What is Population Distribution in Geography?

Understanding population distribution in geography is essential for analyzing how people are spread across different regions. It helps us identify patterns, trends, and factors influencing where populations concentrate or disperse. This knowledge is crucial for urban planning, resource allocation, and environmental management.
What is Population Distribution in Geography?
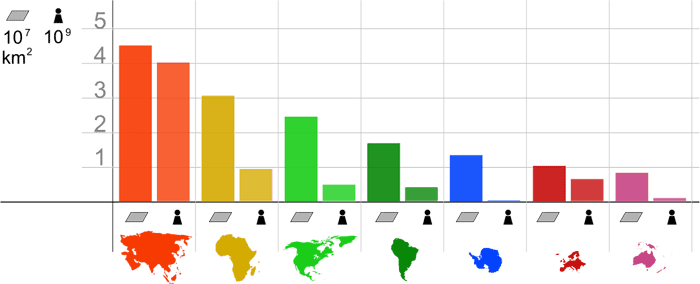
Population distribution refers to the arrangement of people across a specific area, whether it’s a city, country, or the entire globe. It examines density, dispersion, and patterns of human settlement. Factors like climate, topography, economic opportunities, and historical events shape these distributions.
Key Factors Influencing Population Distribution

Several elements determine how populations are distributed:
- Physical Factors: Climate, soil fertility, and water availability play a significant role. For example, fertile river valleys often support higher populations.
- Economic Factors: Job opportunities and industrial growth attract people to urban areas.
- Social and Cultural Factors: Historical migration patterns and cultural preferences influence settlement choices.
- Government Policies: Urbanization policies or rural development initiatives can reshape population distribution.
Types of Population Distribution

Population distribution can be categorized into three main types:
- Uniform Distribution: People are evenly spread across an area, often seen in agricultural regions.
- Clustered Distribution: High concentrations of people in specific areas, typical in cities or industrial zones.
- Random Distribution: No clear pattern, influenced by varied factors like remote settlements.
| Type | Characteristics | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Uniform | Evenly spread | Agricultural areas |
| Clustered | High concentration | Cities, industrial zones |
| Random | No clear pattern | Remote settlements |

Why Population Distribution Matters

Understanding population distribution is vital for:
- Urban Planning: Designing sustainable cities and infrastructure.
- Resource Management: Allocating water, food, and energy efficiently.
- Environmental Impact: Assessing the strain on ecosystems.
- Policy Making: Crafting strategies for economic development and social welfare.
💡 Note: Accurate data on population distribution is critical for effective decision-making in both public and private sectors.
Tools for Analyzing Population Distribution

Geographers use various tools to study population distribution:
- GIS (Geographic Information Systems): Maps and analyzes spatial data.
- Census Data: Provides demographic information.
- Satellite Imagery: Offers visual insights into settlement patterns.
Challenges in Population Distribution
Rapid urbanization, migration, and environmental changes pose challenges. Overcrowding in cities and depopulation in rural areas are growing concerns. Addressing these issues requires balanced policies and sustainable practices.
Final Thoughts
Population distribution is a dynamic and complex topic that reflects the interplay of natural, economic, and social factors. By studying it, we can better understand human settlement patterns and plan for a sustainable future.
What causes uneven population distribution?
+Uneven distribution is caused by factors like climate, economic opportunities, and historical migration patterns.
How does population distribution affect the environment?
+High concentrations of people can strain resources and increase pollution, impacting ecosystems.
What tools are used to study population distribution?
+GIS, census data, and satellite imagery are commonly used tools.
population density, population patterns, urban planning, resource management, environmental impact,population geography, demographic analysis,migration patterns,



