Heat Capacity of Aluminum: Essential Facts & Uses

Aluminum is a versatile and widely used metal known for its lightweight, corrosion resistance, and excellent thermal conductivity. One of its most critical properties is its heat capacity, which plays a vital role in various applications, from engineering to everyday products. Understanding the heat capacity of aluminum is essential for optimizing its use in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. This blog explores the key facts, uses, and importance of aluminum’s heat capacity, tailored for both informational and commercial audiences.
What is Heat Capacity and Why Does it Matter?

Heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius. For aluminum, this property is crucial because it determines how efficiently the metal can absorb, store, and transfer heat.
- Informational Insight: Aluminum has a specific heat capacity of approximately 0.9 J/g°C, which is lower than many other metals like iron or copper. This means it heats up and cools down faster, making it ideal for applications requiring rapid thermal response.
- Commercial Application: In industries like automotive manufacturing, aluminum’s heat capacity allows for efficient heat dissipation in engines and radiators, enhancing performance and longevity.
💡 Note: Aluminum’s heat capacity makes it a preferred material for heat sinks in electronics, ensuring devices remain cool under operation.
Key Facts About Aluminum’s Heat Capacity

1. Low Specific Heat Capacity
Aluminum’s low specific heat capacity means it requires less energy to change its temperature compared to other metals. This property is advantageous in systems where quick heating or cooling is necessary.
2. High Thermal Conductivity
While heat capacity measures heat storage, thermal conductivity measures heat transfer. Aluminum’s high thermal conductivity (around 237 W/mK) complements its heat capacity, making it an excellent material for thermal management.
3. Applications in Everyday Life
From cookware to beverage cans, aluminum’s heat capacity ensures efficient heating and cooling, making it a staple in household items.
| Property | Value | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Specific Heat Capacity | 0.9 J/g°C | Rapid thermal response systems |
| Thermal Conductivity | 237 W/mK | Heat sinks, radiators |

Practical Uses of Aluminum’s Heat Capacity
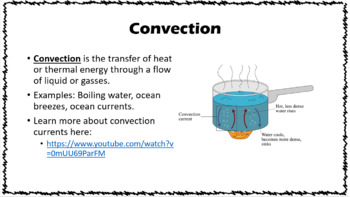
Automotive Industry
Aluminum’s ability to dissipate heat quickly makes it ideal for engine components, reducing the risk of overheating and improving fuel efficiency.
Electronics
In electronics, aluminum is used in heat sinks to protect sensitive components from thermal damage, ensuring optimal performance.
Construction
Aluminum’s heat capacity contributes to energy-efficient buildings by regulating indoor temperatures through reflective roofing and insulation systems.
How to Leverage Aluminum’s Heat Capacity

For informational-intent readers:
- Study aluminum’s thermal properties to understand its role in material science.
- Explore its applications in renewable energy systems like solar panels.
For commercial-intent visitors:
- Consider aluminum for manufacturing heat-sensitive products.
- Invest in aluminum-based solutions for thermal management in electronics or automotive sectors.
🔧 Note: When selecting aluminum for thermal applications, ensure compatibility with other materials to maximize efficiency.
Aluminum’s heat capacity, combined with its lightweight and durability, makes it an indispensable material across industries. Whether you’re an engineer, manufacturer, or simply curious about materials science, understanding this property unlocks new possibilities for innovation and efficiency.
What is the heat capacity of aluminum?
+Aluminum has a specific heat capacity of approximately 0.9 J/g°C.
Why is aluminum used in heat sinks?
+Aluminum’s high thermal conductivity and low heat capacity make it efficient for dissipating heat in electronic devices.
How does aluminum’s heat capacity benefit the automotive industry?
+It helps in efficient heat dissipation, preventing engine overheating and improving fuel efficiency.
thermal conductivity, material science, aluminum applications, heat dissipation, thermal management,aluminum properties,engineering materials,energy efficiency,automotive materials,electronics cooling.