Iodine: Location, Properties & Facts on the Periodic Table
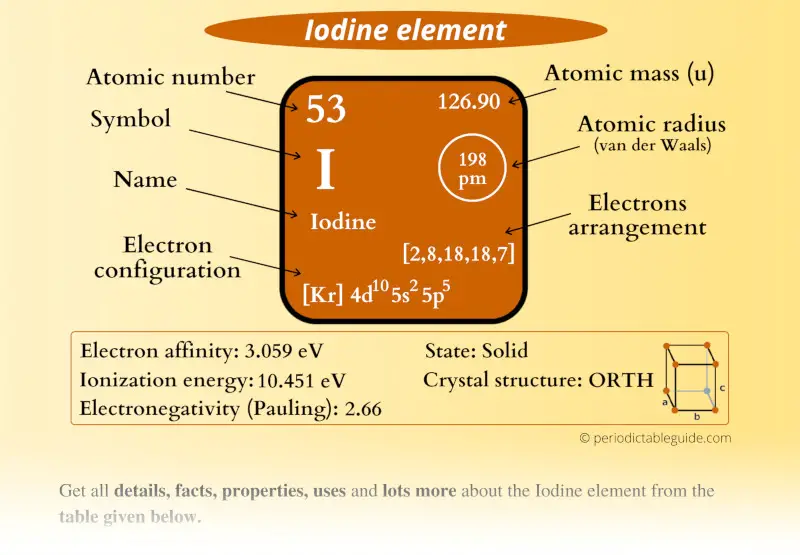
Iodine is a fascinating element with unique properties and essential roles in both nature and industry. Situated in Group 17 of the periodic table, it is a halogen known for its distinct purple-black crystalline form. This element is not only crucial for human health but also plays a significant role in various industrial applications. Understanding its location, properties, and facts on the periodic table can provide valuable insights into its importance and versatility. Whether you’re a chemistry enthusiast or simply curious about the elements, iodine offers a wealth of information worth exploring.
Iodine’s Location on the Periodic Table

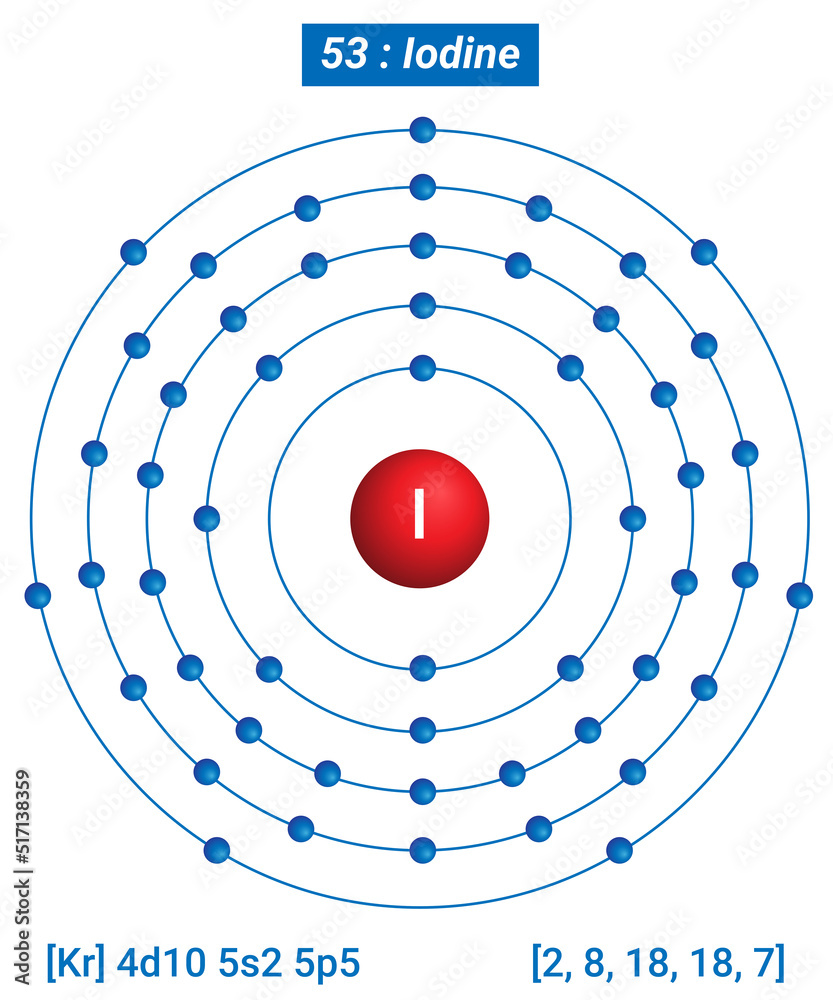
Iodine holds the atomic number 53 and is found in the fifth period of the periodic table. As a member of the halogen group, it shares characteristics with elements like fluorine, chlorine, and bromine. Its position reflects its chemical behavior, including its high reactivity and ability to form compounds with metals.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 53 |
| Symbol | I |
| Group | 17 (Halogens) |
| Period | 5 |

📌 Note: Iodine’s location highlights its role as a halogen, making it highly reactive and essential in chemical processes.
Key Properties of Iodine

Iodine exhibits several distinctive properties that set it apart from other elements. In its solid state, it appears as a shiny, purple-black crystal, while its gaseous form is violet. Iodine is less reactive than chlorine or fluorine but still forms compounds readily, particularly with metals like sodium and potassium.
- Physical State: Solid at room temperature
- Melting Point: 113.7°C (236.7°F)
- Boiling Point: 184.3°C (363.7°F)
- Density: 4.93 g/cm³
📌 Note: Iodine’s physical properties make it useful in applications like photography, pharmaceuticals, and as a disinfectant.
Essential Facts About Iodine
Iodine is not naturally abundant in the Earth’s crust but is found in seawater and certain minerals. It is essential for human health, particularly for thyroid function, as it is a key component of thyroid hormones. Deficiency can lead to disorders like goiter and hypothyroidism.
- Biological Importance: Critical for thyroid hormone production
- Industrial Uses: Used in dyes, catalysts, and water purification
- Dietary Sources: Found in seafood, iodized salt, and dairy products
Iodine in Commercial Applications
For those with commercial intent, iodine is a valuable resource in industries such as healthcare, agriculture, and manufacturing. Its antiseptic properties make it ideal for disinfectants, while its role in radiocontrast agents is vital for medical imaging.
- Healthcare: Thyroid medications, antiseptics
- Agriculture: Animal feed supplements
- Manufacturing: Dyes, photographic chemicals
Summary Checklist

- Location: Group 17, Period 5, Atomic Number 53
- Properties: Purple-black solid, reactive halogen
- Health Role: Essential for thyroid function
- Commercial Uses: Disinfectants, pharmaceuticals, industrial chemicals
What is iodine's atomic number?
+Iodine’s atomic number is 53.
Why is iodine important for health?
+Iodine is crucial for thyroid hormone production, which regulates metabolism and growth.
What are the main commercial uses of iodine?
+Iodine is used in disinfectants, pharmaceuticals, and industrial chemicals like dyes and catalysts.
Iodine’s unique position on the periodic table, combined with its essential properties, makes it a remarkable element. From its role in maintaining human health to its diverse industrial applications, iodine remains a vital component in both natural and synthetic processes. Understanding its characteristics not only enriches our knowledge of chemistry but also highlights its significance in everyday life. Whether for informational or commercial purposes, iodine’s importance is undeniable. periodic table elements, halogen group, thyroid health, industrial chemicals, disinfectants.



