Face Centered Cubic Coordination Number Explained
Understanding the Face Centered Cubic (FCC) Coordination Number is essential for anyone studying materials science, crystallography, or solid-state physics. The FCC structure is one of the most common crystal lattices found in metals and alloys, and its coordination number plays a pivotal role in determining material properties. Let’s dive into what the FCC coordination number is, why it matters, and how it influences material behavior.
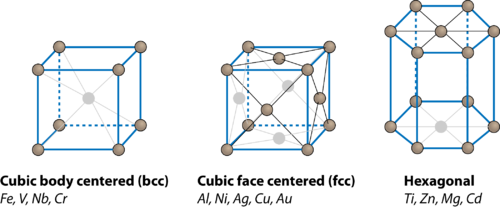
What is Face Centered Cubic (FCC) Structure?

The Face Centered Cubic (FCC) structure is a type of crystal lattice where atoms are arranged at each corner of a cube and at the center of each face. This arrangement maximizes atomic packing efficiency, making FCC structures highly stable and prevalent in materials like gold, silver, and aluminum.
💡 Note: The FCC structure is also known as a cubic close-packed (CCP) structure, highlighting its efficient atomic arrangement.
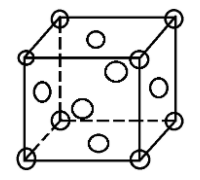
What is the Coordination Number in FCC?

The coordination number in a crystal lattice refers to the number of nearest neighbors an atom has. In the FCC structure, each atom is surrounded by 12 nearest neighbors. This is calculated by considering the atoms at the corners and face centers of the unit cell.
- Corner atoms: Each corner atom contributes 1⁄8 to the central atom’s coordination.
- Face center atoms: Each face center atom contributes 1⁄2 to the central atom’s coordination.
Thus, the total coordination number is:
[ 8 \times \frac{1}{8} + 6 \times \frac{1}{2} = 12 ]
| Structure | Coordination Number |
|---|---|
| Face Centered Cubic (FCC) | 12 |
Why is the FCC Coordination Number Important?

The FCC coordination number directly impacts material properties such as:
- Ductility: FCC metals like copper and aluminum are highly ductile due to the close packing of atoms.
- Electrical Conductivity: The arrangement of atoms in FCC structures facilitates electron movement, enhancing conductivity.
- Strength: Alloying FCC materials can alter their coordination number, improving mechanical strength.
🔍 Note: Understanding the coordination number helps engineers design materials with specific properties for industrial applications.
Comparing FCC with Other Structures

To appreciate the significance of the FCC coordination number, it’s helpful to compare it with other crystal structures like Body Centered Cubic (BCC) and Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP).
- BCC: Coordination number of 8.
- HCP: Coordination number of 12.
- FCC: Coordination number of 12.
While FCC and HCP share the same coordination number, their atomic arrangements differ, leading to variations in material behavior.
Practical Applications of FCC Coordination Number

For commercial-intent visitors, understanding the FCC coordination number is crucial for:
- Material Selection: Choosing the right FCC metal for manufacturing based on its properties.
- Alloy Development: Designing alloys with enhanced strength and durability.
- Nanotechnology: Utilizing FCC structures in nanomaterials for advanced applications.
🛠️ Note: Industries like aerospace and electronics heavily rely on FCC materials for their unique properties.
Key Takeaways
- The FCC coordination number is 12, indicating 12 nearest neighbors per atom.
- This number influences material properties like ductility, conductivity, and strength.
- FCC structures are widely used in metals and alloys due to their stability and efficiency.
What is the coordination number of FCC?
+The coordination number of FCC is 12, as each atom is surrounded by 12 nearest neighbors.
How does FCC coordination number affect material properties?
+It influences properties like ductility, electrical conductivity, and strength due to the close packing of atoms.
What are common examples of FCC materials?
+Gold, silver, aluminum, and copper are common examples of FCC materials.
In summary, the Face Centered Cubic coordination number is a fundamental concept in materials science, shaping the properties and applications of metals and alloys. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or industry professional, mastering this concept is key to unlocking the potential of FCC materials. (crystal structure,material science,metallurgy)



