Temperature and Pressure: Understanding the Crucial Connection
<!DOCTYPE html>
Temperature and pressure are two fundamental concepts in physics and engineering that play a critical role in various industries, from meteorology to manufacturing. Understanding their relationship is essential for optimizing processes, ensuring safety, and achieving desired outcomes. Whether you're a student, a professional, or simply curious, this guide will help you grasp the crucial connection between temperature and pressure, its applications, and how to manage it effectively.
The Basics: What Are Temperature and Pressure?

Before diving into their relationship, let’s define these terms. Temperature measures the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance, indicating how hot or cold it is. Pressure, on the other hand, is the force applied per unit area, often exerted by gases or fluids. Together, they influence the state and behavior of matter, making them indispensable in scientific and industrial contexts. (thermodynamics, gas laws, kinetic energy)
The Relationship Between Temperature and Pressure

Gas Laws: The Foundation
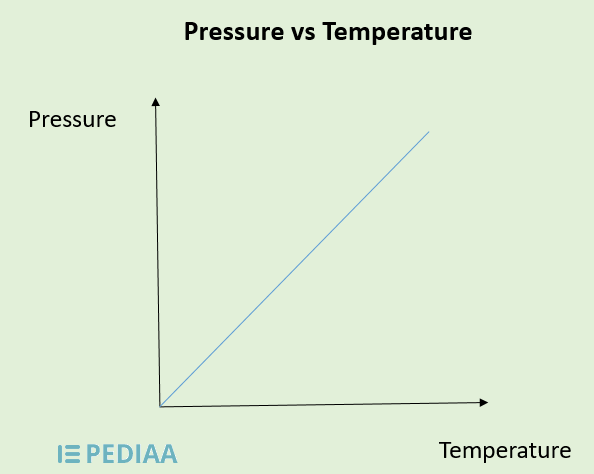
The connection between temperature and pressure is best described by the Ideal Gas Law: PV = nRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles, R is the gas constant, and T is temperature. This law highlights that as temperature increases, so does pressure, assuming volume and the amount of gas remain constant. (ideal gas law, combined gas law, thermodynamics)
Real-World Applications
This relationship is evident in everyday scenarios: - Weather Systems: Warm air rises, reducing pressure, while cold air sinks, increasing it. - Automotive Engines: Combustion increases temperature and pressure, driving pistons. - Cooking: Pressure cookers use heat to increase pressure, cooking food faster. (weather patterns, engine mechanics, pressure cooking)
Managing Temperature and Pressure in Industrial Settings

In industries like manufacturing and energy, controlling temperature and pressure is vital for efficiency and safety. Here’s how:
- Monitoring Systems: Use sensors to track changes in real-time.
- Regulatory Devices: Install valves and thermostats to maintain optimal levels.
- Safety Protocols: Implement measures to prevent overheating or overpressure.
📌 Note: Regular maintenance of monitoring systems is crucial to avoid failures.
Checklist for Temperature and Pressure Management

- Regularly calibrate sensors and gauges.
- Train staff on safety protocols and emergency procedures.
- Monitor environmental conditions to predict fluctuations.
- Use high-quality materials resistant to extreme temperatures and pressures.
Understanding the interplay between temperature and pressure is key to mastering various scientific and industrial processes. By applying this knowledge, you can enhance efficiency, ensure safety, and innovate in your field. (temperature control, pressure regulation, industrial safety)
How does temperature affect gas pressure?
+As temperature increases, gas molecules move faster, colliding with container walls more frequently and with greater force, thus increasing pressure.
What industries rely heavily on temperature and pressure control?
+Industries like manufacturing, energy, aerospace, and food processing depend on precise temperature and pressure control for safety and efficiency.
Can changes in pressure affect temperature?
+Yes, compressing a gas increases its temperature (adiabatic heating), while allowing it to expand decreases its temperature (adiabatic cooling).



