Solid Dissolved in Solid: Surprising Examples Explained How Solids Dissolve in Solids: Real-World Cases Solid-Solid Dissolution: 5 Examples You Need to Know Uncommon Solids Dissolving in Solids: A Quick Guide Exploring Solid-Solid Dissolution: Practical Examples

Have you ever wondered how one solid can dissolve in another? It might seem counterintuitive, but solid-solid dissolution is a fascinating phenomenon with real-world applications. From metallurgy to pharmaceuticals, understanding how solids interact and dissolve into each other is crucial. In this post, we’ll explore surprising examples of solids dissolving in solids, explain the science behind it, and provide practical insights for both informational and commercial audiences.
How Solids Dissolve in Solids: The Science Behind It

Solid-solid dissolution occurs when the atoms or molecules of one solid material diffuse into another, forming a homogeneous mixture. This process is driven by factors like temperature, pressure, and the chemical compatibility of the materials involved. Unlike liquid dissolution, which is more common, solid-solid dissolution requires specific conditions to overcome the strong intermolecular forces in solids.
💡 Note: Solid-solid dissolution is slower compared to liquid dissolution due to the rigid structure of solids.
5 Real-World Examples of Solid-Solid Dissolution

Here are five compelling examples that demonstrate how solids dissolve in solids:
1. Alloys in Metallurgy
Alloys like steel (iron and carbon) are classic examples of solid-solid dissolution. Carbon atoms dissolve into the iron lattice, enhancing its strength and durability. This process is essential in manufacturing industries.
2. Doping in Semiconductors
In electronics, semiconductor doping involves dissolving impurities like phosphorus or boron into silicon crystals. This alters the material’s conductivity, making it suitable for transistors and microchips.
3. Solid Solutions in Geology
Minerals like olivine can form solid solutions where magnesium and iron atoms dissolve into each other’s crystal structures. This is common in Earth’s mantle and volcanic rocks.
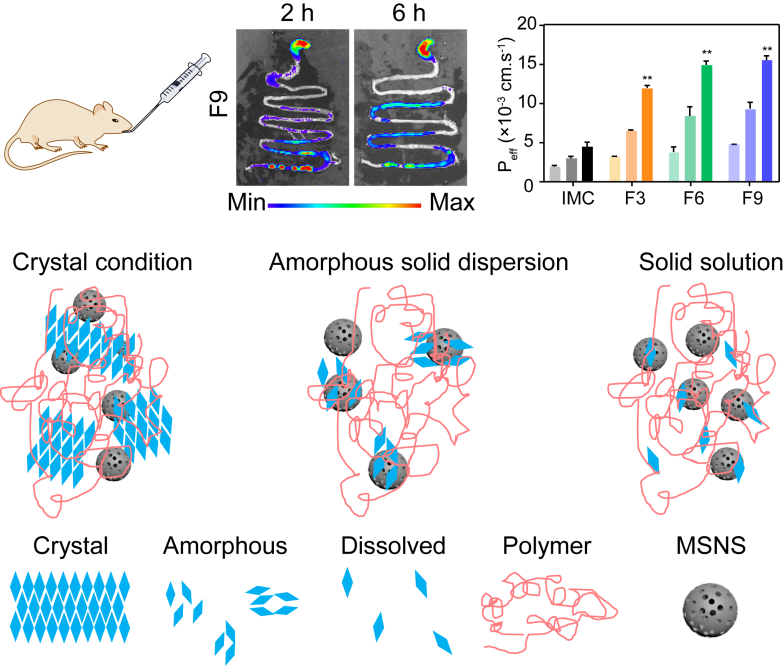
4. Pharmaceutical Co-Crystals
In pharmaceuticals, co-crystals are formed when two or more molecules dissolve into a solid lattice. This improves drug stability and bioavailability, benefiting the healthcare industry.
5. Polymer Blends
In materials science, polymer blends like ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) involve dissolving different polymers into a single solid material. This enhances properties like flexibility and impact resistance.
Practical Applications and Commercial Insights
For commercial audiences, understanding solid-solid dissolution opens doors to innovation. Industries like automotive, electronics, and healthcare rely on this process to develop advanced materials. For instance, alloy development in metallurgy drives the production of lightweight, high-strength components for vehicles.
✨ Note: Investing in research on solid-solid dissolution can lead to breakthroughs in material science and product development.
Checklist for Understanding Solid-Solid Dissolution
- Key Factors: Temperature, pressure, and chemical compatibility.
- Examples: Alloys, semiconductor doping, mineral solid solutions, co-crystals, and polymer blends.
- Applications: Metallurgy, electronics, geology, pharmaceuticals, and materials science.
Wrapping Up

Solid-solid dissolution is a remarkable process with wide-ranging applications. Whether you’re a science enthusiast or a professional in a related field, understanding this phenomenon can inspire innovation and problem-solving. From alloys to pharmaceuticals, the examples we’ve explored highlight the importance of this process in everyday life and industry.
What is solid-solid dissolution?
+Solid-solid dissolution is the process where atoms or molecules of one solid material diffuse into another, forming a homogeneous mixture.
Why is solid-solid dissolution important in industry?
+It’s crucial for developing advanced materials like alloys, semiconductors, and pharmaceuticals, driving innovation in various sectors.
What factors influence solid-solid dissolution?
+Temperature, pressure, and the chemical compatibility of the materials are key factors in this process.
solid-solid dissolution, solid dissolved in solid, alloys, semiconductor doping, pharmaceutical co-crystals, polymer blends, material science.


