Understanding Lead Nitrate Molecular Formula
Understanding Lead Nitrate Molecular Formula
Lead nitrate, a compound with diverse applications in chemistry, pyrotechnics, and manufacturing, is often a topic of interest for students, researchers, and industry professionals. Its molecular formula, Pb(NO₃)₂, is fundamental to understanding its properties, uses, and safety precautions. This blog post delves into the molecular structure, composition, and significance of lead nitrate, catering to both informational and commercial audiences.
What is Lead Nitrate?

Lead nitrate, also known as plumbic nitrate or lead(II) nitrate, is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula Pb(NO₃)₂. It is a white or colorless crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. Lead nitrate is commonly used in explosives, matches, and as a heat stabilization agent in nylon and polyesters.
📌 Note: Lead nitrate is toxic and should be handled with care to avoid ingestion or skin contact.
Breaking Down the Molecular Formula

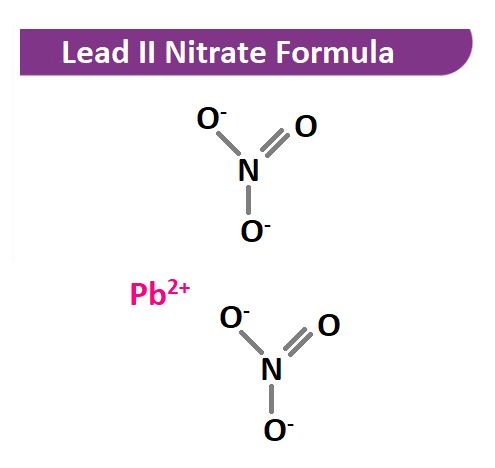
The molecular formula Pb(NO₃)₂ consists of:
- Pb: Lead (a heavy metal)
- NO₃: Nitrate ion (a polyatomic ion composed of nitrogen and oxygen)
The subscript ₂ indicates that there are two nitrate ions for every lead atom in the compound.
Chemical Composition
Lead nitrate is formed by the combination of lead(II) ions (Pb²⁺) and nitrate ions (NO₃⁻). Its structure can be visualized as one lead atom bonded to two nitrate groups.
| Component | Symbol | Charge |
|---|---|---|
| Lead | Pb | 2+ |
| Nitrate | NO₃ | 1- |

Key Properties
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water
- Density: 4.53 g/cm³
- Melting Point: 270°C (decomposes)
- Appearance: White crystalline solid
Applications of Lead Nitrate

Lead nitrate is widely used in various industries due to its unique properties.
Informational-Intent Audience
For students and researchers, understanding lead nitrate’s molecular formula is crucial for:
- Chemical Reactions: Studying its role in precipitation reactions or redox processes.
- Safety Protocols: Learning how to handle toxic compounds in laboratory settings.
Commercial-Intent Audience
For industry professionals, lead nitrate is essential in:
- Pyrotechnics: Used in fireworks and flares for its oxidizing properties.
- Manufacturing: Applied as a catalyst in certain chemical processes.
- Textiles: Used in heat stabilization for synthetic fibers.
📌 Note: Commercial users must comply with regulations regarding lead-based compounds.
Safety and Handling

Lead nitrate is toxic and poses health risks if not handled properly. Key precautions include:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear gloves, goggles, and lab coats.
- Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area or fume hood.
- Storage: Store in a cool, dry place away from flammable materials.
Summarizing Key Points

Lead nitrate, with the molecular formula Pb(NO₃)₂, is a versatile compound used in pyrotechnics, manufacturing, and research. Its structure consists of lead(II) ions bonded to nitrate ions, and it exhibits properties like high solubility and toxicity. Proper handling and safety measures are essential when working with this compound.
Checklist for Handling Lead Nitrate
- Wear appropriate PPE.
- Ensure proper ventilation.
- Store in a secure, dry location.
- Dispose of according to local regulations.
(Lead Nitrate Uses, Lead Nitrate Properties, Chemical Safety)
What is the molecular formula of lead nitrate?
+
The molecular formula of lead nitrate is Pb(NO₃)₂.
Is lead nitrate soluble in water?
+
Yes, lead nitrate is highly soluble in water.
What are the main uses of lead nitrate?
+
Lead nitrate is used in pyrotechnics, manufacturing, and as a heat stabilizer in textiles.
How should lead nitrate be handled safely?
+
Wear PPE, work in a ventilated area, and store it securely away from flammable materials.

