Understanding the Rf Value Formula: A Quick Guide
<!DOCTYPE html>
The Rf value is a critical concept in chromatography, helping scientists separate and analyze mixtures effectively. Whether you're a student, researcher, or professional, understanding the Rf value formula is essential for accurate results. This guide breaks down the formula, its components, and practical applications, ensuring you grasp the concept effortlessly.
What is the Rf Value Formula? (Rf value calculation, chromatography basics)
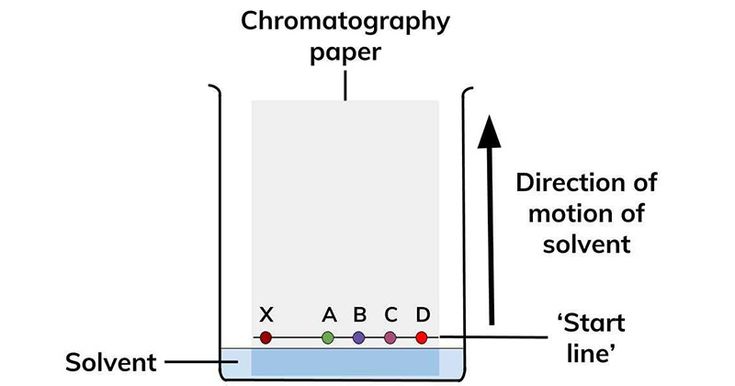
The Rf value (Retention Factor) is a measure of how far a substance travels on a chromatography plate compared to the solvent front. The formula is:
Rf = Distance traveled by the substance / Distance traveled by the solvent
This value is always between 0 and 1, providing insights into a compound’s polarity and behavior in a given solvent system.
Key Components of the Rf Value Formula (chromatography components, solvent front)
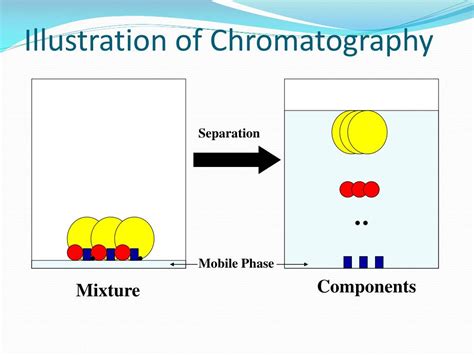
To calculate the Rf value accurately, you need to measure two distances:
- Distance traveled by the substance: Measure from the baseline to the center of the substance spot.
- Distance traveled by the solvent: Measure from the baseline to the solvent front.
📌 Note: Ensure precise measurements for reliable Rf values.
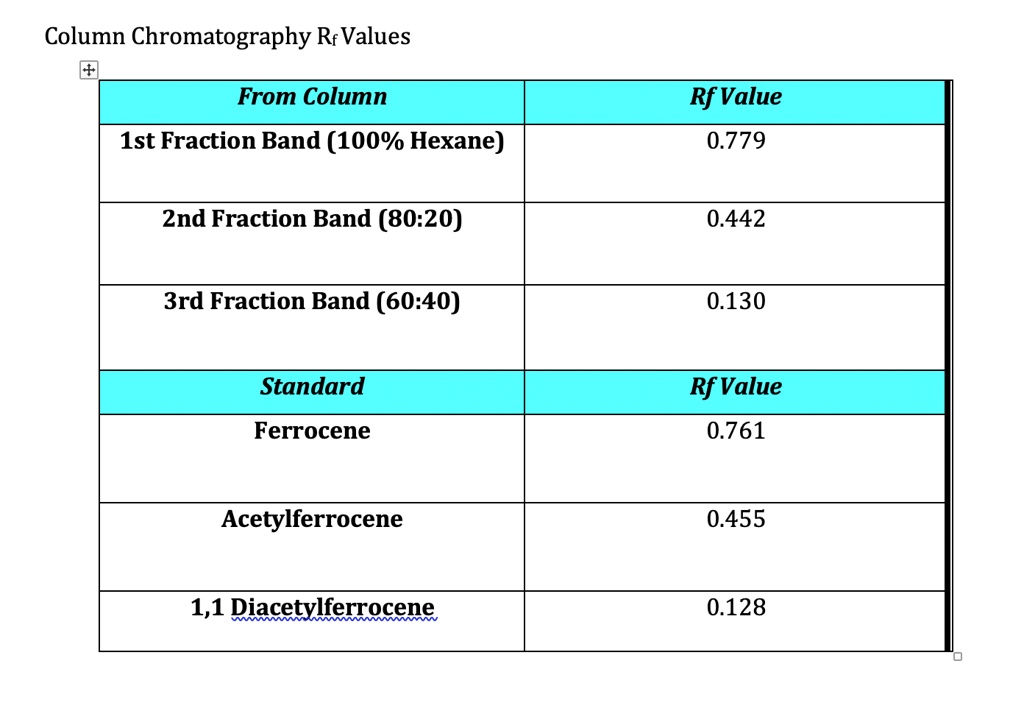
Practical Applications of Rf Values (thin-layer chromatography, compound identification)

Rf values are widely used in:
- Compound Identification: Comparing Rf values helps identify unknown substances.
- Purity Analysis: Multiple spots indicate impurities in a sample.
- Optimization of Solvent Systems: Adjusting solvents to improve separation efficiency.
Factors Affecting Rf Values (chromatography factors, solvent choice)
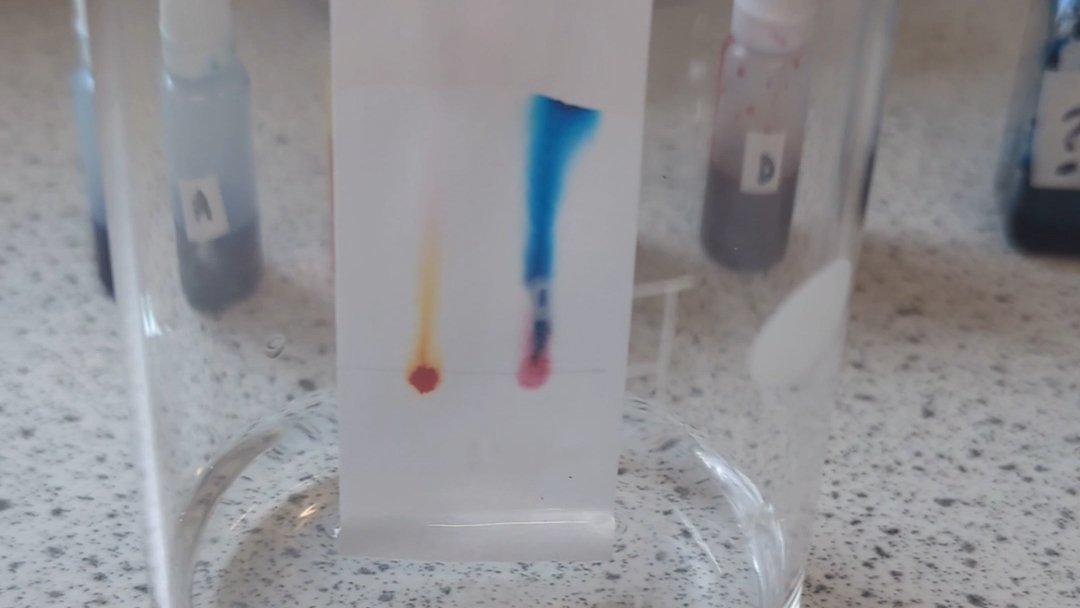

Several factors influence Rf values:
| Factor | Effect on Rf Value |
|---|---|
| Solvent Polarity | Higher polarity solvents increase Rf values for polar compounds. |
| Temperature | Higher temperatures can decrease Rf values. |
| Plate Quality | Uniform plates ensure consistent Rf values. |
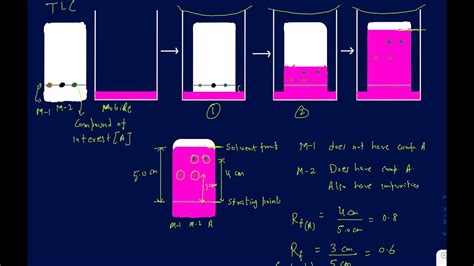
Checklist for Accurate Rf Value Calculation (chromatography tips, lab techniques)
Follow these steps for precise Rf value calculations:
- Use a consistent solvent system.
- Measure distances accurately from the baseline.
- Ensure the chromatography plate is uniformly coated.
- Repeat experiments for reliability.
Mastering the Rf value formula is crucial for successful chromatography experiments. By understanding its components, applications, and influencing factors, you can achieve accurate and reproducible results. Whether you're identifying compounds or analyzing purity, this guide ensures you're well-equipped for your lab work.
What does an Rf value of 1 indicate?
+An Rf value of 1 indicates that the substance traveled the same distance as the solvent front, suggesting it is highly soluble in the solvent.
Can Rf values be compared between different experiments?
+Rf values can only be compared if the same solvent system, temperature, and chromatography conditions are used.
How does temperature affect Rf values?
+Higher temperatures generally decrease Rf values by increasing solvent viscosity and reducing interaction between the substance and the stationary phase.