Trauma Patient Assessment: EMT Guide for Quick Action

As an EMT, every second counts when assessing a trauma patient. Quick, accurate, and systematic evaluation can mean the difference between life and death. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to trauma patient assessment, ensuring you’re prepared to act swiftly and effectively in high-pressure situations. Whether you’re a seasoned EMT or just starting, mastering these techniques is crucial for delivering optimal care. (trauma patient assessment, EMT guide, quick action)
Step 1: Scene Safety and Initial Impression

Before approaching the patient, ensure the scene is safe for both you and the victim. Take a moment to observe the environment for potential hazards like traffic, fire, or unstable structures. Your initial impression of the patient’s condition will guide your next steps. Look for signs of severe bleeding, difficulty breathing, or altered mental status. (scene safety, initial impression, trauma assessment)
Step 2: Primary Assessment (ABCs)
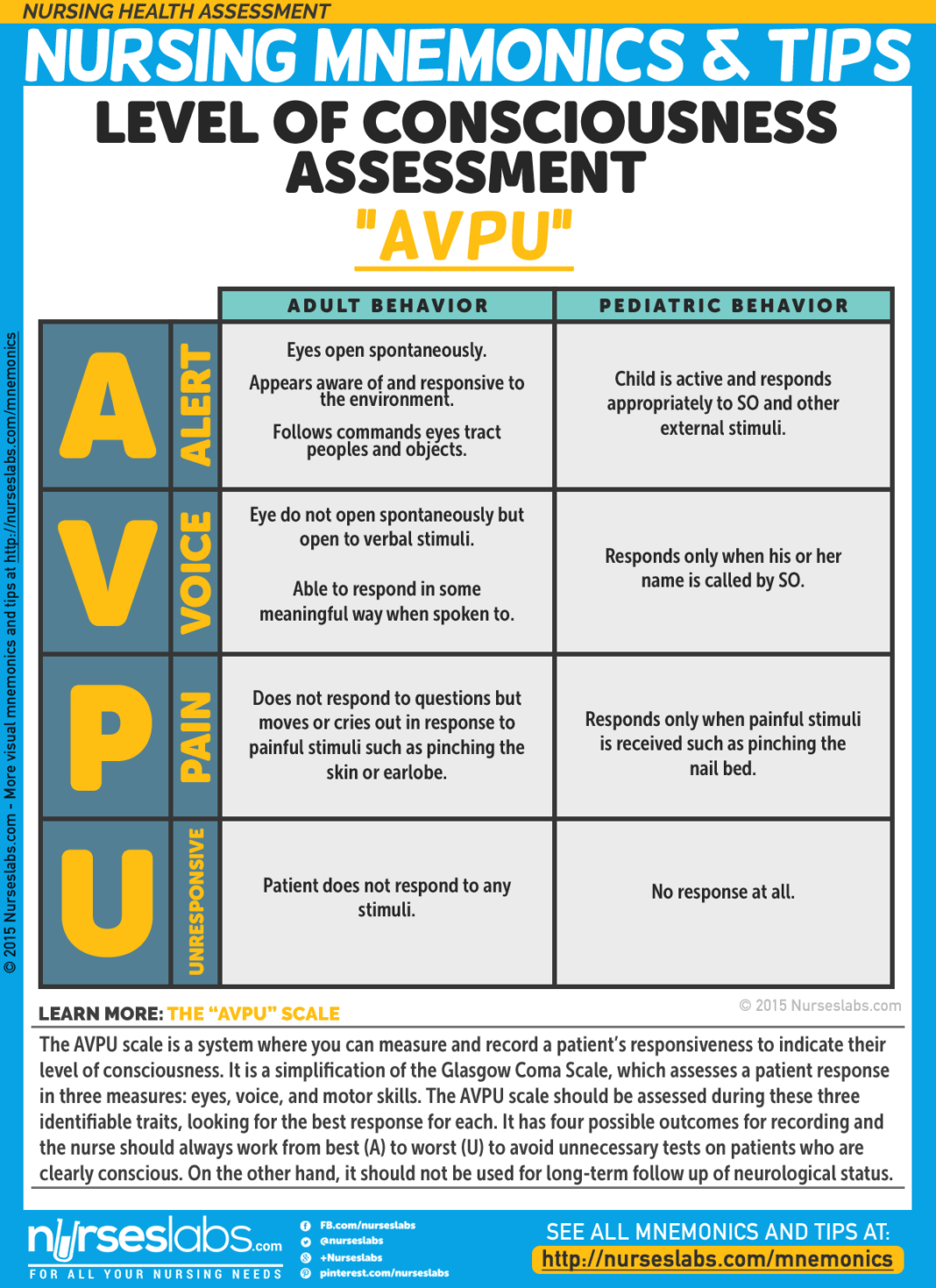
Follow the ABCs of trauma care: Airway, Breathing, and Circulation. These are the most critical factors in stabilizing a patient.
- Airway: Ensure the patient’s airway is clear and open. Use techniques like head-tilt chin-lift or jaw thrust if necessary.
- Breathing: Check for adequate respiration. Look for chest rise and fall, and listen for breath sounds. Administer oxygen if needed.
- Circulation: Control severe bleeding using direct pressure or tourniquets. Monitor for signs of shock, such as pale skin or rapid pulse.
📌 Note: Always prioritize the ABCs before moving to secondary assessments.
Step 3: Secondary Assessment

Once the patient is stabilized, conduct a head-to-toe evaluation to identify hidden injuries. This includes checking for:
- Deformities or swelling
- Tenderness or pain
- Open wounds or burns
Document all findings clearly for handover to the next level of care. (secondary assessment, head-to-toe evaluation, trauma care)
Step 4: Vital Signs and Monitoring

Continuously monitor the patient’s vital signs, including blood pressure, pulse, and oxygen saturation. Use a trauma score like the Revised Trauma Score (RTS) to assess severity and guide treatment decisions. (vital signs, trauma score, patient monitoring)
| Vital Sign | Normal Range | Action if Abnormal |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Pressure | 90-120/60-80 mmHg | Administer fluids or medications as needed |
| Pulse Rate | 60-100 BPM | Monitor for signs of shock or arrhythmia |

Trauma Assessment Checklist

- Ensure scene safety
- Perform primary assessment (ABCs)
- Conduct secondary assessment (head-to-toe)
- Monitor vital signs
- Document all findings
Mastering trauma patient assessment is a cornerstone of EMT practice. By following this systematic approach, you can provide timely and effective care, improving outcomes for your patients. Remember, every step counts—from scene safety to vital sign monitoring. Stay prepared, stay focused, and save lives. (EMT practice, systematic approach, patient care)
What is the first step in trauma patient assessment?
+
The first step is ensuring scene safety to protect both the EMT and the patient.
Why are the ABCs critical in trauma care?
+
The ABCs (Airway, Breathing, Circulation) address life-threatening issues first, ensuring the patient’s immediate survival.
How often should vital signs be monitored in a trauma patient?
+
Vital signs should be monitored continuously, especially during transport, to detect any changes in the patient’s condition.



