Unlocking Plasma Membrane Secrets: Two Key Functions Explained

The plasma membrane, often referred to as the cell membrane, is a dynamic and intricate structure that plays a pivotal role in maintaining cellular integrity and function. It acts as a gatekeeper, regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell while also facilitating communication with the external environment. Understanding its functions is crucial for both scientific research and practical applications in fields like medicine and biotechnology. In this post, we’ll explore two key functions of the plasma membrane and their significance, tailored for both informational and commercial audiences.
1. Selective Permeability: The Gatekeeper Function
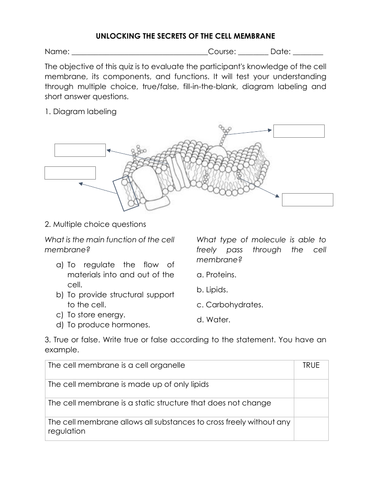
The plasma membrane’s primary role is to act as a selectively permeable barrier, allowing only specific molecules to pass through while blocking others. This function is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis.
How It Works
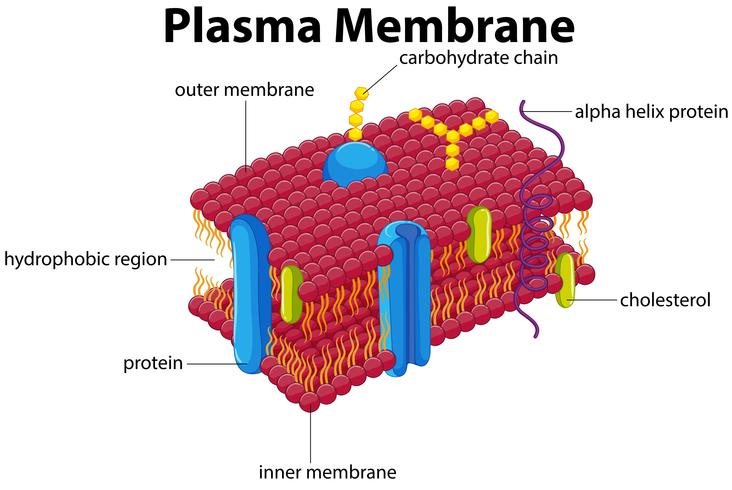
The membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. These proteins, such as channels and carriers, facilitate the movement of ions, nutrients, and waste products. For example, aquaporins allow water to pass through, while glucose transporters regulate sugar intake.
Why It Matters
Without selective permeability, cells would be unable to control their internal environment, leading to dysfunction or death. This function is vital in processes like osmoregulation and metabolism.
💡 Note: Selective permeability is also the basis for drug delivery systems, where molecules are engineered to cross the membrane efficiently.
2. Cell Signaling: The Communication Hub

Another critical function of the plasma membrane is its role in cell signaling, enabling cells to communicate with each other and respond to external stimuli.
Mechanisms of Signaling
The membrane houses receptor proteins that bind to specific molecules like hormones or neurotransmitters. Once activated, these receptors trigger intracellular pathways, leading to responses such as muscle contraction or enzyme activation.
Real-World Applications
Understanding cell signaling has led to breakthroughs in pharmaceutical development, particularly in creating targeted therapies for diseases like cancer and diabetes.
| Function | Key Components | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Selective Permeability | Phospholipid bilayer, transport proteins | Drug delivery, osmoregulation |
| Cell Signaling | Receptor proteins, intracellular pathways | Pharmaceuticals, disease research |
Key Takeaways
- The plasma membrane ensures cellular survival through selective permeability.
- It facilitates intercellular communication via cell signaling pathways.
- Both functions have practical applications in medicine and biotechnology.
For those looking to delve deeper, here’s a checklist to explore further:
- Research the role of membrane proteins in disease.
- Investigate how lipid composition affects membrane fluidity.
- Explore emerging technologies in membrane-based drug delivery.
(Plasma Membrane Function, Cell Biology, Biotechnology Advances)
What is the plasma membrane made of?
+
The plasma membrane is primarily composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates.
How does selective permeability benefit cells?
+
Selective permeability allows cells to regulate the entry and exit of molecules, maintaining internal balance and protecting against harmful substances.
What are some commercial applications of plasma membrane research?
+
Research on the plasma membrane has led to advancements in drug delivery systems, targeted therapies, and biotechnology innovations.


