Iron II Oxide: Properties, Uses, and Facts Explained

Iron II Oxide, also known as ferrous oxide, is a chemical compound with the formula FeO. This reddish-black solid is a key material in various industries, from manufacturing to pigments. Its unique properties make it invaluable in applications ranging from ceramics to electronics. Understanding its characteristics, uses, and fascinating facts can help you appreciate its significance in both scientific and commercial contexts. (Iron II Oxide Properties, Iron II Oxide Uses, Iron II Oxide Facts)
What is Iron II Oxide?

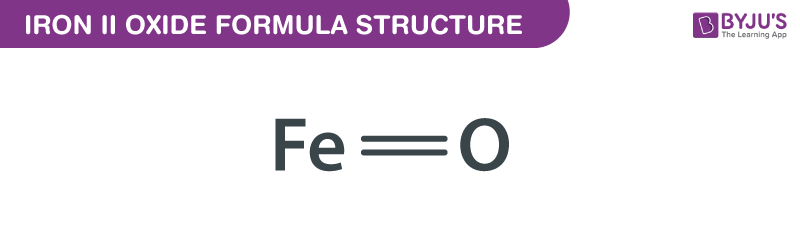
Iron II Oxide is an inorganic compound composed of iron and oxygen. It is one of the simplest iron oxides and exists in a crystalline form. Unlike other iron oxides, FeO is less common in nature but is widely synthesized for industrial purposes. Its distinct color and magnetic properties set it apart from other iron compounds. (Iron II Oxide Composition, Iron II Oxide Structure)
Key Properties of Iron II Oxide

Chemical and Physical Characteristics
Iron II Oxide is known for its reddish-black hue and magnetic nature. It has a melting point of approximately 1,377°C (2,511°F) and is insoluble in water. Its chemical stability makes it resistant to decomposition under normal conditions. Below is a table summarizing its key properties:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | FeO |
| Color | Reddish-Black |
| Melting Point | 1,377°C (2,511°F) |
| Solubility | Insoluble in Water |
(Iron II Oxide Chemical Properties, Iron II Oxide Physical Properties)
Industrial Uses of Iron II Oxide

Applications Across Industries
Iron II Oxide is versatile and used in multiple sectors. Its applications include:
- Ceramics and Glass: As a coloring agent and opacifier.
- Electronics: In the production of magnetic materials.
- Construction: As a pigment in paints and coatings.
- Chemical Manufacturing: As a catalyst or intermediate in reactions.
For commercial buyers, sourcing high-quality Iron II Oxide is crucial for achieving desired product outcomes. (Iron II Oxide Applications, Iron II Oxide Industrial Uses)
Fascinating Facts About Iron II Oxide

Did You Know?
Here are some intriguing facts about Iron II Oxide:
- It is rarely found in its pure form in nature but is often mixed with other iron oxides.
- Its magnetic properties are weaker compared to other iron oxides like magnetite.
- Iron II Oxide plays a role in geological processes, contributing to the formation of certain rocks.
(Iron II Oxide Natural Occurrence, Iron II Oxide Magnetic Properties)
💡 Note: Iron II Oxide should be handled with care in industrial settings due to its potential health risks when inhaled or ingested.
Iron II Oxide is a fascinating compound with a wide range of applications and unique properties. Whether you're exploring its chemical characteristics or considering its industrial uses, understanding FeO can unlock new possibilities in science and commerce. From its role in ceramics to its significance in electronics, Iron II Oxide continues to be a vital material in modern technology. (Iron II Oxide Summary, Iron II Oxide Importance)
What is Iron II Oxide used for?
+
Iron II Oxide is used in ceramics, electronics, construction, and chemical manufacturing as a pigment, magnetic material, and catalyst.
Is Iron II Oxide magnetic?
+
Yes, Iron II Oxide exhibits magnetic properties, though weaker than other iron oxides like magnetite.
Where is Iron II Oxide found in nature?
+
Iron II Oxide is rarely found in its pure form but is often mixed with other iron oxides in rocks and minerals.



