Rabbit Ears ECG: Understanding the Unique Waveform Pattern
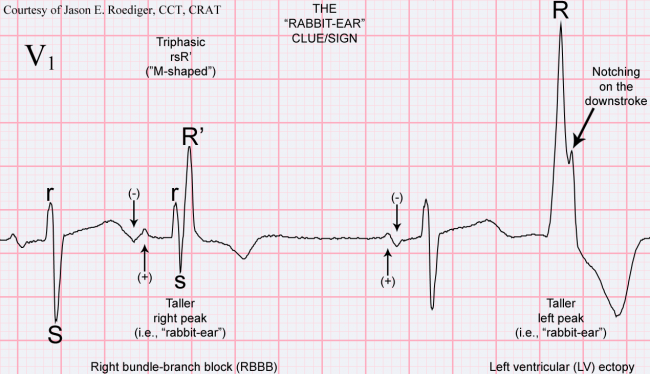
The Rabbit Ears ECG is a unique waveform pattern that has gained attention in the medical community for its distinct characteristics and diagnostic implications. This pattern, often observed in electrocardiograms (ECGs), resembles the shape of rabbit ears due to its notched or split appearance in the QRS complex. Understanding this pattern is crucial for healthcare professionals, as it can indicate specific cardiac conditions or electrical abnormalities. In this post, we’ll explore the Rabbit Ears ECG in detail, its significance, and how to interpret it effectively, (ECG interpretation, cardiac diagnostics, waveform analysis)
What is Rabbit Ears ECG?

The Rabbit Ears ECG is characterized by a notched or split QRS complex, typically seen in leads V1 to V3. This pattern occurs due to the delayed activation of the ventricles, often associated with conditions like bundle branch block or ventricular hypertrophy. Recognizing this waveform is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning, (cardiac conditions, ECG patterns, ventricular activation)
Key Features of Rabbit Ears ECG
- Notched QRS Complex: The QRS appears split or notched, resembling rabbit ears.
- Lead Specificity: Most commonly observed in precordial leads V1 to V3.
- Duration: The QRS duration is typically prolonged, exceeding 120 ms.
Causes and Clinical Significance

The Rabbit Ears ECG pattern is often linked to underlying cardiac issues. Common causes include: - Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB): Delayed activation of the right ventricle. - Ventricular Hypertrophy: Enlargement of the ventricular walls. - Myocardial Infarction: Previous heart attacks affecting electrical conduction, (bundle branch block, ventricular hypertrophy, myocardial infarction)
Diagnostic Checklist for Rabbit Ears ECG
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| QRS Notching | Presence of a split or notched QRS complex |
| Lead Location | Observed in V1 to V3 leads |
| QRS Duration | Prolonged >120 ms |
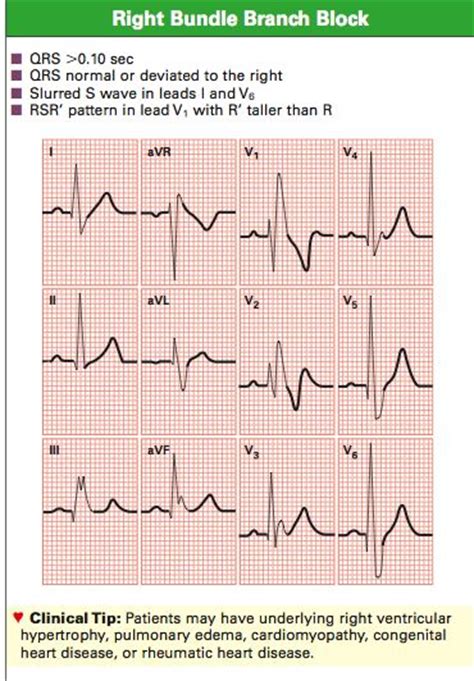
📌 Note: Always correlate ECG findings with clinical symptoms and other diagnostic tests for accurate interpretation.
How to Interpret Rabbit Ears ECG

Interpreting the Rabbit Ears ECG involves: 1. Identifying the Pattern: Look for the notched QRS in V1 to V3. 2. Measuring QRS Duration: Confirm prolongation >120 ms. 3. Assessing Clinical Context: Consider patient history and symptoms, (ECG interpretation, cardiac diagnosis, clinical correlation)
Steps for Accurate Interpretation
- Review the ECG for notched QRS complexes.
- Measure the QRS duration in affected leads.
- Correlate findings with patient symptoms and medical history.
The Rabbit Ears ECG is a distinctive pattern that requires careful interpretation to diagnose underlying cardiac conditions accurately. By understanding its features, causes, and clinical significance, healthcare professionals can improve patient outcomes. Always combine ECG findings with clinical data for a comprehensive diagnosis, (cardiac diagnostics, ECG patterns, patient care)
What causes the Rabbit Ears ECG pattern?
+
The pattern is often caused by right bundle branch block, ventricular hypertrophy, or myocardial infarction.
Which leads show the Rabbit Ears ECG?
+
It is most commonly observed in precordial leads V1 to V3.
How is Rabbit Ears ECG diagnosed?
+
Diagnosis involves identifying a notched QRS complex, measuring QRS duration, and correlating with clinical findings.



