Carbon Atom Electron Configuration Explained Simply
Understanding the carbon atom electron configuration is essential for anyone studying chemistry or materials science. Carbon, with its atomic number 6, is a cornerstone element in organic chemistry and plays a vital role in life as we know it. Its electron configuration determines its chemical behavior, bonding capabilities, and overall properties. In this post, we’ll break down the electron configuration of carbon in simple terms, making it easy for both students and enthusiasts to grasp. Whether you're exploring carbon atom structure for academic purposes or practical applications, this guide has you covered.
What is the Electron Configuration of Carbon?
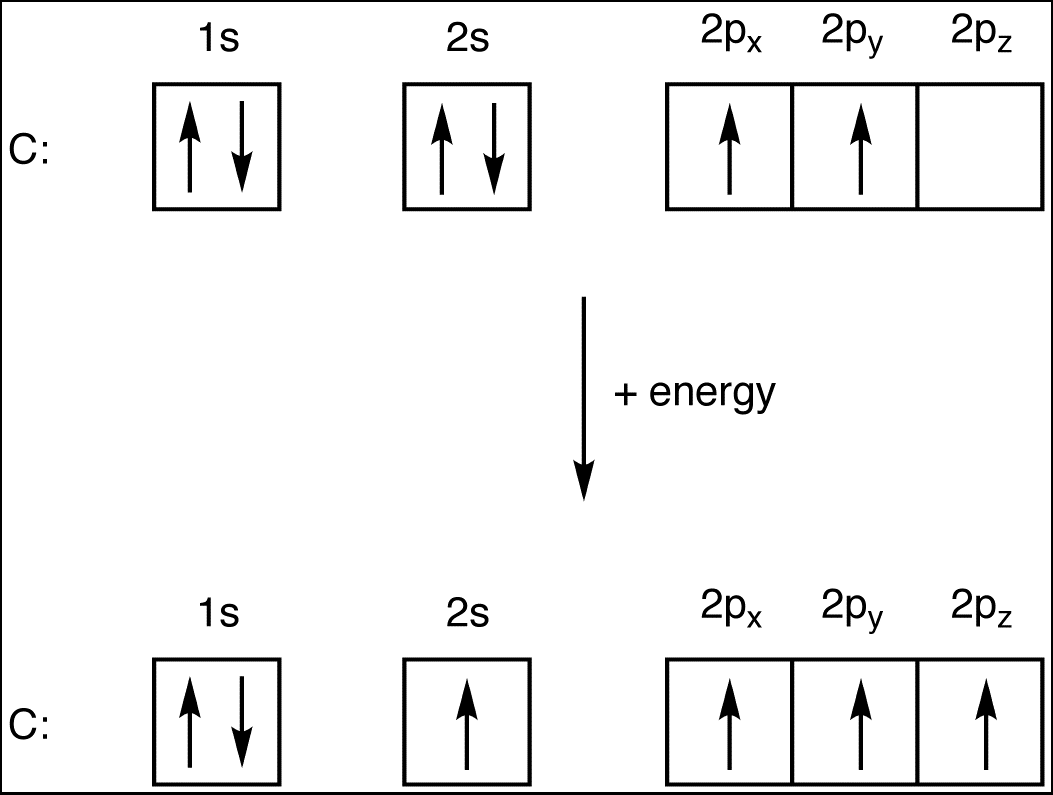
The electron configuration of carbon refers to how its six electrons are arranged in energy levels or shells around the nucleus. Carbon’s electron configuration is written as 1s² 2s² 2p². Let’s break this down:
- 1s²: The first shell (n=1) has two electrons in the s orbital.
- 2s²: The second shell (n=2) has two electrons in the s orbital.
- 2p²: The second shell also has two electrons in the p orbital.
This arrangement allows carbon to form four strong covalent bonds, making it a key player in organic compounds. (carbon atom structure, electron configuration of carbon, carbon electron arrangement)
Why is Carbon’s Electron Configuration Unique?
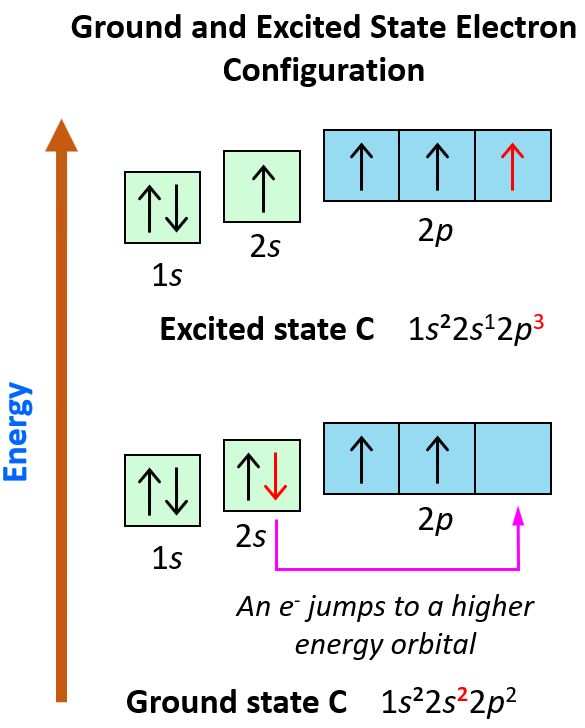
Carbon’s electron configuration is unique due to its ability to form multiple stable bonds, a property known as catenation. This uniqueness stems from its:
- Valence electrons: Carbon has four valence electrons, allowing it to bond with other atoms in various ways.
- Hybridization: Carbon can undergo sp³, sp², or sp hybridization to form different types of bonds.
- Versatility: This flexibility enables carbon to create complex molecules like proteins, DNA, and plastics.
Understanding this uniqueness is crucial for fields like organic chemistry and materials science. (carbon atom properties, carbon bonding, organic chemistry)
How to Determine Carbon’s Electron Configuration

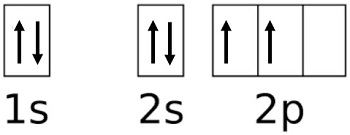
Determining the electron configuration of carbon involves following the Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle, and Hund’s rule. Here’s a simple step-by-step guide:
- Start with the lowest energy level (1s) and fill it with two electrons.
- Move to the next level (2s) and fill it with two electrons.
- Finally, add the remaining two electrons to the 2p orbital.
📌 Note: Electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy, following the diagonal rule in the periodic table.
Mastering this process helps in predicting carbon’s behavior in chemical reactions. (Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle, Hund’s rule)
Practical Applications of Carbon’s Electron Configuration

The carbon atom electron configuration has numerous practical applications across industries. Some key areas include:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Organic Chemistry | Forms the basis for studying hydrocarbons, alcohols, and other organic compounds. |
| Nanotechnology | Carbon nanotubes and graphene rely on carbon’s unique bonding properties. |
| Biochemistry | Essential for understanding biomolecules like carbohydrates and lipids. |
These applications highlight the importance of carbon’s electron configuration in modern science and technology. (carbon applications, nanotechnology, biochemistry)
Key Takeaways: Carbon Atom Electron Configuration
To summarize, here’s a checklist of what we’ve covered:
- Carbon’s electron configuration is 1s² 2s² 2p².
- Its four valence electrons enable versatile bonding.
- The Aufbau principle guides electron arrangement.
- Carbon’s configuration is vital in organic chemistry and nanotechnology.
By mastering these concepts, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of carbon’s role in the chemical world. (carbon atom summary, electron configuration checklist, carbon chemistry)
What is the electron configuration of carbon?
+The electron configuration of carbon is 1s² 2s² 2p².
Why does carbon have four valence electrons?
+Carbon has four valence electrons because its outermost shell (n=2) contains two electrons in the 2s orbital and two in the 2p orbital.
How does carbon’s electron configuration affect its bonding?
+Carbon’s four valence electrons allow it to form four strong covalent bonds, making it highly versatile in chemical reactions.
In wrapping up, the carbon atom electron configuration is a fundamental concept that underpins much of chemistry and materials science. By understanding its arrangement and properties, you’ll be better equipped to explore its applications in various fields. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or simply curious, this knowledge is a valuable addition to your scientific toolkit. (carbon atom electron configuration, carbon chemistry, materials science)



