What Are Shared Derived Characteristics?
<!DOCTYPE html>
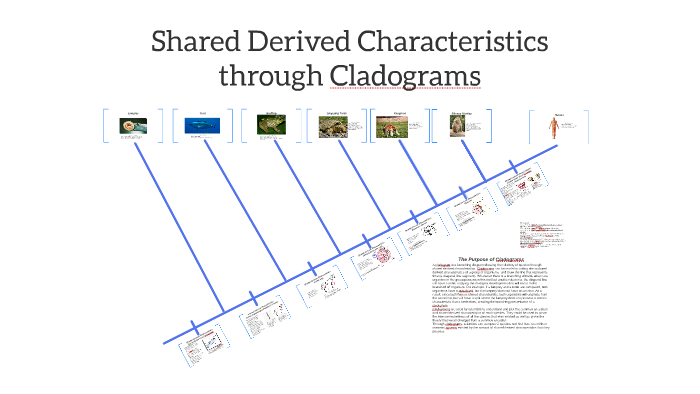
Shared derived characteristics, also known as synapomorphies, are traits that are present in a group of organisms and their common ancestor but not in other related groups. These characteristics are crucial in understanding evolutionary relationships and constructing phylogenetic trees. By identifying shared derived traits, scientists can trace the evolutionary history of species and determine how they are related. (evolutionary biology, phylogenetic trees, synapomorphies)
Understanding Shared Derived Characteristics

Shared derived characteristics are essential in taxonomy and systematics, helping to classify organisms based on their evolutionary relationships. These traits can be morphological, molecular, or behavioral, providing a comprehensive view of how species have diverged over time. (taxonomy, systematics, evolutionary relationships)
Key Features of Shared Derived Characteristics
- Ancestral Connection: These traits are inherited from a common ancestor.
- Group Specificity: They are unique to a particular group of organisms.
- Evolutionary Insight: They provide evidence of evolutionary changes and relationships.
How Shared Derived Characteristics Are Identified

Identifying shared derived characteristics involves comparing traits across different species and determining their evolutionary significance. This process often includes:
Steps to Identify Shared Derived Characteristics
- Trait Comparison: Analyze traits in various species to find similarities and differences.
- Ancestral State Reconstruction: Infer the traits of common ancestors based on current species.
- Phylogenetic Analysis: Use these traits to construct evolutionary trees and understand relationships.
💡 Note: Shared derived characteristics are distinct from shared ancestral traits, which are present in both the ancestor and other related groups.
Applications of Shared Derived Characteristics

Shared derived characteristics have wide-ranging applications in biology and beyond. They are used in:
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| Biology | Classifying species and understanding biodiversity |
| Medicine | Studying evolutionary relationships of pathogens |
| Conservation | Identifying endangered species and their evolutionary significance |

Checklist for Identifying Shared Derived Characteristics
- Compare traits across species.
- Determine the ancestral state of the trait.
- Assess the uniqueness of the trait to a specific group.
- Use phylogenetic analysis to confirm relationships.
In summary, shared derived characteristics are vital tools in understanding the evolutionary connections between species. By identifying these traits, scientists can construct detailed phylogenetic trees, classify organisms accurately, and gain insights into the history of life on Earth. Whether in biology, medicine, or conservation, these characteristics play a pivotal role in advancing our knowledge of the natural world. (phylogenetic trees, evolutionary connections, biodiversity)
What is the difference between shared derived and shared ancestral characteristics?
+Shared derived characteristics are unique to a specific group and their common ancestor, while shared ancestral traits are present in both the ancestor and other related groups.
How are shared derived characteristics used in phylogenetic analysis?
+They are used to construct evolutionary trees by identifying traits that indicate common ancestry and evolutionary relationships among species.
Can shared derived characteristics be behavioral?
+Yes, shared derived characteristics can be morphological, molecular, or behavioral, providing a comprehensive view of evolutionary relationships.



