Potassium on the Periodic Table: Essential Facts & Uses
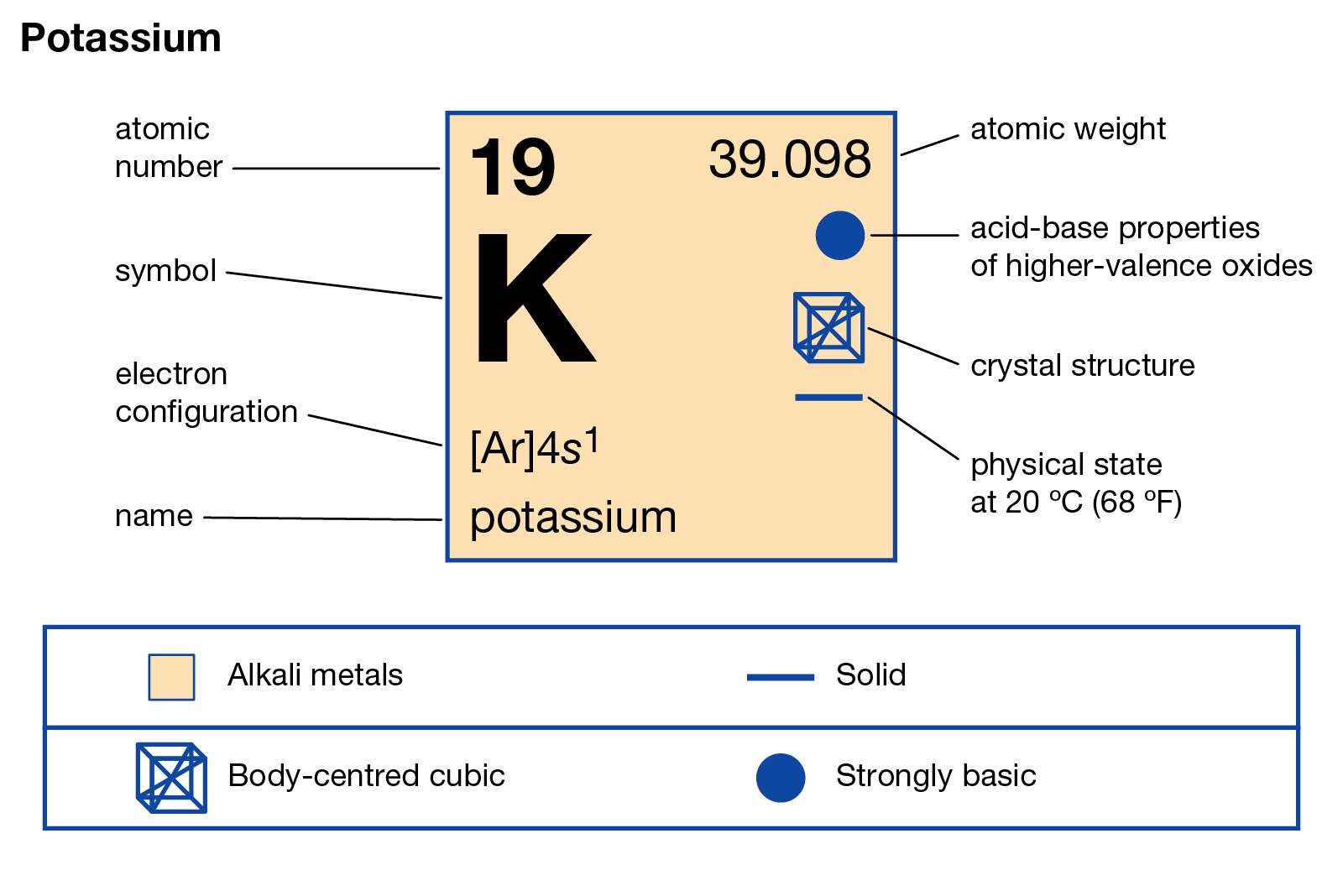
Potassium, a vital element on the periodic table, plays a crucial role in various aspects of our lives, from biological functions to industrial applications. With the symbol K and atomic number 19, this soft, silvery-white metal is highly reactive and essential for maintaining health and driving technological advancements. Whether you’re curious about its properties or looking to purchase potassium-based products, this guide covers everything you need to know. (potassium properties, potassium uses, periodic table elements)
Potassium on the Periodic Table: Key Properties

Potassium is classified as an alkali metal, residing in Group 1 and Period 4 of the periodic table. Its electron configuration ([Ar] 4s¹) explains its high reactivity, especially with water, producing hydrogen gas and potassium hydroxide. This element has a melting point of 63.29°C (145.92°F) and a boiling point of 759°C (1,398°F), making it relatively low compared to other metals. (alkali metals, electron configuration, potassium reactivity)
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 19 |
| Atomic Mass | 39.0983 u |
| State at Room Temperature | Solid |
| Electronegativity | 0.82 |
Essential Biological Role of Potassium

Potassium is indispensable for human health, primarily functioning as an electrolyte to regulate nerve signals, muscle contractions, and fluid balance. A deficiency can lead to hypokalemia, causing symptoms like muscle weakness and irregular heartbeats. Conversely, excessive potassium intake can result in hyperkalemia, a potentially life-threatening condition. (electrolytes, hypokalemia, hyperkalemia)
💡 Note: The recommended daily potassium intake for adults is 2,600–3,400 mg, depending on age and sex.
Industrial and Commercial Uses of Potassium

Beyond biology, potassium has diverse applications across industries. Potassium chloride (KCl) is widely used in fertilizers to enhance crop growth, while potassium hydroxide (KOH) is essential in soap and detergent manufacturing. Additionally, potassium is used in batteries, glass production, and as a heat transfer medium in nuclear reactors. (potassium chloride, potassium hydroxide, industrial applications)
- Fertilizers: Enhances soil fertility and plant growth.
- Soap Manufacturing: Acts as a strong alkali in saponification.
- Batteries: Used in alkaline and rechargeable batteries.
Where to Buy Potassium Products

For those looking to purchase potassium-based products, options are available both online and in specialty stores. Common products include potassium supplements, potassium salts, and potassium-rich fertilizers. Always ensure the product meets safety and quality standards before purchasing. (potassium supplements, potassium salts, fertilizers)
⚠️ Note: Handle potassium compounds with care, as they can be corrosive or reactive.
To summarize, potassium is a versatile and essential element with significant roles in biology, industry, and commerce. Understanding its properties and applications can help you appreciate its importance and make informed decisions, whether for health or industrial purposes.
What is potassium’s role in the human body?
+
Potassium acts as an electrolyte, regulating nerve signals, muscle contractions, and fluid balance.
Why is potassium important in agriculture?
+
Potassium chloride (KCl) is a key component in fertilizers, promoting healthy plant growth and soil fertility.
Can potassium be harmful?
+
Yes, excessive potassium intake can lead to hyperkalemia, while deficiency causes hypokalemia. Always follow recommended dosages.