Understanding the Half Equivalence Point in Acid-Base Titrations

Acid-base titrations are a fundamental technique in chemistry, allowing precise determination of the concentration of an unknown solution. Among the critical points in this process is the half equivalence point, a concept often misunderstood but crucial for accurate analysis. This point signifies when half of the acid (or base) has been neutralized by the titrant, providing valuable insights into the solution’s properties. Understanding this concept not only enhances your analytical skills but also ensures reliable results in laboratory experiments.
What is the Half Equivalence Point?

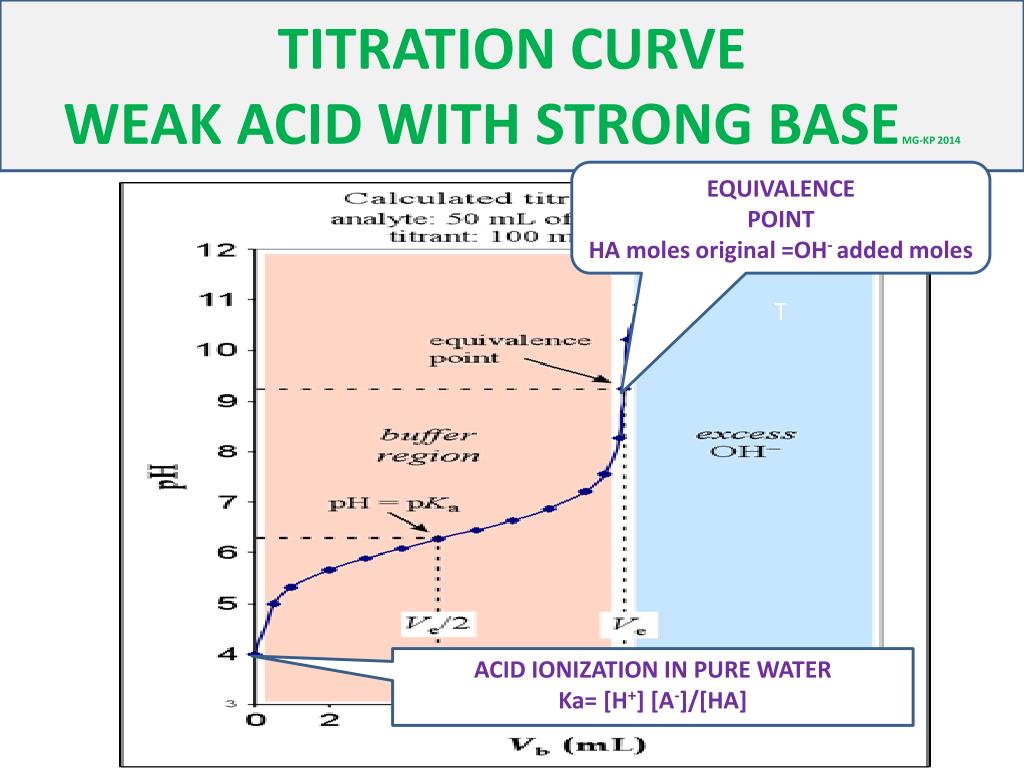
The half equivalence point in an acid-base titration occurs when the volume of the titrant added is exactly half of what is required to reach the equivalence point. At this stage, the concentration of the weak acid (or base) is equal to the concentration of its conjugate base (or acid), resulting in a buffer solution. This point is particularly important because it corresponds to the pKa (acid dissociation constant) of the weak acid, making it a key parameter in pH calculations and solution analysis.
📌 Note: The half equivalence point is not the same as the equivalence point. While the equivalence point marks complete neutralization, the half equivalence point is halfway to this stage.
How to Identify the Half Equivalence Point
Identifying the half equivalence point involves monitoring the pH of the solution during titration. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Plot a Titration Curve: Graph the pH of the solution against the volume of titrant added.
- Locate the Inflection Point: The half equivalence point appears as an inflection point on the curve, where the pH changes rapidly.
- Use a pH Meter: For precise measurements, a pH meter is essential to track pH changes accurately.
| Step | Action | Tool Required |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Add titrant gradually | Burette |
| 2 | Measure pH after each addition | pH Meter |
| 3 | Plot data on a graph | Graph Paper or Software |
Key Indicators of the Half Equivalence Point
- pH Value: For a weak acid, the pH at the half equivalence point equals the pKa of the acid.
- Buffer Formation: The solution acts as a buffer, resisting significant pH changes.
- Visual Clues: In some cases, indicators like phenolphthalein may show a slight color change, but pH measurement is more reliable.
Applications of the Half Equivalence Point

Understanding the half equivalence point is vital in various fields, including:
- Pharmaceutical Analysis: Determining the potency of drugs.
- Environmental Testing: Measuring acidity or basicity of water samples.
- Quality Control: Ensuring product consistency in manufacturing.
Checklist for Accurate Half Equivalence Point Determination
- Use a calibrated pH meter for precise measurements.
- Ensure the titrant and analyte are properly mixed after each addition.
- Plot the titration curve carefully to identify the inflection point.
- Verify the pKa value of the weak acid for accurate pH calculations.
The half equivalence point is a cornerstone in acid-base titrations, offering critical insights into solution properties. By mastering its identification and application, you can enhance the accuracy and reliability of your chemical analyses. Whether in academia, industry, or research, this knowledge is indispensable for anyone working with titration techniques.
What is the significance of the half equivalence point?
+The half equivalence point is crucial as it corresponds to the pKa of the weak acid, aiding in pH calculations and buffer solution identification.
How does the half equivalence point differ from the equivalence point?
+The half equivalence point occurs when half of the acid is neutralized, while the equivalence point marks complete neutralization.
Can the half equivalence point be determined visually?
+While indicators may show slight changes, pH measurement using a meter is the most accurate method.
acid-base titrations,half equivalence point,pH calculations,buffer solutions,titration curve,pKa value,laboratory techniques,chemical analysis,acid dissociation constant,inflection point,pH meter,titration process,analytical chemistry,weak acid,conjugate base,acid neutralization,equivalence point,titrant volume,pH changes,buffer formation,phenolphthalein indicator,pharmaceutical analysis,environmental testing,quality control,chemical manufacturing,academic research,industrial applications,solution properties,reliable results,laboratory experiments.



