Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: Aluminum Insights

Understanding the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is crucial for engineers, designers, and manufacturers working with aluminum. This property determines how much aluminum expands or contracts when exposed to temperature changes, impacting its performance in various applications. Whether you’re designing aerospace components or everyday household items, knowing aluminum’s CTE ensures durability and efficiency.
What is the Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE)?

The coefficient of thermal expansion measures the degree to which a material expands or contracts with temperature fluctuations. For aluminum, this value is relatively low compared to materials like plastics or steel, making it ideal for applications requiring dimensional stability.
💡 Note: Aluminum's CTE is approximately 23 x 10⁻⁶/°C, which is essential for precise engineering calculations.
Why is Aluminum’s CTE Important?
Aluminum’s low CTE makes it a preferred material in industries such as automotive, construction, and electronics. Its ability to maintain structural integrity under temperature variations reduces the risk of warping or failure, ensuring long-term reliability.
Applications Benefiting from Aluminum’s CTE
- Automotive: Engine components and heat exchangers.
- Aerospace: Aircraft structures and thermal shielding.
- Electronics: Heat sinks and enclosures.
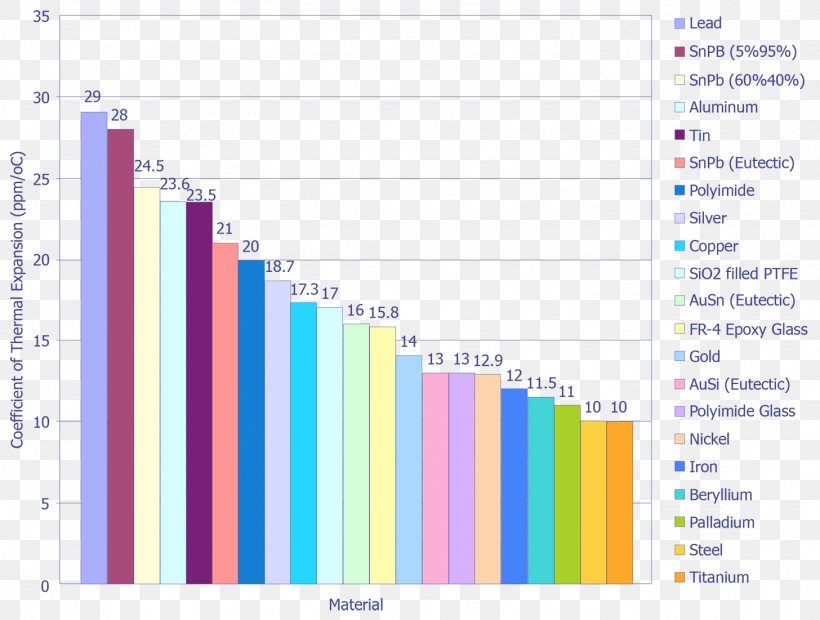
Comparing Aluminum’s CTE to Other Materials

To appreciate aluminum’s advantages, let’s compare its CTE with other common materials:
| Material | CTE (x 10⁻⁶/°C) |
|---|---|
| Aluminum | 23 |
| Steel | 12 |
| Copper | 17 |
| Plastics | 50–200 |

Aluminum strikes a balance between low expansion and cost-effectiveness, making it a versatile choice for thermal management.
How to Calculate Thermal Expansion in Aluminum
To predict how aluminum components will behave under temperature changes, use the formula:
ΔL = α × L₀ × ΔT
Where:
- ΔL = Change in length
- α = CTE of aluminum (23 x 10⁻⁶/°C)
- L₀ = Original length
- ΔT = Temperature change
⚠️ Note: Accurate measurements are critical for high-precision applications like aerospace or electronics.
Tips for Working with Aluminum’s CTE

- Design for Thermal Stress: Incorporate expansion joints in structures.
- Material Pairing: Combine aluminum with materials of similar CTE to minimize stress.
- Temperature Control: Maintain stable operating temperatures for critical components.
Final Thoughts
Aluminum’s coefficient of thermal expansion is a key factor in its widespread use across industries. Its low CTE ensures dimensional stability, making it ideal for applications where temperature fluctuations are common. By understanding and leveraging this property, engineers and manufacturers can optimize designs for performance and longevity.
What is the coefficient of thermal expansion for aluminum?
+Aluminum's coefficient of thermal expansion is approximately 23 x 10⁻⁶/°C.
Why is aluminum's CTE important in engineering?
+Aluminum's low CTE ensures dimensional stability, reducing the risk of warping or failure in temperature-sensitive applications.
How does aluminum's CTE compare to steel?
+Aluminum has a higher CTE than steel (23 vs. 12 x 10⁻⁶/°C), but it remains a preferred choice due to its lightweight and corrosion resistance.
coefficient of thermal expansion,aluminum properties,thermal expansion in engineering,material science,aluminum applications



