Is Potassium Hydroxide a Strong or Weak Base?

Potassium hydroxide, often referred to as KOH or caustic potash, is a widely used chemical compound in various industries, including soap making, biodiesel production, and as a pH regulator. One common question that arises is whether potassium hydroxide is a strong or weak base. Understanding its properties is crucial for its safe and effective use. In this post, we’ll explore the nature of potassium hydroxide, its classification as a base, and its applications, ensuring you have all the information you need.
What is Potassium Hydroxide?

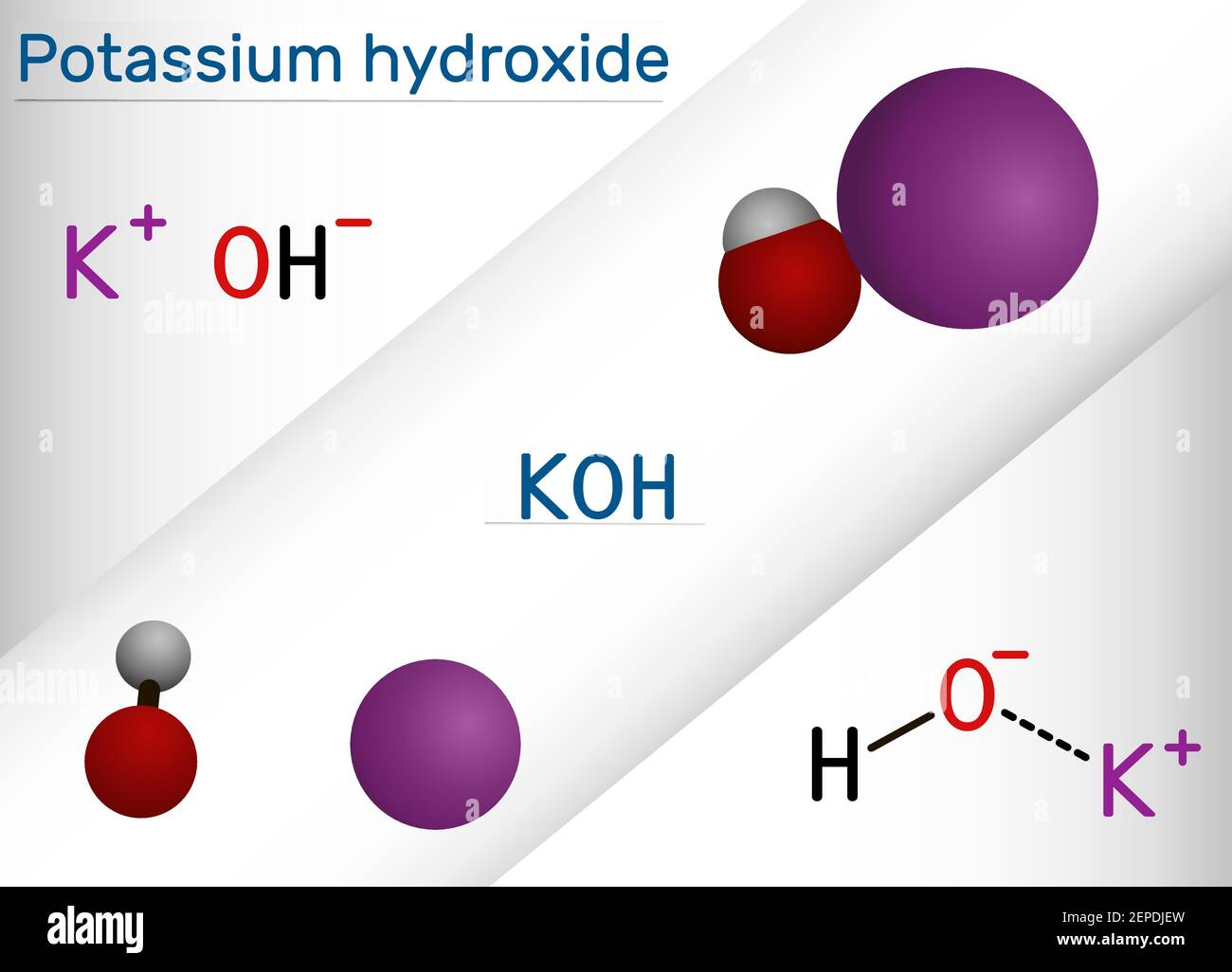
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula KOH. It is a white, solid substance that is highly soluble in water, producing an alkaline solution. This compound is known for its strong corrosive properties and is commonly used in industrial and laboratory settings.
Is Potassium Hydroxide a Strong or Weak Base?

To determine whether potassium hydroxide is a strong or weak base, we need to understand its behavior in aqueous solutions. A strong base fully dissociates into its ions in water, releasing a high concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻). In contrast, a weak base only partially dissociates, resulting in fewer hydroxide ions.
Potassium hydroxide is classified as a strong base because it completely dissociates in water, producing a high concentration of OH⁻ ions. This makes it highly effective in neutralizing acids and increasing the pH of solutions.
Key Properties of Potassium Hydroxide as a Strong Base
- Complete Dissociation: KOH fully breaks down into K⁺ and OH⁻ ions in water.
- High pH: Solutions of KOH are highly alkaline, typically with a pH greater than 12.
- Corrosive Nature: Its strong alkaline properties make it corrosive to skin, metals, and other materials.
📌 Note: Always handle potassium hydroxide with care, wearing protective gear like gloves and goggles.
Applications of Potassium Hydroxide
Given its strong base properties, potassium hydroxide is used in a variety of applications:
Industrial Uses
- Soap Making: KOH is a key ingredient in liquid soaps and detergents.
- Biodiesel Production: It acts as a catalyst in converting fats and oils into biodiesel.
- pH Regulation: Used in industries to neutralize acidic solutions.
Laboratory Uses
- Titrations: KOH is used in acid-base titrations to determine the concentration of acids.
- Chemical Synthesis: It serves as a reactant in producing various chemicals.
Safety Precautions When Handling Potassium Hydroxide

Due to its strong base nature, potassium hydroxide requires careful handling:
- Protective Gear: Wear gloves, goggles, and lab coats to avoid skin and eye contact.
- Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes.
- Storage: Store in a cool, dry place away from acids and other reactive substances.
📌 Note: In case of contact with skin or eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical attention.
Potassium Hydroxide vs. Sodium Hydroxide
Both potassium hydroxide (KOH) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) are strong bases, but they have distinct properties:
| Property | Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) | Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) |
|---|---|---|
| Solubility in Water | Highly soluble | Highly soluble |
| Corrosiveness | Highly corrosive | Highly corrosive |
| Common Uses | Biodiesel, soaps | Drain cleaners, paper |
Final Thoughts
Potassium hydroxide is unequivocally a strong base due to its complete dissociation in water and high concentration of hydroxide ions. Its properties make it invaluable in industries like soap making, biodiesel production, and chemical synthesis. However, its corrosive nature demands careful handling and adherence to safety precautions. Whether you’re a chemist, manufacturer, or hobbyist, understanding KOH’s strength as a base is essential for its effective and safe use.
What makes potassium hydroxide a strong base?
+Potassium hydroxide is a strong base because it fully dissociates into K⁺ and OH⁻ ions in water, releasing a high concentration of hydroxide ions.
Can potassium hydroxide be used in food products?
+While KOH is used in food processing (e.g., making olives or soft pretzels), it must be handled carefully and used in controlled amounts due to its corrosive nature.
How does potassium hydroxide compare to sodium hydroxide?
+Both are strong bases, but KOH is more expensive and often preferred in applications like biodiesel production, while NaOH is commonly used in drain cleaners and paper manufacturing.
strong base,weak base,potassium hydroxide uses,KOH safety,chemical properties,industrial chemicals,soap making,biodiesel production,pH regulation,laboratory chemicals