Essential EMS Patient Assessment Tips for Paramedics

As a paramedic, mastering EMS patient assessment is crucial for delivering effective and timely care. A thorough assessment not only ensures accurate diagnosis but also guides appropriate interventions. Whether you're a seasoned paramedic or a new EMT, these essential tips will enhance your skills and improve patient outcomes. From scene safety to vital signs, every step matters in emergency medical services (EMS). Let’s dive into the key strategies for conducting a comprehensive patient assessment, ensuring you’re prepared for any scenario. (EMS patient assessment, paramedic tips, emergency medical services)
1. Prioritize Scene Safety Before Starting the Assessment

Before approaching the patient, always assess the scene for safety. This includes checking for hazards like traffic, electrical wires, or unstable structures. Scene safety is the foundation of any successful EMS patient assessment. Once the area is secure, you can focus on the patient without risking additional injuries. (scene safety, EMS protocols, patient assessment)
2. Master the Primary Assessment: ABCs and More

The primary assessment focuses on the patient’s Airway, Breathing, and Circulation (ABCs). These are the most critical elements to evaluate initially. Ensure the airway is clear, assess breathing patterns, and check for circulation by monitoring pulse and skin condition. Additionally, evaluate the patient’s level of consciousness using the AVPU scale (Alert, Voice, Pain, Unresponsive). (primary assessment, ABCs, AVPU scale)
Key Steps in Primary Assessment:
- Airway: Clear obstructions and position the patient for optimal airflow.
- Breathing: Observe chest rise, listen for abnormal sounds, and measure respiratory rate.
- Circulation: Check for bleeding, pallor, or cyanosis, and monitor pulse strength.
3. Conduct a Detailed Secondary Assessment
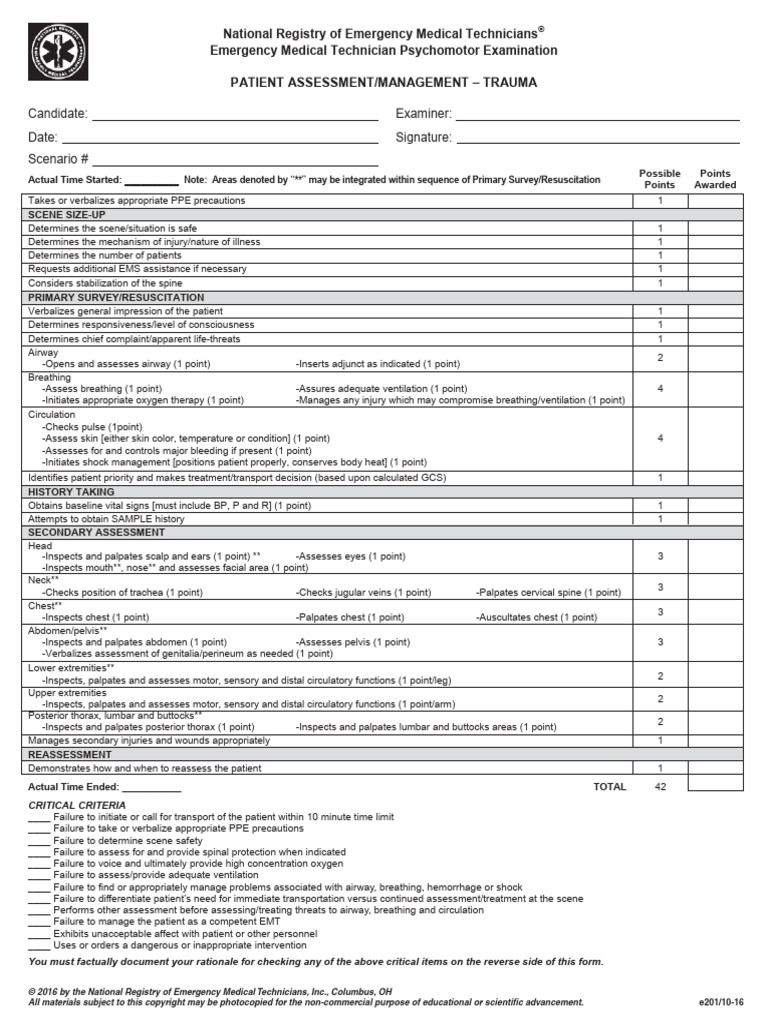
Once the primary assessment is complete, proceed to the secondary assessment. This involves a head-to-toe evaluation to identify injuries, underlying conditions, or other concerns. Use a systematic approach to ensure no detail is missed. (secondary assessment, head-to-toe evaluation, EMS checklist)
Steps for Secondary Assessment:
- Head and Neck: Check for trauma, deformities, or swelling.
- Chest and Abdomen: Assess for pain, tenderness, or abnormal sounds.
- Extremities: Look for fractures, bruising, or decreased sensation.
📌 Note: Always document findings clearly and concisely during the assessment.
4. Monitor Vital Signs and Reassess Regularly

Vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation provide critical insights into the patient’s condition. Use portable monitoring devices to track these parameters continuously. Reassess the patient’s status regularly, especially during transport, to detect any changes early. (vital signs monitoring, EMS equipment, patient reassessment)
| Vital Sign | Normal Range | Concerning Signs |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Pressure | 90/60 - 120/80 mmHg | Hypotension (<90/60), Hypertension (>180/120) |
| Heart Rate | 60 - 100 bpm | Tachycardia (>100), Bradycardia (<60) |
| Oxygen Saturation | 95% - 100% | <92% |

5. Communicate Effectively with the Patient and Team

Clear communication is essential during EMS patient assessment. Speak calmly to the patient, explain procedures, and address their concerns. Equally important is team communication, ensuring everyone is informed about the patient’s condition and next steps. (communication in EMS, patient interaction, team coordination)
EMS Patient Assessment Checklist:
- ✅ Ensure scene safety before approaching the patient.
- ✅ Complete the primary assessment (ABCs and AVPU).
- ✅ Perform a systematic head-to-toe secondary assessment.
- ✅ Monitor and document vital signs regularly.
- ✅ Communicate clearly with the patient and team.
Mastering EMS patient assessment is a cornerstone of paramedic practice. By prioritizing scene safety, conducting thorough primary and secondary assessments, monitoring vital signs, and communicating effectively, you can deliver high-quality care in any emergency. These tips not only enhance your skills but also ensure better outcomes for your patients. Stay prepared, stay vigilant, and keep refining your techniques for excellence in EMS. (EMS patient assessment, paramedic skills, emergency care)
What is the first step in EMS patient assessment?
+
The first step is to ensure scene safety before approaching the patient. This prevents additional injuries and ensures a secure environment for assessment.
Why is the primary assessment critical in EMS?
+
The primary assessment focuses on Airway, Breathing, and Circulation (ABCs), which are vital for the patient’s immediate survival. It helps identify life-threatening conditions quickly.
How often should vital signs be reassessed during transport?
+
Vital signs should be reassessed regularly, ideally every 5-15 minutes during transport, depending on the patient’s condition and stability.



