Understanding Secondary Pollutants: Causes and Effects
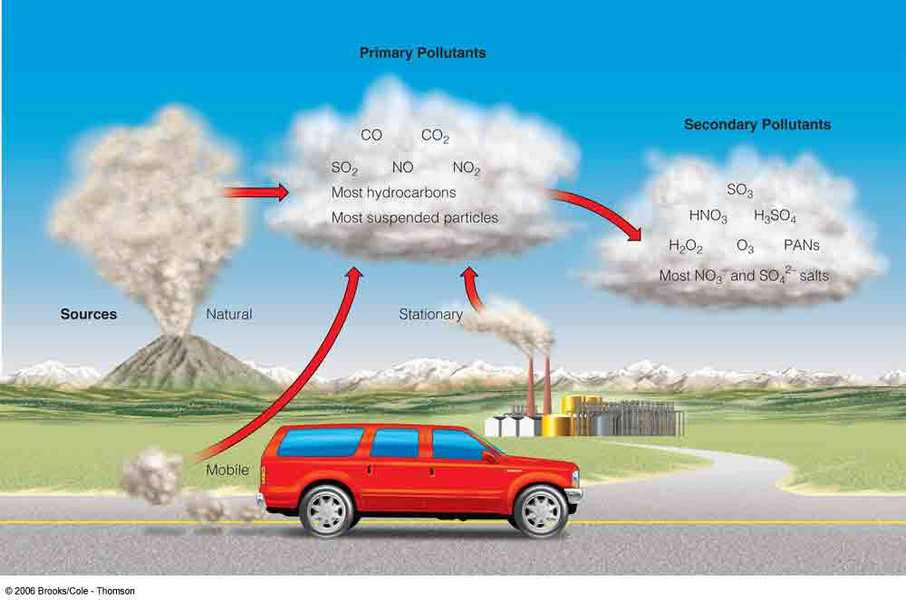
Secondary pollutants are a significant concern in today’s environment, formed when primary pollutants interact with other substances in the atmosphere. Unlike primary pollutants, which are directly emitted from sources like vehicles and factories, secondary pollutants are the result of chemical reactions. Understanding their causes, effects, and prevention methods is crucial for improving air quality and public health. This post explores the key aspects of secondary pollutants, offering actionable insights for both informational and commercial audiences. (air quality, environmental health, pollution control)
What Are Secondary Pollutants?

Secondary pollutants are harmful substances created when primary pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), react with sunlight, air, or other chemicals. Common examples include ground-level ozone, secondary particulate matter, and acid rain. These pollutants are not emitted directly but form over time, often traveling long distances from their source. (ground-level ozone, acid rain, particulate matter)
Causes of Secondary Pollutants

The formation of secondary pollutants involves complex chemical reactions, primarily driven by:
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Emitted from vehicle exhausts and industrial processes.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Released from solvents, paints, and natural sources like plants.
- Sunlight: Acts as a catalyst for photochemical reactions, especially in warm weather.
These factors combine to create pollutants that worsen air quality, particularly in urban areas. (urban pollution, photochemical smog, industrial emissions)
Effects of Secondary Pollutants

The impact of secondary pollutants is far-reaching, affecting both the environment and human health:
- Health Issues: Respiratory problems, aggravated asthma, and cardiovascular diseases.
- Environmental Damage: Harm to ecosystems, soil degradation, and water contamination.
- Economic Costs: Increased healthcare expenses and reduced crop yields.
Addressing these effects requires collective efforts to reduce emissions and improve air quality monitoring. (respiratory health, ecosystem damage, air quality monitoring)
Preventing Secondary Pollutants

Reducing secondary pollutants involves both individual and systemic actions:
- Use Clean Energy: Transition to renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
- Improve Transportation: Adopt electric vehicles and promote public transit.
- Regulate Industries: Enforce stricter emission standards for factories and power plants.
📌 Note: Governments and businesses play a key role in implementing policies to combat secondary pollutants. (renewable energy, emission standards, sustainable transportation)
Checklist: Steps to Reduce Secondary Pollutants
| Action | Impact |
|---|---|
| Switch to clean energy | Reduces NOx and VOC emissions |
| Use public transportation | Lowers vehicle emissions |
| Support green policies | Encourages systemic change |

Secondary pollutants pose a significant threat to air quality, health, and the environment. By understanding their causes and effects, we can take proactive steps to mitigate their impact. Whether through individual actions or policy changes, every effort counts in the fight against pollution. (air quality improvement, pollution mitigation, environmental conservation)
What are the main examples of secondary pollutants?
+
Common examples include ground-level ozone, secondary particulate matter, and acid rain.
How do secondary pollutants affect human health?
+
They can cause respiratory issues, aggravate asthma, and lead to cardiovascular diseases.
What can individuals do to reduce secondary pollutants?
+
Using public transportation, reducing energy consumption, and supporting green policies are effective steps.



