Electron Configuration of Mn²⁺: Simplified Guide

Understanding the electron configuration of Mn²⁺ is essential for students and professionals in chemistry, physics, and materials science. Manganese (Mn) is a fascinating element with unique properties, and its Mn²⁺ ion plays a crucial role in various chemical processes. This guide simplifies the concept, making it accessible for both informational and commercial audiences. Whether you’re studying for an exam or looking for practical applications, this post has you covered.
What is Mn²⁺ and Why Does it Matter?
Manganese (Mn) is a transition metal with an atomic number of 25. When it loses two electrons to form Mn²⁺, its electron configuration changes significantly. This ion is vital in biological systems, industrial processes, and even in the production of batteries. Understanding its electron configuration helps predict its behavior in chemical reactions and its role in various compounds.
Step-by-Step Electron Configuration of Mn²⁺

To determine the electron configuration of Mn²⁺, follow these steps:
Write the Ground State Configuration of Mn:
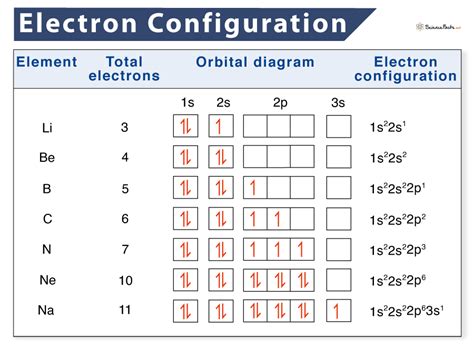
Manganese (Mn) has an atomic number of 25, so its ground state electron configuration is:
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d⁵.Remove Electrons to Form Mn²⁺:
When Mn loses two electrons, they are removed from the 4s orbital first, resulting in:
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d⁵.Final Configuration of Mn²⁺:
The electron configuration of Mn²⁺ is:
[Ar] 3d⁵.
📌 Note: The 4s orbital loses electrons before the 3d orbital due to the higher energy level of 4s in transition metals.
Key Properties of Mn²⁺
- Magnetic Behavior: Mn²⁺ has five unpaired electrons in its 3d orbital, making it paramagnetic.
- Color in Solutions: It often imparts a pale pink color to solutions due to its d-orbital transitions.
- Oxidation State: Mn²⁺ is a common oxidation state of manganese in compounds.
Practical Applications of Mn²⁺

- Batteries: Used in lithium-manganese oxide batteries for improved performance.
- Biological Systems: Essential in enzymes like manganese superoxide dismutase.
- Industrial Catalysts: Acts as a catalyst in various chemical reactions.
Checklist for Mastering Mn²⁺ Electron Configuration
- Understand the ground state electron configuration of Mn.
- Know the order of electron removal (4s before 3d).
- Memorize the final configuration: [Ar] 3d⁵.
- Relate the configuration to its magnetic and chemical properties.
Wrapping Up
The electron configuration of Mn²⁺ is a fundamental concept in chemistry, bridging theoretical knowledge with practical applications. By mastering this topic, you’ll gain insights into the behavior of transition metals and their ions. Whether you’re a student or a professional, this simplified guide ensures you have the tools to succeed.
What is the electron configuration of Mn²⁺?
+The electron configuration of Mn²⁺ is [Ar] 3d⁵.
Why does Mn lose electrons from the 4s orbital first?
+In transition metals, the 4s orbital has higher energy than the 3d orbital, so electrons are removed from 4s first.
What are the practical applications of Mn²⁺?
+Mn²⁺ is used in batteries, biological systems, and as an industrial catalyst.
electron configuration of Mn²⁺, Mn²⁺ ion properties, transition metals, manganese applications



