Unveiling the Purpose of the Kirby-Bauer Test: A Quick Guide
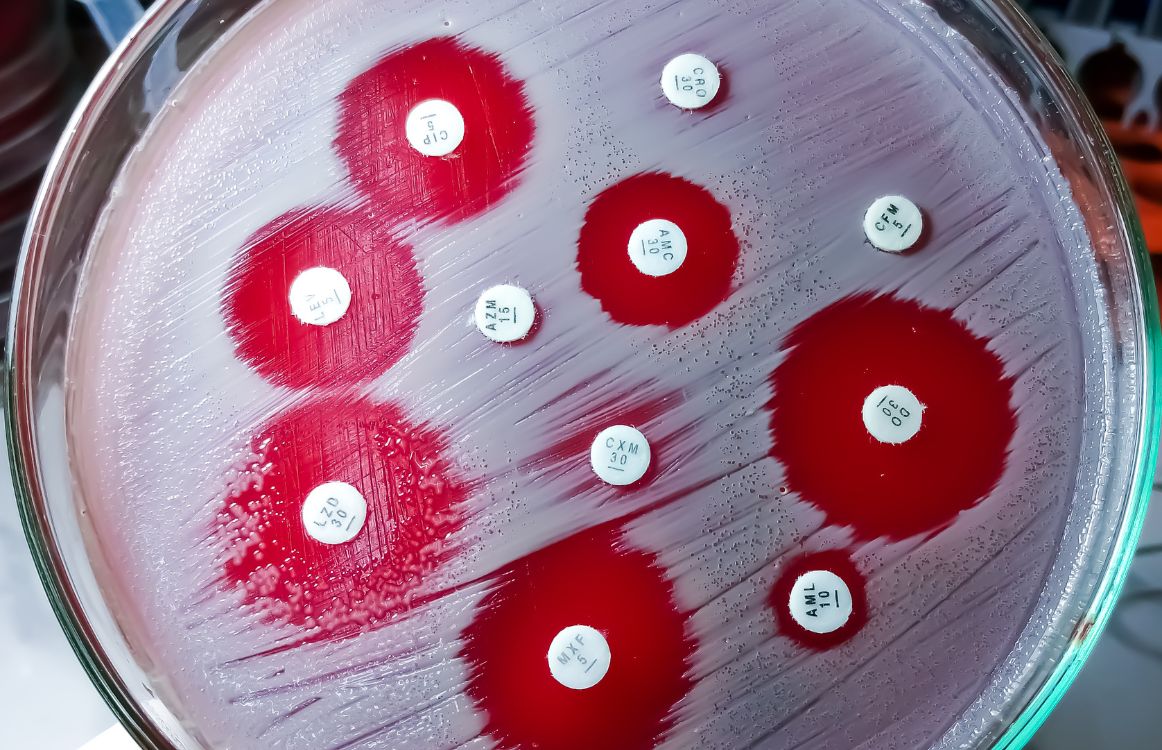

The Kirby-Bauer test, also known as the disk diffusion method, is a widely used laboratory technique to determine the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics. This test plays a crucial role in guiding effective treatment for bacterial infections, ensuring patients receive the most appropriate medication. Understanding its purpose and process is essential for healthcare professionals and anyone interested in microbiology. (antibiotic susceptibility testing, disk diffusion method, bacterial infections)
What is the Kirby-Bauer Test?
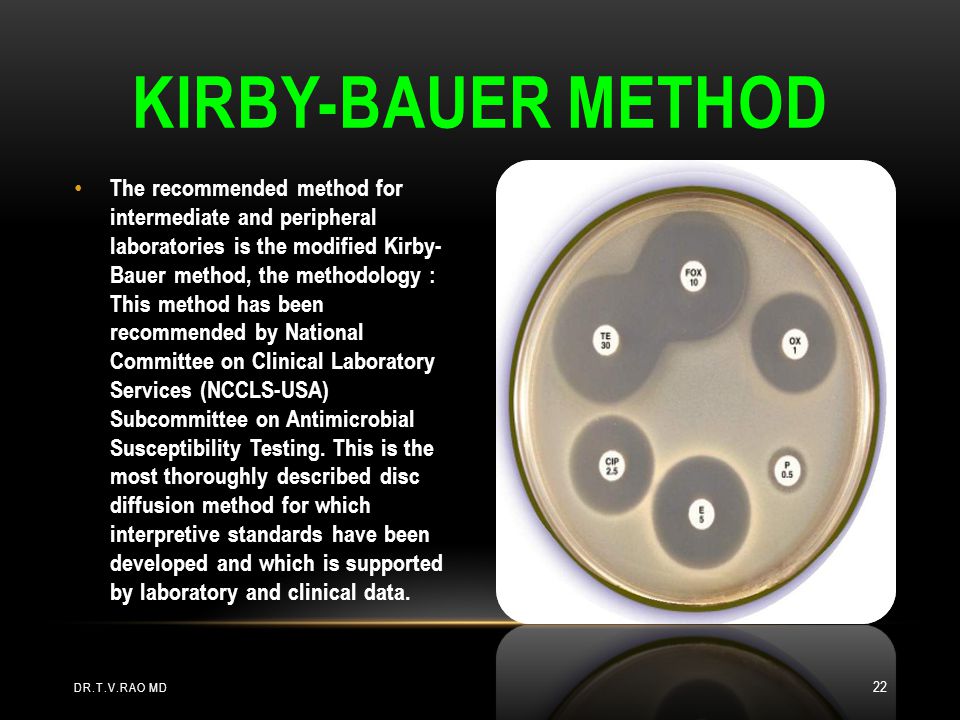
The Kirby-Bauer test is a simple yet powerful tool for assessing antibiotic resistance. It involves placing antibiotic-impregnated disks on an agar plate inoculated with a bacterial culture. The antibiotics diffuse into the agar, creating zones of inhibition around the disks where bacterial growth is suppressed. The size of these zones indicates the bacterium’s susceptibility to the antibiotic. (antibiotic resistance, zones of inhibition, bacterial culture)
Why is the Kirby-Bauer Test Important?
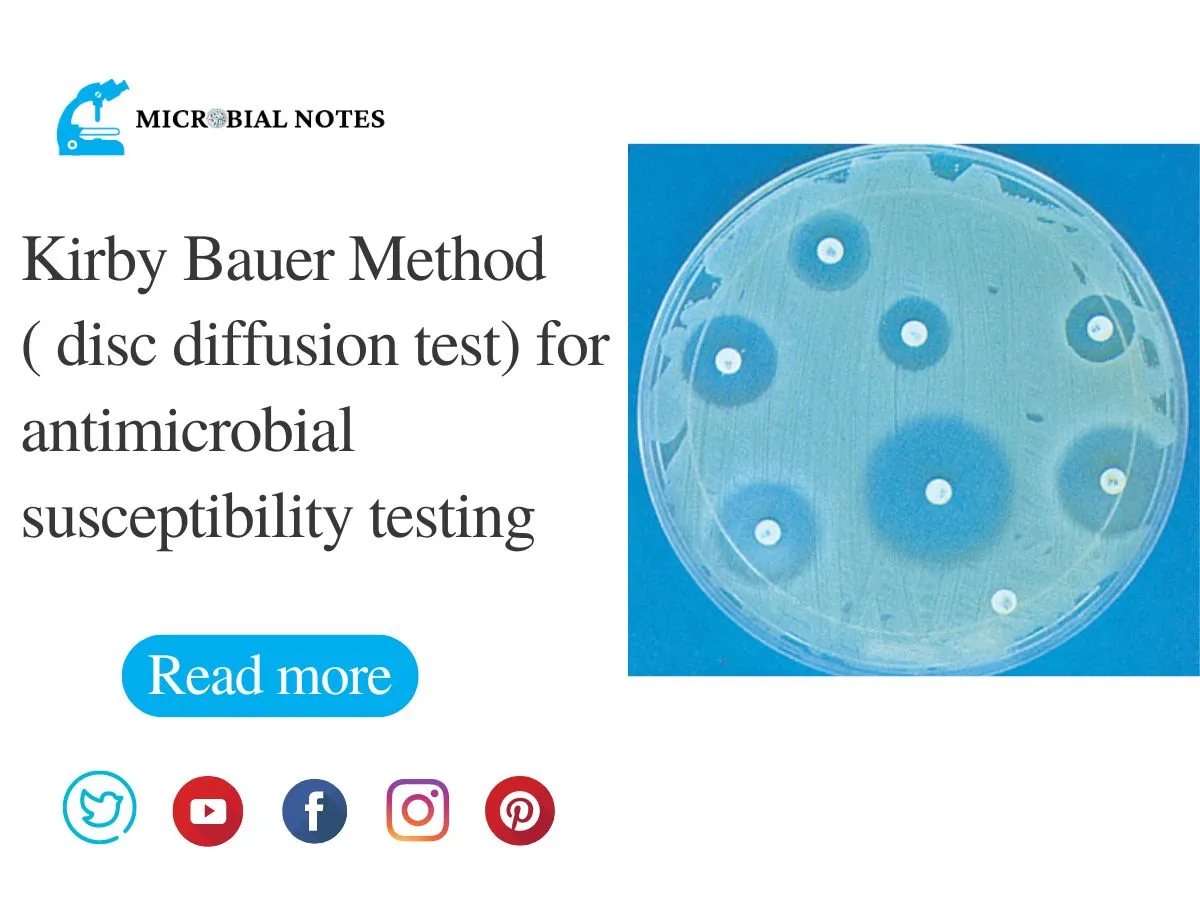
This test is vital for several reasons:
Guiding Treatment: It helps doctors choose the most effective antibiotic for a specific infection, improving patient outcomes and reducing the risk of treatment failure. (antibiotic selection, treatment efficacy)
Monitoring Resistance: By tracking changes in susceptibility patterns over time, the test helps identify emerging antibiotic resistance, allowing for proactive measures to combat this growing threat. (antibiotic resistance surveillance, public health)
Research and Development: The Kirby-Bauer test is used in research to evaluate new antibiotics and study bacterial resistance mechanisms. (antibiotic development, microbiology research)
How is the Kirby-Bauer Test Performed?

The procedure involves several steps:
Bacterial Culture Preparation: A pure culture of the bacteria is grown on an agar plate.
Disk Placement: Antibiotic disks are placed on the surface of the inoculated agar plate.
Incubation: The plate is incubated at a controlled temperature for a specific period, allowing antibiotic diffusion and bacterial growth.
Zone Measurement: The diameter of the zones of inhibition around each disk is measured.
Interpretation: Zone sizes are compared to standardized tables to determine the bacterium’s susceptibility (susceptible, intermediate, or resistant) to each antibiotic.
📌 Note: Proper technique and adherence to standardized protocols are crucial for accurate results.
Interpreting Kirby-Bauer Test Results

The size of the zone of inhibition is categorized as:
Susceptible (S): The bacterium is likely to respond to the antibiotic.
Intermediate (I): The antibiotic may be effective, but higher doses or alternative options should be considered.
Resistant ®: The bacterium is unlikely to be inhibited by the antibiotic.
| Zone Diameter (mm) | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| > [Threshold Value] | Susceptible (S) |
| [Lower Threshold] - [Upper Threshold] | Intermediate (I) |
| < [Lower Threshold] | Resistant (R) |

📌 Note: Specific threshold values vary depending on the antibiotic and bacterial species.
Key Takeaways:The Kirby-Bauer test is a cornerstone of antibiotic susceptibility testing, providing valuable information for guiding treatment decisions and monitoring antibiotic resistance. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it an indispensable tool in the fight against bacterial infections. (antibiotic stewardship, infectious disease management)
What are the limitations of the Kirby-Bauer test?
+While highly useful, the test has limitations. It provides qualitative results (susceptible/resistant) rather than quantitative data on antibiotic potency. Additionally, factors like agar composition and incubation conditions can influence results.
What are alternative methods for antibiotic susceptibility testing?
+Other methods include broth dilution, Etest, and automated systems. Each method has advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on factors like accuracy, turnaround time, and cost.
Where can I learn more about the Kirby-Bauer test?
+Reputable sources like the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) provide detailed guidelines and protocols for performing and interpreting the Kirby-Bauer test.



