What is a Primary Reinforcer? Explained Simply
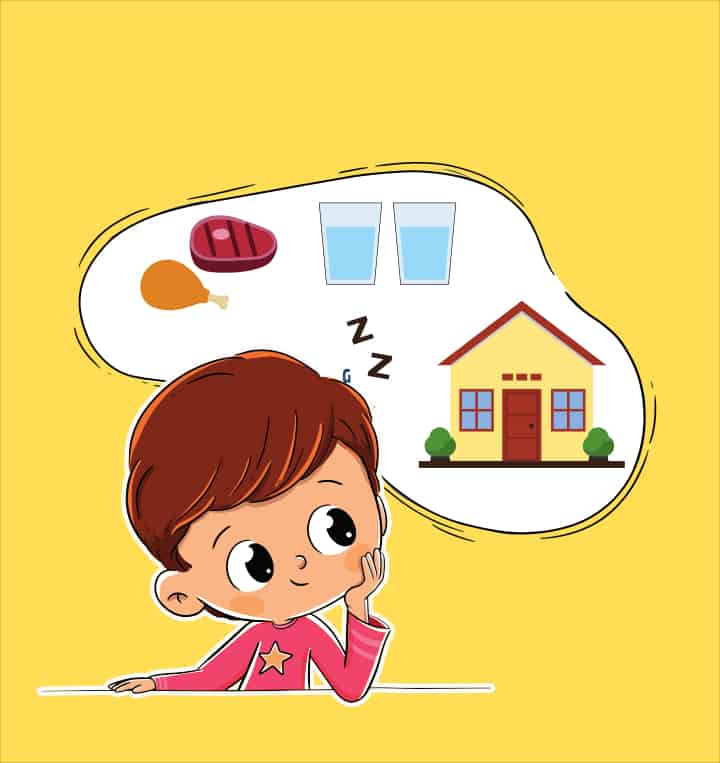

Understanding the concept of a primary reinforcer is essential in fields like psychology, education, and even marketing. A primary reinforcer is a stimulus that inherently satisfies a biological need, such as food, water, or shelter. Unlike secondary reinforcers, which gain their value through association, primary reinforcers have an immediate and natural impact on behavior. This article will delve into what primary reinforcers are, their significance, and how they are applied in various contexts, such as behavioral psychology, education, and marketing.
What is a Primary Reinforcer?

A primary reinforcer is a stimulus that fulfills a basic biological need, directly influencing behavior. These reinforcers are universal and do not require learned associations to be effective. Examples include:
- Food: Satisfies hunger.
- Water: Quenches thirst.
- Shelter: Provides safety and comfort.
Primary reinforcers are powerful because they address fundamental survival needs, making them effective in shaping behavior across species, including humans. (behavioral psychology, operant conditioning, intrinsic motivation)
Primary Reinforcers vs. Secondary Reinforcers
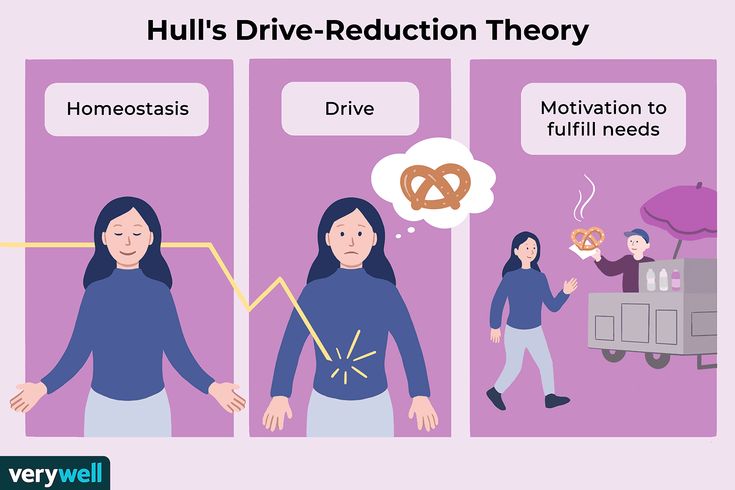
While primary reinforcers are innate, secondary reinforcers gain their value through association with primary reinforcers. For example, money is a secondary reinforcer because it can be exchanged for food, shelter, or other primary needs. Here’s a comparison:
| Primary Reinforcer | Secondary Reinforcer |
|---|---|
| Food, water, shelter | Money, praise, grades |
| Inherently satisfying | Learned value |

Understanding this distinction is crucial for designing effective reinforcement strategies in education and marketing. (positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, conditioning)
Applications of Primary Reinforcers

Behavioral Psychology
In behavioral psychology, primary reinforcers are used to shape behavior through operant conditioning. For example, rewarding a child with food for completing a task reinforces the desired behavior. This method is widely used in animal training and human behavior modification.
📌 Note: Consistency is key when using primary reinforcers to ensure long-term behavioral changes.
Education
In education, primary reinforcers like snacks or breaks can motivate students. However, educators often pair them with secondary reinforcers like stickers or praise to create a balanced reward system. (classroom management, student motivation, teaching strategies)
Marketing
In marketing, understanding primary reinforcers helps businesses appeal to basic human needs. For instance, advertising a product as essential for comfort or survival can increase its perceived value. (consumer behavior, brand loyalty, marketing strategies)
Summary Checklist

- Primary reinforcers fulfill basic biological needs.
- Examples include food, water, and shelter.
- They differ from secondary reinforcers, which have learned value.
- Applications span behavioral psychology, education, and marketing.
What are examples of primary reinforcers?
+Examples include food, water, shelter, and other stimuli that fulfill basic biological needs.
How do primary reinforcers differ from secondary reinforcers?
+Primary reinforcers are inherently satisfying, while secondary reinforcers gain value through association with primary reinforcers.
Where are primary reinforcers applied?
+They are used in behavioral psychology, education, marketing, and other fields to shape behavior and motivate actions.
Primary reinforcers play a vital role in shaping behavior by addressing fundamental needs. Whether in behavioral psychology, education, or marketing, understanding their application can lead to more effective strategies. By distinguishing between primary and secondary reinforcers, you can create targeted approaches that resonate with intrinsic motivations. (behavior modification, reinforcement techniques, psychological principles)


