Photosynthesis: Catabolic or Not?
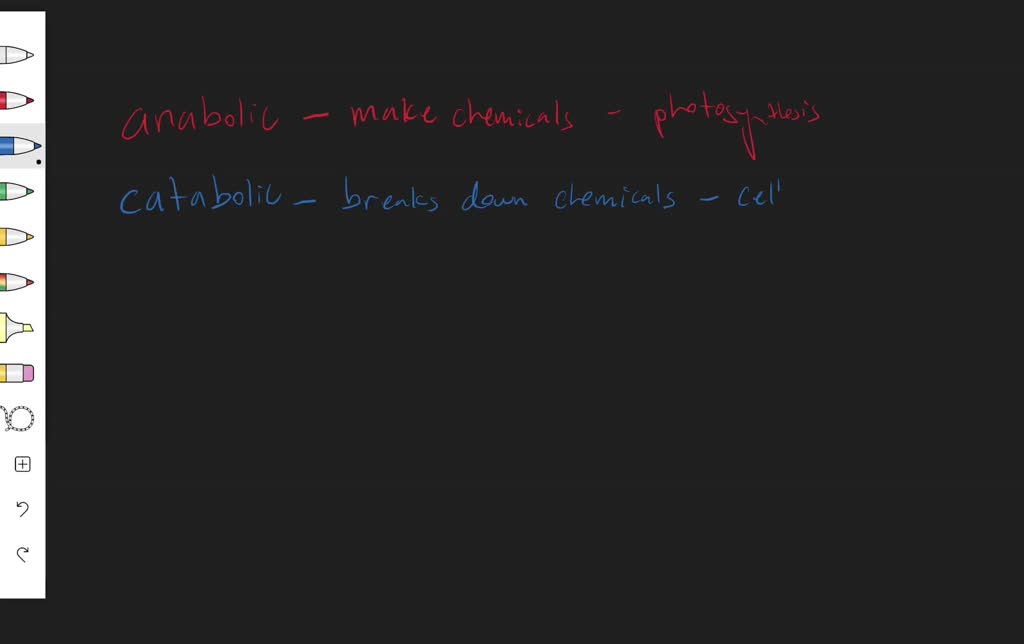
Photosynthesis is a fundamental biological process that sustains life on Earth, but is it a catabolic process? This question often sparks curiosity among students, educators, and biology enthusiasts. Understanding whether photosynthesis falls under catabolic or anabolic metabolism is crucial for grasping its role in energy transformation. In this post, we’ll explore the nature of photosynthesis, its metabolic classification, and why it matters in the broader context of biology. (photosynthesis process, catabolic vs anabolic, plant biology)
What is Photosynthesis?

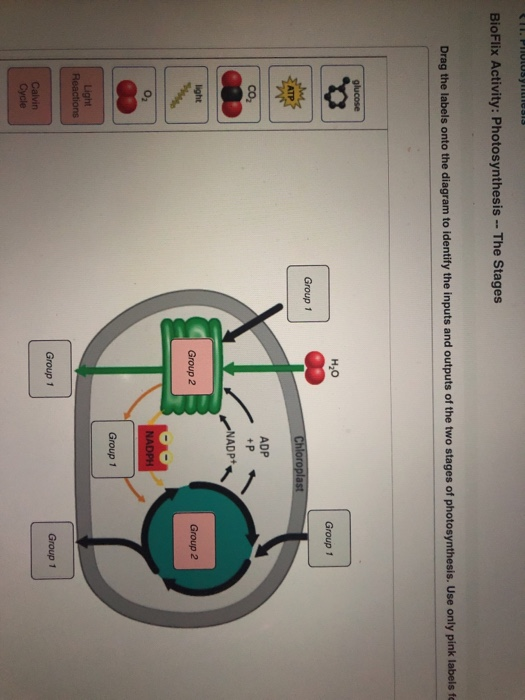
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, storing it in glucose. It occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells and involves two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle. This process is essential for producing oxygen and sustaining the food chain. (photosynthesis definition, chloroplasts, Calvin cycle)
Catabolic vs. Anabolic: What’s the Difference?

To determine if photosynthesis is catabolic, we must first understand these metabolic types:
- Catabolic Processes: Break down complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy. Examples include cellular respiration. (catabolic definition, cellular respiration)
- Anabolic Processes: Build complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring energy. Examples include protein synthesis. (anabolic definition, protein synthesis)
Is Photosynthesis a Catabolic Process?
Photosynthesis is not a catabolic process. Instead, it is an anabolic process because it synthesizes glucose from carbon dioxide and water, requiring energy from light. While it does involve breaking down water molecules during the light-dependent reactions, its primary function is to build complex carbohydrates. (photosynthesis metabolism, anabolic process)
📌 Note: Although photosynthesis includes some catabolic steps, it is classified as anabolic due to its overall energy-storing function.
Why Does the Classification Matter?
Understanding whether photosynthesis is catabolic or anabolic helps in:
- Differentiating metabolic pathways in biology education.
- Appreciating the balance between energy production and consumption in ecosystems. (ecosystem balance, metabolic pathways)
| Aspect | Catabolic | Anabolic |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Breaks down molecules | Builds molecules |
| Energy | Releases energy | Requires energy |
| Example | Cellular respiration | Photosynthesis |

Key Takeaways Checklist:
- ✅ Photosynthesis is an anabolic process, not catabolic.
- ✅ It converts light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose.
- ✅ Understanding metabolic classifications aids in biology education and ecosystem studies.
In summary, photosynthesis is an anabolic process that plays a vital role in energy transformation and ecosystem stability. While it includes some catabolic steps, its primary function is to build complex molecules, making it distinct from catabolic processes like cellular respiration. By clarifying this classification, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate balance of life on Earth. (photosynthesis importance, ecosystem stability, metabolic balance)
Is photosynthesis a catabolic process?
+
No, photosynthesis is an anabolic process because it synthesizes glucose from simpler molecules, requiring energy from light.
What is the difference between catabolic and anabolic processes?
+
Catabolic processes break down molecules and release energy, while anabolic processes build molecules and require energy.
Why is photosynthesis important for ecosystems?
+
Photosynthesis produces oxygen and glucose, which are essential for sustaining life and maintaining the food chain in ecosystems.