Understanding Head Loss Units: A Quick Guide
Understanding head loss is crucial for anyone involved in fluid dynamics, plumbing, or HVAC systems. Head loss refers to the reduction in pressure or energy in a fluid as it flows through a system due to friction, obstructions, or changes in direction. Whether you’re a professional engineer or a DIY enthusiast, grasping the concept of head loss units can help you optimize system efficiency and troubleshoot issues effectively.
What Are Head Loss Units?
Head loss units measure the energy dissipation in a fluid system, typically expressed in terms of pressure head, velocity head, or elevation head. These units are essential for calculating the total head loss in pipes, pumps, and other components. Common units include meters (m), feet (ft), or pascals (Pa), depending on the system and region.
Types of Head Loss
Major Head Loss
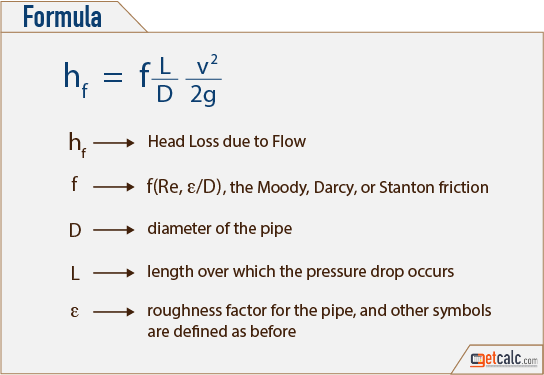
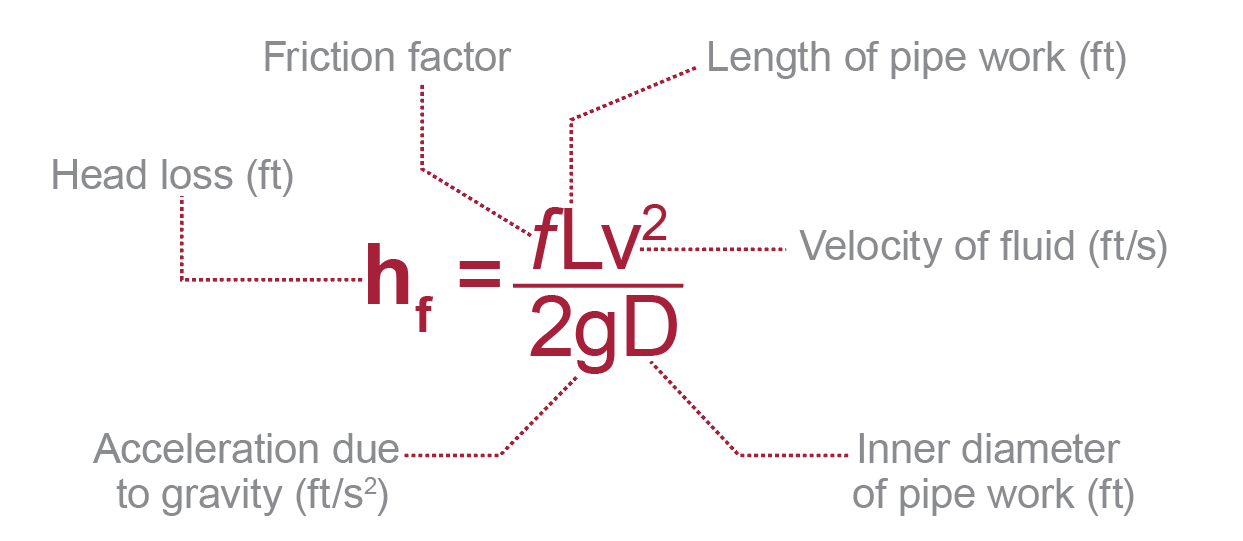
Major head loss occurs due to frictional resistance in straight pipes. It depends on factors like fluid velocity, pipe length, and pipe diameter. The Darcy-Weisbach equation is widely used to calculate major head loss:
hₗ = (f ⋅ L/D ⋅ v²) / (2g)
Where:
- f = friction factor
- L = pipe length
- D = pipe diameter
- v = fluid velocity
- g = acceleration due to gravity
Minor Head Loss
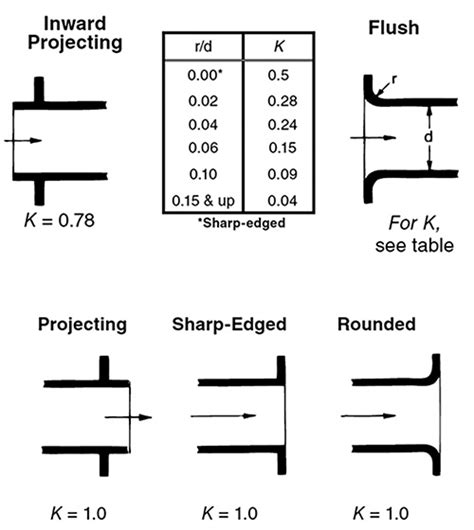
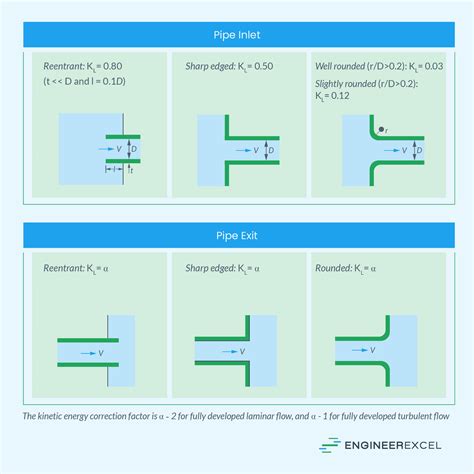
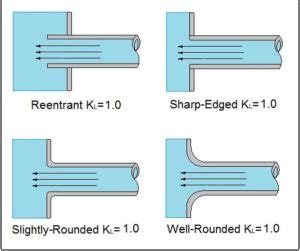
Minor head loss results from local disturbances such as valves, fittings, or bends. It is often quantified using the K-factor or loss coefficient:
hₗ = K ⋅ (v² / 2g)
Minor losses are cumulative and can significantly impact system performance.
💡 Note: Always account for both major and minor head losses when designing or analyzing fluid systems.
Factors Affecting Head Loss
Several factors influence head loss, including:
- Fluid Properties: Viscosity and density affect friction.
- Pipe Characteristics: Material, roughness, and diameter play a key role.
- Flow Rate: Higher velocities increase head loss.
- System Design: Bends, fittings, and obstructions contribute to minor losses.
Calculating Head Loss: A Practical Approach
To calculate head loss, follow these steps:
1. Identify System Components: List pipes, fittings, and equipment.
2. Determine Flow Parameters: Measure velocity, pipe dimensions, and fluid properties.
3. Apply Equations: Use the Darcy-Weisbach or K-factor formulas for major and minor losses.
4. Sum Losses: Add all head losses to find the total head loss.
📊 Note: Use software tools or charts for accurate friction factor calculations.
Optimizing Systems to Minimize Head Loss

Reducing head loss improves efficiency and saves energy. Here’s how:
- Choose Smooth Pipes: Minimize friction with smooth interior surfaces.
- Increase Pipe Diameter: Larger pipes reduce velocity and friction.
- Limit Fittings: Use fewer bends and fittings to decrease minor losses.
- Regular Maintenance: Clean pipes to prevent buildup and obstructions.
Head Loss Units in Real-World Applications
Understanding head loss units is vital in industries like:
- Plumbing: Ensuring water flows efficiently through pipes.
- HVAC: Optimizing air and refrigerant flow in systems.
- Manufacturing: Maintaining fluid processes in machinery.
Checklist for Head Loss Calculations
- [ ] Identify all system components.
- [ ] Measure flow rate and fluid properties.
- [ ] Calculate major head loss using the Darcy-Weisbach equation.
- [ ] Calculate minor head loss using K-factors.
- [ ] Sum all losses for total head loss.
Wrapping Up
Mastering head loss units is essential for designing and maintaining efficient fluid systems. By understanding the types, factors, and calculation methods, you can optimize performance and troubleshoot issues effectively. Whether you’re working on a small plumbing project or a large industrial system, this knowledge will serve as a valuable tool in your toolkit.
What causes head loss in pipes?
+Head loss in pipes is primarily caused by frictional resistance (major loss) and local disturbances like fittings or bends (minor loss).
How can I reduce head loss in my system?
+Reduce head loss by using larger pipes, minimizing fittings, maintaining smooth surfaces, and ensuring proper flow rates.
Why is head loss important in HVAC systems?
+In HVAC systems, head loss affects airflow and system efficiency, impacting heating and cooling performance.
(head loss calculation, fluid dynamics, plumbing efficiency, HVAC optimization, pipe friction)