid is invaluable. By recognizing its role and significance, you can better appreciate the complexity of human health. (Extracellular Fluid, Physiological Processes, Human Health)
What is the main function of ECF?
+
The main function of ECF is to transport nutrients, remove waste, and maintain pH and temperature balance in the body.
How is ECF different from ICF?
+
ECF refers to fluids outside cells, while ICF refers to fluids inside cells. Both are essential for bodily functions.
What happens if ECF levels are imbalanced?
+
Imbalanced ECF levels can lead to conditions like dehydration, edema, or electrolyte disorders, requiring medical attention.



