Strong Base, Weak Acid: Chemical Reactions Explained
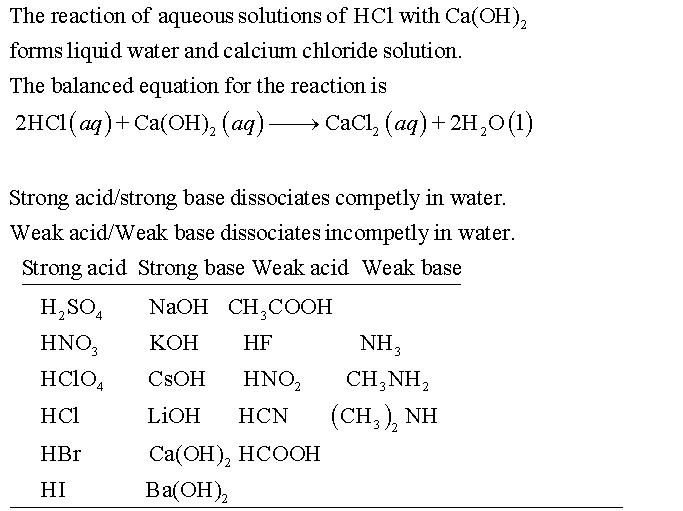
Understanding the dynamics of strong bases and weak acids is crucial in chemistry, whether you’re a student, researcher, or industry professional. These concepts not only form the foundation of chemical reactions but also play a significant role in applications like pharmaceuticals, environmental science, and manufacturing. In this post, we’ll explore the principles behind strong bases, weak acids, and their interactions, ensuring you grasp the essentials for both informational and commercial purposes.
What Are Strong Bases and Weak Acids?

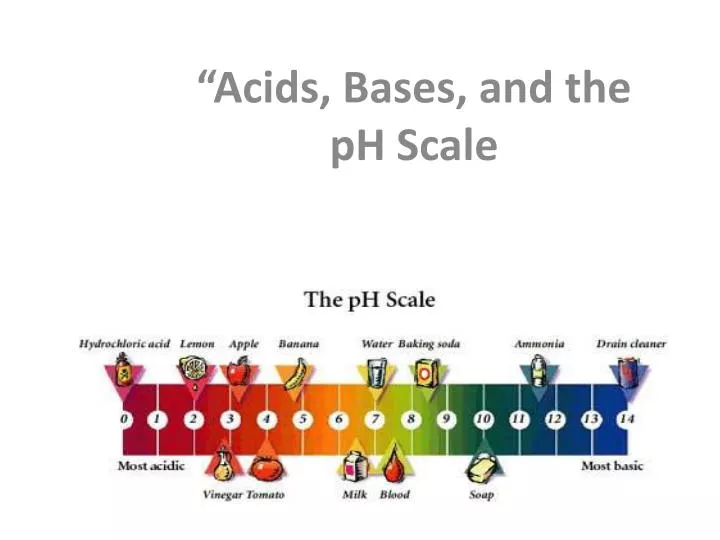
Strong bases are substances that fully dissociate in water, releasing a high concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻). Common examples include sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and potassium hydroxide (KOH). These bases are highly reactive and can neutralize acids effectively.
Weak acids, on the other hand, only partially dissociate in water, producing a low concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺). Examples include acetic acid (CH₃COOH) and citric acid. Their partial dissociation makes them less corrosive but still reactive in specific conditions.
💡 Note: Strong bases and weak acids are fundamental in acid-base chemistry, often used in titrations and pH adjustments.
Chemical Reactions: Strong Base and Weak Acid Interaction
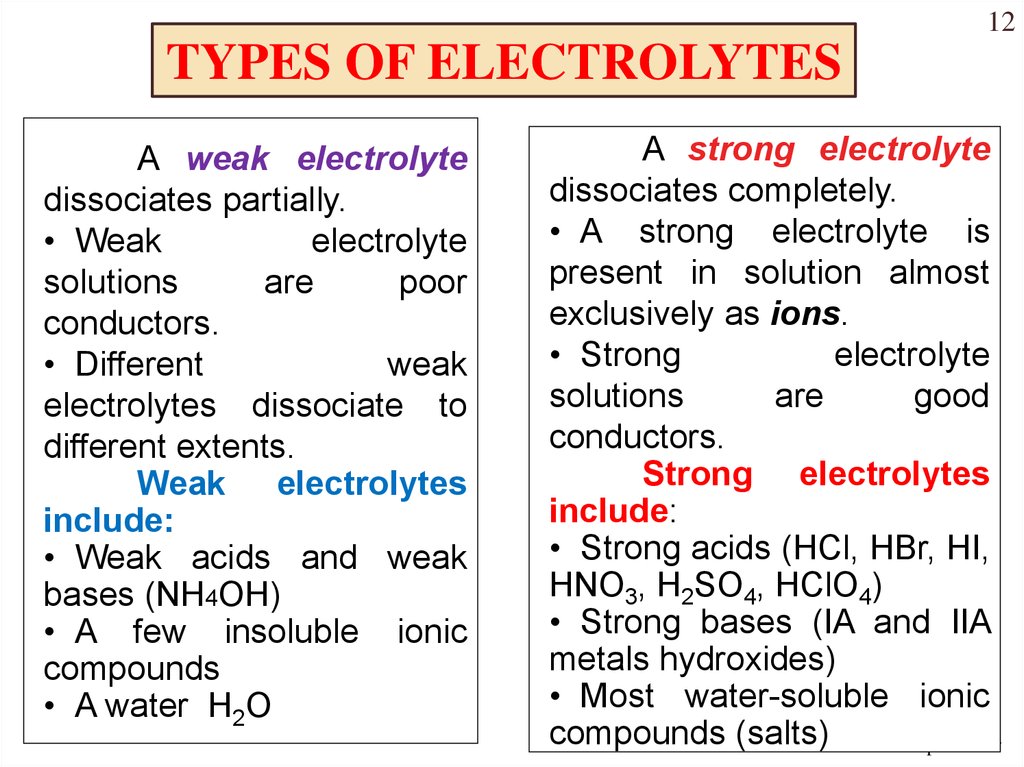
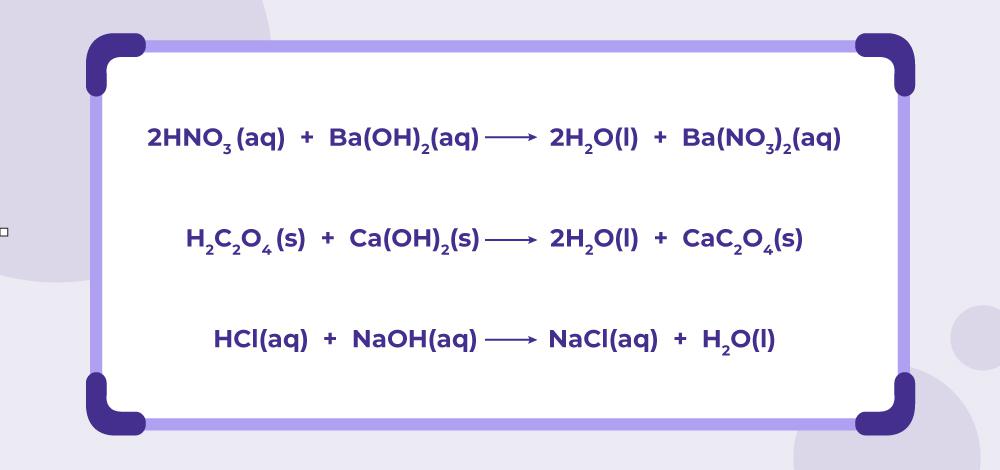
When a strong base reacts with a weak acid, the reaction typically proceeds to completion. The strong base neutralizes the weak acid, forming water and a salt. For instance:
NaOH (strong base) + CH₃COOH (weak acid) → CH₃COONa (salt) + H₂O (water)
This reaction is essential in industries like food processing, where pH control is critical.
Key Factors Influencing the Reaction
- Concentration: Higher concentrations of the strong base or weak acid can speed up the reaction.
- Temperature: Elevated temperatures generally increase reaction rates.
- Catalysts: Certain catalysts can enhance the reaction efficiency.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
Pharmaceuticals
In drug manufacturing, understanding strong bases and weak acids is vital for formulating medications with precise pH levels. For example, antacids often contain weak bases to neutralize stomach acid.
Environmental Science
Strong bases are used in wastewater treatment to neutralize acidic pollutants, while weak acids help in soil pH adjustment for agriculture.
Commercial Products
Household cleaners often contain strong bases to dissolve grease, while weak acids are used in skincare products for gentle exfoliation.
Checklist for Working with Strong Bases and Weak Acids
- Safety First: Always wear protective gear when handling strong bases.
- Precise Measurements: Use accurate tools for mixing solutions.
- pH Monitoring: Regularly check pH levels to ensure desired outcomes.
- Disposal Guidelines: Follow proper disposal methods for chemical waste.
Wrapping Up

Mastering the behavior of strong bases and weak acids opens doors to countless applications across industries. Whether you’re conducting experiments or developing products, this knowledge is indispensable. By understanding their reactions and applications, you can optimize processes and achieve better results.
What is the difference between a strong base and a weak acid?
+A strong base fully dissociates in water, releasing OH⁻ ions, while a weak acid partially dissociates, releasing H⁺ ions.
Why is the reaction between a strong base and weak acid important?
+This reaction is crucial for neutralization processes in industries like pharmaceuticals, environmental science, and manufacturing.
How can I safely handle strong bases?
+Always wear protective gear, work in a well-ventilated area, and follow proper disposal guidelines.
acid-base reactions,chemical neutralization,pH control,industrial applications,laboratory safety



