Unveiling the Male Human Skull: Anatomy and Facts
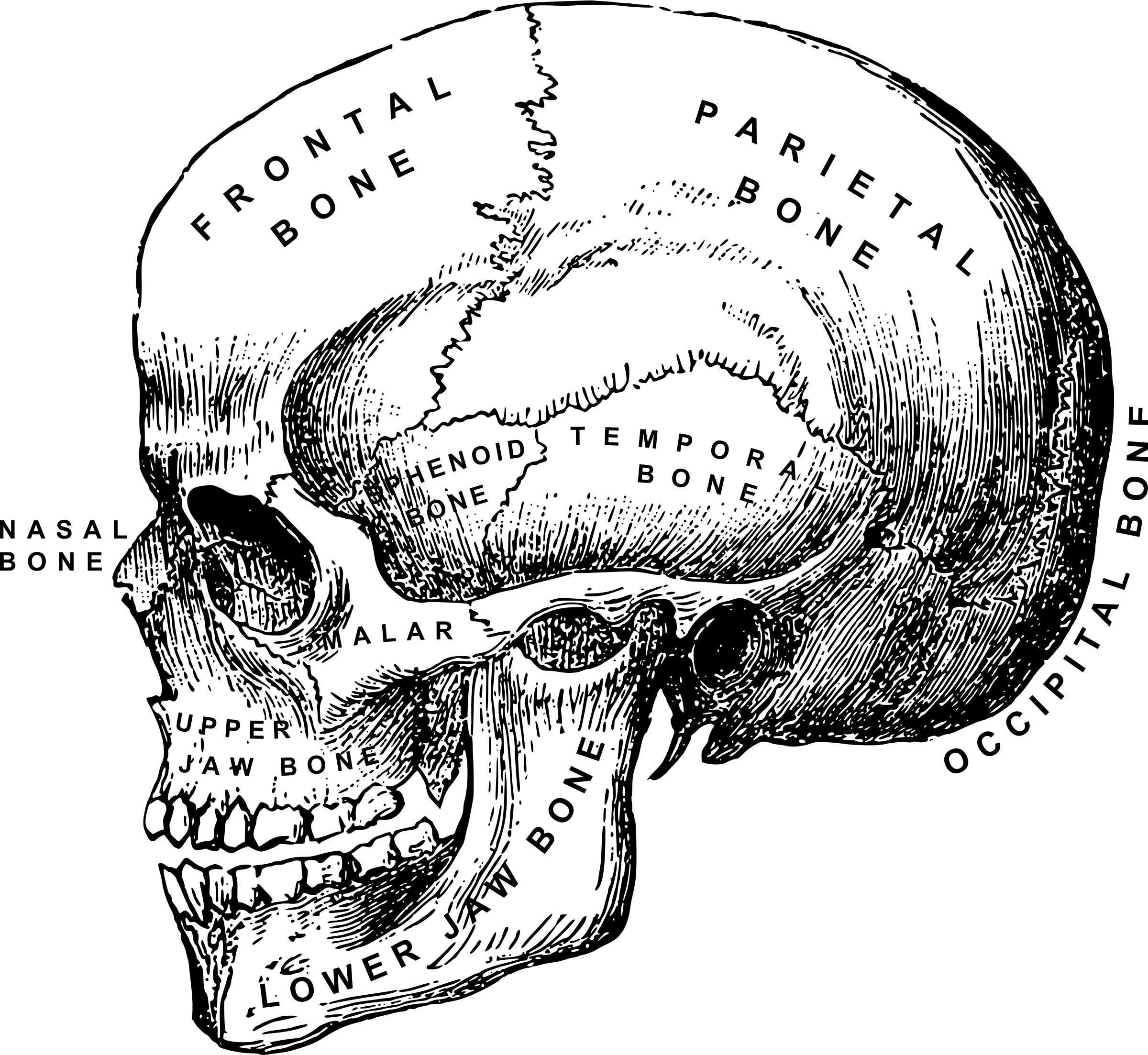
The male human skull is a fascinating structure, serving as the protective casing for the brain and housing several sensory organs. Its intricate design is a testament to the complexity of human anatomy. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or simply curious about the human body, understanding the male skull’s anatomy and its unique features can be both enlightening and educational. From its robust structure to its evolutionary significance, the male skull offers a wealth of information. (male human skull anatomy, human skull facts, male skull structure)
Key Features of the Male Human Skull
The male human skull is characterized by its robust and well-defined features. It consists of 22 bones, which are divided into the cranium (8 bones) and the facial skeleton (14 bones). The cranium, also known as the neurocranium, protects the brain, while the facial skeleton supports the eyes, nose, and mouth. Key features include the frontal bone, parietal bones, temporal bones, and the mandible, which is the only movable bone in the skull. (skull bone structure, cranium anatomy, facial skeleton)
Cranial Bones and Their Functions
The cranium is a vital component of the skull, providing a protective shell for the brain. It comprises the following bones:
- Frontal Bone: Forms the forehead and the roof of the eye sockets.
- Parietal Bones: Located on the sides and roof of the cranium.
- Temporal Bones: Found at the sides and base of the skull, housing the ears.
- Occipital Bone: Forms the back and base of the cranium.
- Sphenoid and Ethmoid Bones: Located at the base of the skull, supporting the brain and nasal cavity.
📌 Note: The cranial bones are fused together in adults, providing rigidity and protection.
Facial Bones and Their Roles
The facial skeleton is responsible for the skull’s facial features and supports sensory organs. Key bones include:
- Mandible: The lower jawbone, crucial for chewing and speech.
- Maxilla: Forms the upper jaw, holding the upper teeth and supporting the nose.
- Zygomatic Bones: Also known as cheekbones, they define the facial contour.
- Nasal Bones: Form the bridge of the nose.
Interesting Facts About the Male Skull

The male skull exhibits several unique characteristics, often influenced by hormonal and genetic factors. Here are some intriguing facts:
- Robustness: Male skulls are generally larger and more robust than female skulls due to higher levels of testosterone during development.
- Brow Ridges: Prominent brow ridges are a common feature in male skulls, providing attachment points for strong jaw muscles.
- Mastoid Processes: These bony projections behind the ears are typically more pronounced in males.
| Feature | Male Skull | Female Skull |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Larger | Smaller |
| Brow Ridges | Prominent | Less Prominent |
| Mastoid Processes | More Pronounced | Less Pronounced |

Practical Applications of Skull Anatomy

Understanding the male skull’s anatomy has practical applications in various fields:
- Forensics: Skull analysis helps in identifying individuals and determining cause of death.
- Medicine: Knowledge of skull anatomy is crucial for surgeries and treating injuries.
- Anthropology: Studying skulls provides insights into human evolution and migration patterns.
Checklist for Studying the Male Skull
- Identify the cranial bones and their functions.
- Examine the facial bones and their roles in facial structure.
- Compare male and female skulls to note differences.
- Explore practical applications in forensics, medicine, and anthropology.
The male human skull is a marvel of anatomy, offering insights into human evolution, biology, and medicine. Its robust structure and unique features make it a subject of great interest across various disciplines. By understanding its anatomy and functions, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity of the human body. Whether for academic purposes or personal curiosity, exploring the male skull is both rewarding and enlightening. (human skull anatomy, male skull features, skull study guide)
What are the main differences between male and female skulls?
+Male skulls are generally larger and more robust, with prominent brow ridges and mastoid processes. Female skulls tend to be smaller and smoother in appearance.
How many bones make up the male human skull?
+The male human skull consists of 22 bones, divided into the cranium (8 bones) and the facial skeleton (14 bones).
Why is the mandible the only movable bone in the skull?
+The mandible, or lower jawbone, is connected to the skull by the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), allowing movement for functions like chewing and speaking.



