lewis dot for hcl

Understanding the Lewis dot structure for HCl is essential for anyone studying chemistry, as it provides a clear visualization of the bonding between hydrogen and chlorine atoms. This simple yet powerful tool helps in predicting molecular geometry, reactivity, and polarity. Whether you're a student, researcher, or chemistry enthusiast, mastering the Lewis dot structure for HCl will enhance your understanding of chemical bonding. Below, we’ll break down the process step-by-step, ensuring you grasp the concept effortlessly. (Lewis dot structure, HCl bonding, chemical bonding)
What is a Lewis Dot Structure?

A Lewis dot structure is a diagram that represents the distribution of valence electrons in an atom or molecule. It uses dots to symbolize electrons and lines to indicate bonds between atoms. For HCl (hydrogen chloride), the Lewis dot structure helps illustrate how hydrogen (H) and chlorine (Cl) share electrons to form a covalent bond. This structure is fundamental in chemistry for understanding molecular properties. (valence electrons, covalent bond, molecular properties)
Steps to Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for HCl

Drawing the Lewis dot structure for HCl involves a few straightforward steps:
- Step 1: Determine the total number of valence electrons. Hydrogen has 1 valence electron, and chlorine has 7 valence electrons, totaling 8 electrons. (valence electrons, electron counting)
- Step 2: Place the atoms and connect them with a bond. Hydrogen and chlorine are connected by a single covalent bond, represented by a line. (covalent bond, molecular structure)
- Step 3: Distribute the remaining electrons. Place the remaining 6 electrons around chlorine to complete its octet. (electron distribution, octet rule)
📌 Note: Hydrogen can only hold 2 electrons, so it doesn’t need to complete an octet.
Key Properties of HCl from Its Lewis Dot Structure
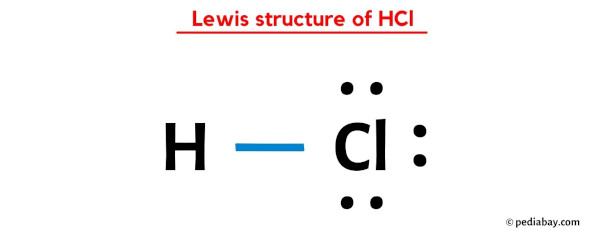
The Lewis dot structure of HCl reveals important properties:
- Polarity: HCl is a polar molecule due to the electronegativity difference between hydrogen and chlorine. (molecular polarity, electronegativity)
- Bond Type: The single covalent bond between H and Cl indicates a strong bond. (covalent bond, bond strength)
- Molecular Geometry: HCl has a linear geometry, which is typical for diatomic molecules. (molecular geometry, diatomic molecules)
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Valence Electrons | 8 (1 from H, 7 from Cl) |
| Bond Type | Single Covalent Bond |
| Molecular Polarity | Polar |
| Molecular Geometry | Linear |
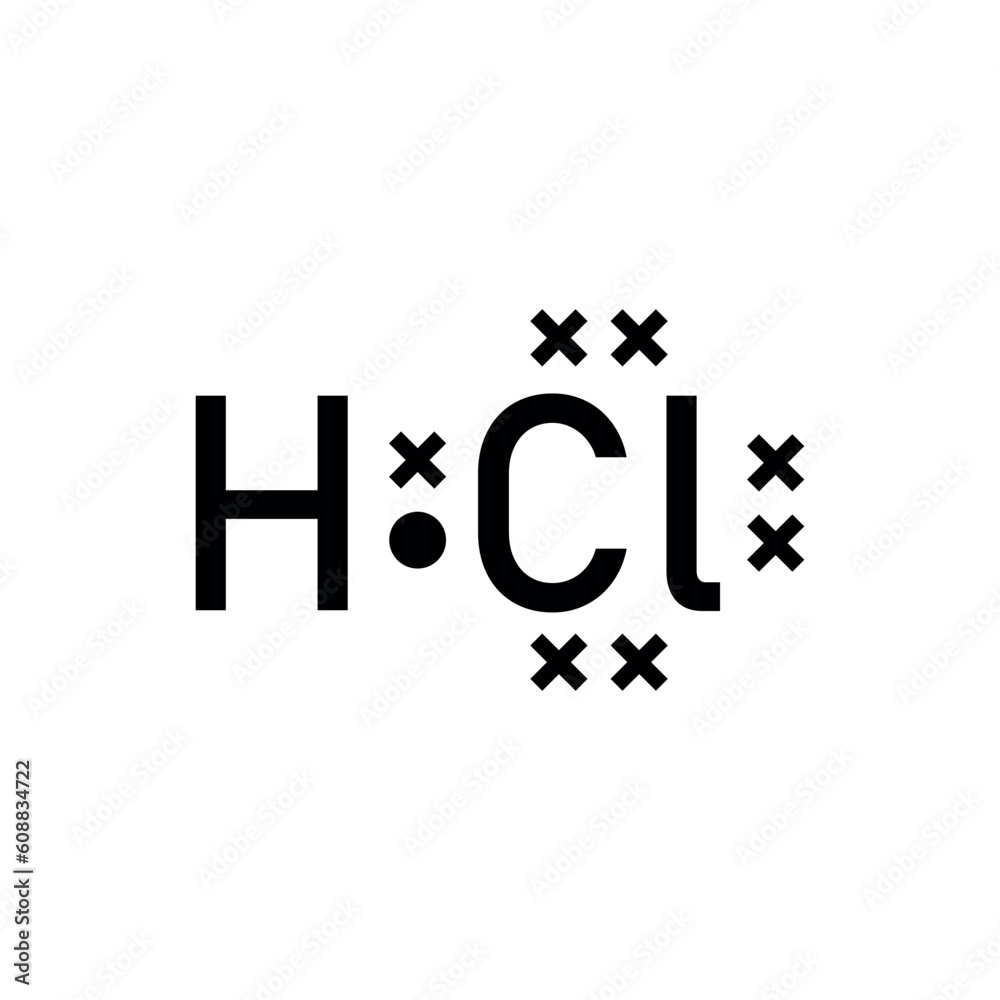
Checklist: Steps to Draw HCl Lewis Dot Structure
- Count valence electrons (H: 1, Cl: 7)
- Connect H and Cl with a single bond
- Distribute remaining electrons around Cl
- Verify the octet rule for Cl (H does not need an octet)
In summary, the Lewis dot structure for HCl is a simple yet powerful tool for understanding the molecule’s bonding, polarity, and geometry. By following the steps outlined above, you can easily draw the structure and analyze its properties. Whether for academic purposes or practical applications, mastering this concept will deepen your chemistry knowledge. (Lewis dot structure, HCl properties, chemical bonding)
What is the Lewis dot structure for HCl?
+
The Lewis dot structure for HCl shows hydrogen connected to chlorine by a single covalent bond, with 6 electrons around chlorine to complete its octet.
Why is HCl considered a polar molecule?
+
HCl is polar due to the significant electronegativity difference between hydrogen and chlorine, causing an uneven distribution of charge.
How many valence electrons are in HCl?
+
HCl has a total of 8 valence electrons: 1 from hydrogen and 7 from chlorine.



